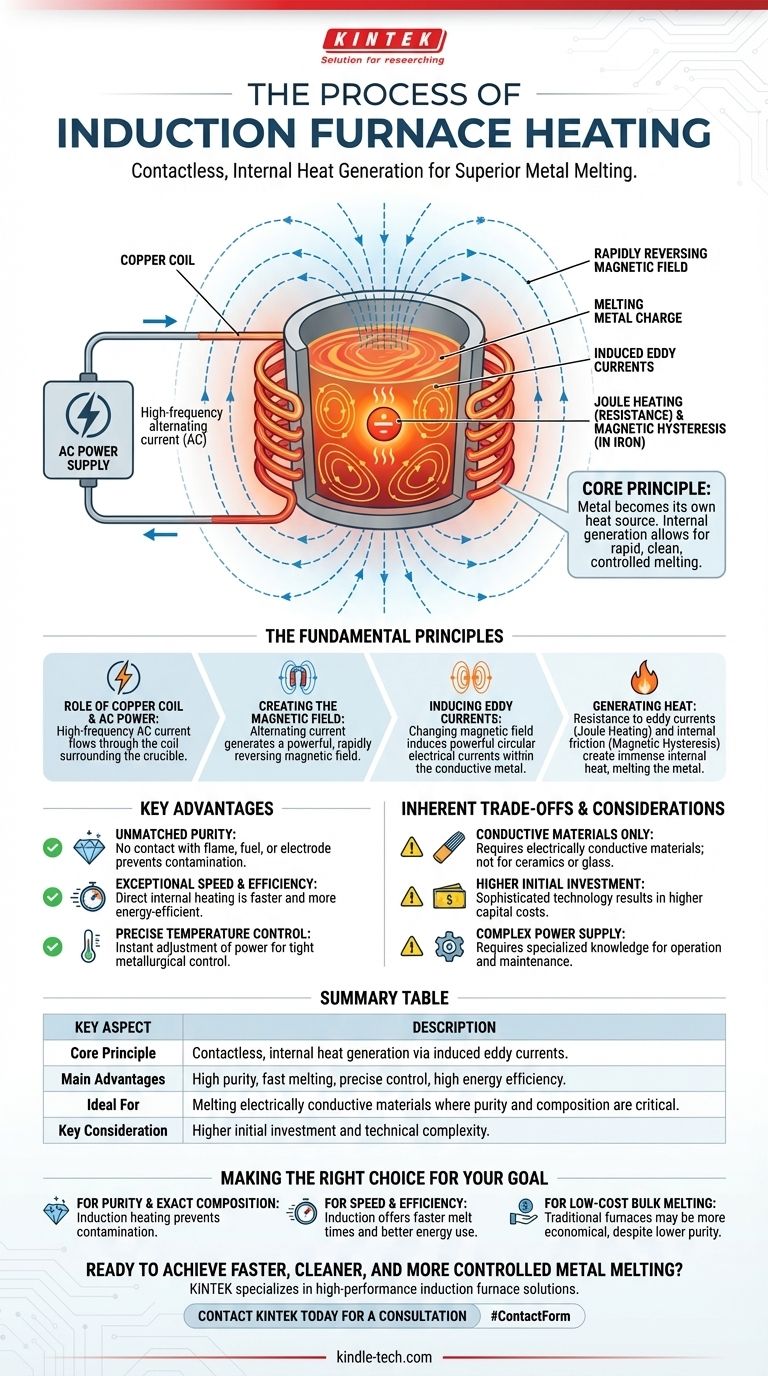
At its core, induction furnace heating is a process of contactless, internal heat generation. An induction furnace uses a powerful, alternating electrical current flowing through a copper coil to create a rapidly reversing magnetic field. This field penetrates the conductive metal held within a crucible, inducing internal electrical currents called eddy currents. The metal’s own resistance to these currents generates intense heat, causing it to melt from the inside out.
The critical principle of induction heating is that the metal becomes its own heat source. Unlike conventional furnaces that apply external heat, this internal generation provides rapid, clean, and highly controlled melting without direct contact or combustion.

The Fundamental Principles of Induction Heating
To truly grasp how an induction furnace operates, it's essential to understand the sequence of physical principles that convert electrical energy into thermal energy within the metal itself.
The Role of the Copper Coil and AC Power
The process begins with a specialized power supply that sends a high-frequency alternating current (AC) through a multi-turn copper coil. This coil is carefully constructed to surround, but not touch, the crucible containing the metal to be melted.
Creating the Magnetic Field
According to the laws of electromagnetism, any electrical current generates a magnetic field. Because the current is alternating, it creates a powerful and rapidly reversing magnetic field that radiates from the coil and easily passes through the non-conductive crucible.
Inducing Eddy Currents
This is the central mechanism of induction. As the magnetic field rapidly changes direction, it induces powerful, circular electrical currents within the conductive metal charge. These are known as eddy currents. The furnace effectively acts like a transformer, where the copper coil is the primary and the metal charge itself becomes the secondary.
Generating Heat Through Resistance (Joule Heating)
All conductive materials have some level of electrical resistance. As the induced eddy currents flow through the metal, they encounter this resistance, which generates immense heat. This phenomenon is known as Joule heating, and it is the primary source of the heat that melts the metal.
The Secondary Effect: Magnetic Hysteresis
For ferromagnetic materials like iron, there is an additional source of heat. The rapid reversal of the magnetic field causes the magnetic domains within the iron to rapidly flip back and forth. This internal friction, known as magnetic hysteresis, also contributes to the overall heating effect.
Understanding the Key Advantages
The method of internal heat generation gives induction furnaces several distinct operational advantages over traditional fuel-fired or arc furnaces.
Unmatched Purity
Because the heat is generated within the charge, there is no contact with a flame, fuel, or electrode. This eliminates a major source of contamination, making induction furnaces ideal for producing high-purity metals and precisely formulated alloys.
Exceptional Speed and Efficiency
Heat is generated exactly where it's needed: inside the metal. This direct transfer of energy is extremely efficient and allows for significantly faster melting cycles compared to methods that must first heat the furnace walls and then transfer that heat to the charge.
Precise Temperature Control
The power delivered to the induction coil can be adjusted instantly and with great precision. This gives operators tight control over the melt temperature, which is critical for meeting the strict metallurgical requirements of specialized alloys.
The Inherent Trade-offs and Considerations
Despite its advantages, induction technology is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is crucial for making an informed decision.
Requirement for Conductive Materials
The entire process relies on inducing electrical currents within the charge. Therefore, induction heating is only effective for electrically conductive materials. It cannot be used to directly heat non-conductive materials like ceramics or glass.
Higher Initial Investment
Induction furnace systems, particularly their high-frequency power supplies, are technologically sophisticated. This results in a higher capital cost compared to simpler combustion-based furnaces.
Complexity of Power Supply
The power units that drive the induction coil are complex electronic devices. They require specialized knowledge for operation and maintenance, which can be a consideration for facilities without dedicated technical staff.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heating technology depends entirely on your operational priorities and the materials you are working with.
- If your primary focus is alloy purity and exact composition: Induction heating is the superior choice because it prevents contamination from fuel or electrodes.
- If your primary focus is production speed and efficiency: The rapid, direct heating of induction furnaces offers significantly faster melt times and better energy utilization than many conventional methods.
- If your primary focus is low-cost bulk melting of less sensitive metals: A traditional fuel-fired or arc furnace may be a more economical solution, despite the lower control and purity.
Understanding this principle of internal heat generation is the key to leveraging induction technology for superior metallurgical results.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Contactless, internal heat generation via induced electrical currents (eddy currents). |
| Main Advantages | High purity (no contamination), fast melting, precise temperature control, and high energy efficiency. |
| Ideal For | Melting electrically conductive materials, especially when high purity and precise alloy composition are critical. |
| Key Consideration | Higher initial investment and technical complexity compared to some conventional furnaces. |
Ready to achieve faster, cleaner, and more controlled metal melting?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment, including advanced induction furnace solutions. Our systems are designed to deliver the purity, speed, and precision your laboratory or production facility requires.
Let our experts help you select the perfect induction heating solution for your specific materials and goals.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and discover how our technology can enhance your metallurgical processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting



















