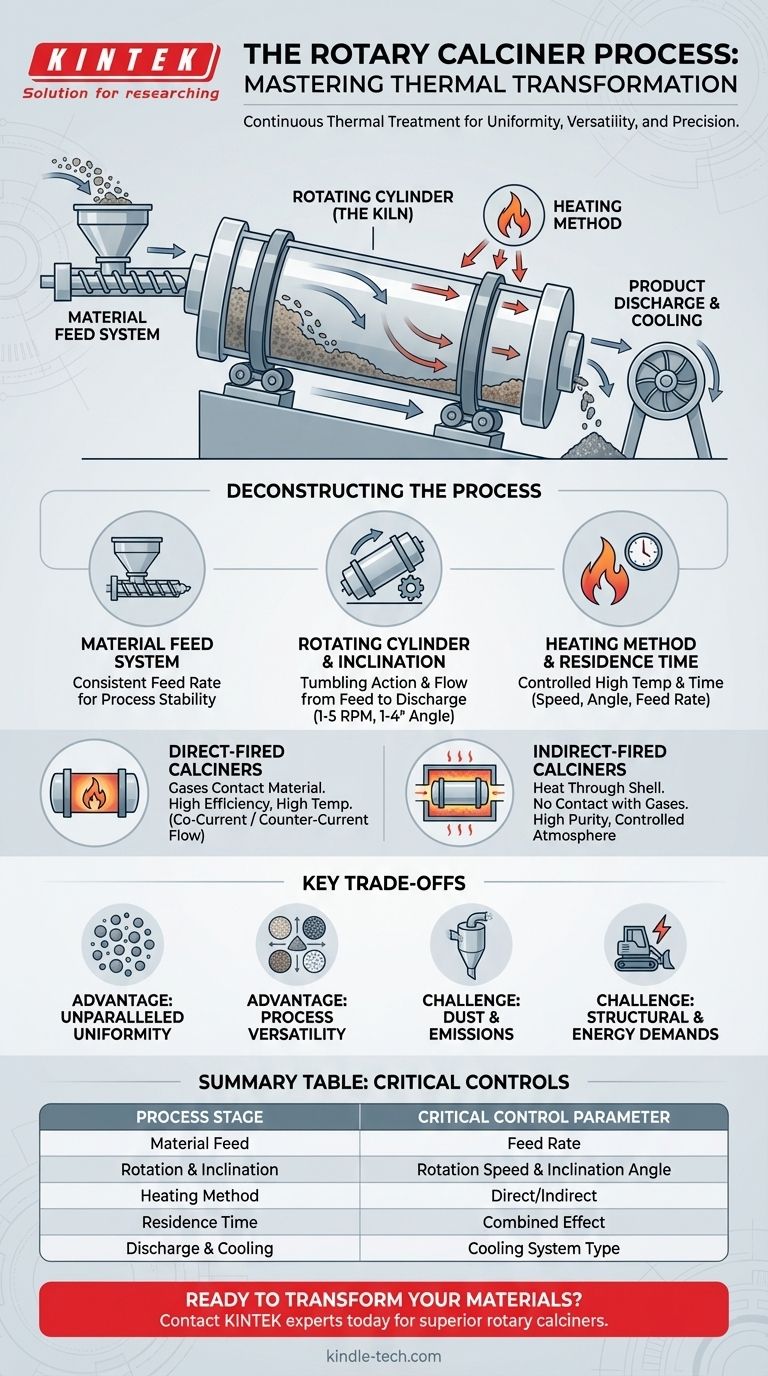
At its core, the rotary calciner process is a continuous thermal treatment method used to induce physical or chemical changes in solid materials. Material is fed into one end of a large, rotating, and slightly inclined cylinder. As the cylinder rotates, the material tumbles and gradually moves toward the lower discharge end, ensuring every particle is uniformly exposed to a controlled high temperature, which drives the desired reaction or phase change.
The central challenge in processing bulk solids is achieving a perfectly uniform and consistent final product. The rotary calciner excels by combining three critical actions—continuous movement, constant agitation, and precise thermal control—into a single, robust process.

Deconstructing the Rotary Calciner Process
To understand its effectiveness, we must examine the key stages and components that define the operation of a rotary calciner, often called a rotary kiln.
The Material Feed System
The process begins by introducing raw material into the upper, or "feed," end of the calciner. This is typically accomplished using a controlled system like a screw feeder or a sealed chute to ensure a consistent and predictable feed rate, which is critical for process stability.
The Rotating Cylinder (The Kiln)
This is the heart of the system. The long, cylindrical steel shell is lined with refractory material to withstand high temperatures and protect the shell. It is mounted on rollers and driven by a large gear system, allowing it to rotate at a controlled speed (typically 1-5 RPM).
The cylinder is also set at a slight angle, usually between 1 and 4 degrees. This inclination, combined with the rotation, is what causes the material to cascade and flow steadily from the feed end to the discharge end.
The Heating Method
The method used to heat the material is the most significant design variable and dictates the calciner's application. There are two primary approaches.
- Direct-Fired Calciners: In this design, hot combustion gases flow directly through the cylinder, making intimate contact with the material. This can be done in a co-current flow (gases move in the same direction as the material) or a counter-current flow (gases move in the opposite direction).
- Indirect-Fired Calciners: Here, the rotating cylinder is enclosed within a larger furnace or is fitted with an external heating jacket. The heat transfers through the cylinder shell wall to the material inside. The combustion gases never contact the material, which is critical for high-purity applications.
Residence Time Control
The amount of time the material spends inside the calciner is known as residence time. This is a crucial parameter controlled by three main factors: the rotation speed of the cylinder, the inclination angle (slope), and the material feed rate. Adjusting these variables allows operators to precisely control the extent of the thermal treatment.
Product Discharge and Cooling
Once the material reaches the lower end of the cylinder, it is discharged as the final product. It often exits into a rotary cooler or another type of cooling system to lower its temperature for safe handling and to prevent unwanted secondary reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, rotary calciners are not a universal solution. Understanding their inherent advantages and challenges is key to proper application.
Key Advantage: Unparalleled Uniformity
The tumbling or cascading motion of the material is the calciner's greatest strength. It constantly exposes new surfaces to the heat source and promotes mixing, resulting in an exceptionally uniform temperature distribution throughout the material bed and, consequently, a highly consistent product.
Key Advantage: Process Versatility
Rotary calciners can handle a vast range of materials, from fine powders and granules to larger aggregates and even slurries. They are well-suited for a wide array of processes including drying, roasting, thermal desorption, and complex chemical reactions.
Potential Challenge: Dust and Emissions
The same tumbling action that ensures uniformity can create dust, especially with fine or friable materials. This necessitates a robust off-gas handling system, including cyclones and baghouses, to capture particulate matter and meet environmental regulations.
Potential Challenge: Structural and Energy Demands
These are large, heavy, and capital-intensive machines. Their large surface area can lead to significant radiant heat loss, making insulation and energy efficiency primary design considerations. The maximum achievable temperature in indirect-fired units is also limited by the metallurgical properties of the cylinder shell itself.
Direct vs. Indirect Firing: The Critical Decision
The choice between direct and indirect heating fundamentally alters the calciner's capabilities and is the most important decision for any specific application.
When to Choose Direct-Fired
Direct-fired systems are ideal for high-volume, robust processes where contact with combustion gases is acceptable or even beneficial. They are generally more thermally efficient and can achieve higher process temperatures, making them the standard for industries like cement and mineral ore processing.
When to Choose Indirect-Fired
Indirect-fired systems are essential when product purity is paramount. By isolating the material from the heating source, it prevents contamination from fuel byproducts. This design also allows for precise control over the internal atmosphere, enabling processes that require an inert (e.g., nitrogen) or reducing environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct calcination approach requires aligning the equipment's capabilities with your primary process objective.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and thermal efficiency for robust materials: A direct-fired, counter-current calciner is almost always the most effective and economical solution.
- If your primary focus is product purity and atmosphere control: An indirect-fired calciner is non-negotiable to prevent contamination and manage the specific process environment.
- If you are processing delicate or heat-sensitive materials: The precise control over residence time and temperature profile, achievable in both types but often more refined in indirect systems, should be your top priority.
By understanding these core process principles, you can approach the rotary calciner not just as a piece of equipment, but as a precision instrument for material transformation.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Function | Critical Control Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Material Feed | Introduces raw material into the cylinder | Feed Rate |
| Rotation & Inclination | Tumbles and moves material through the kiln | Rotation Speed & Inclination Angle |
| Heating Method | Applies controlled high temperature | Direct-Fired (for efficiency) or Indirect-Fired (for purity) |
| Residence Time | Determines duration of thermal treatment | Combined effect of Speed, Angle, and Feed Rate |
| Discharge & Cooling | Removes and stabilizes the final product | Cooling System Type |
Ready to transform your materials with precision?
Whether your goal is high-volume processing with a direct-fired rotary calciner or achieving ultimate product purity with an indirect-fired system, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your specific laboratory needs. Our rotary calciners are engineered for superior uniformity, versatility, and control.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK rotary calciner can optimize your thermal processing and deliver a consistent, high-quality product.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing



















