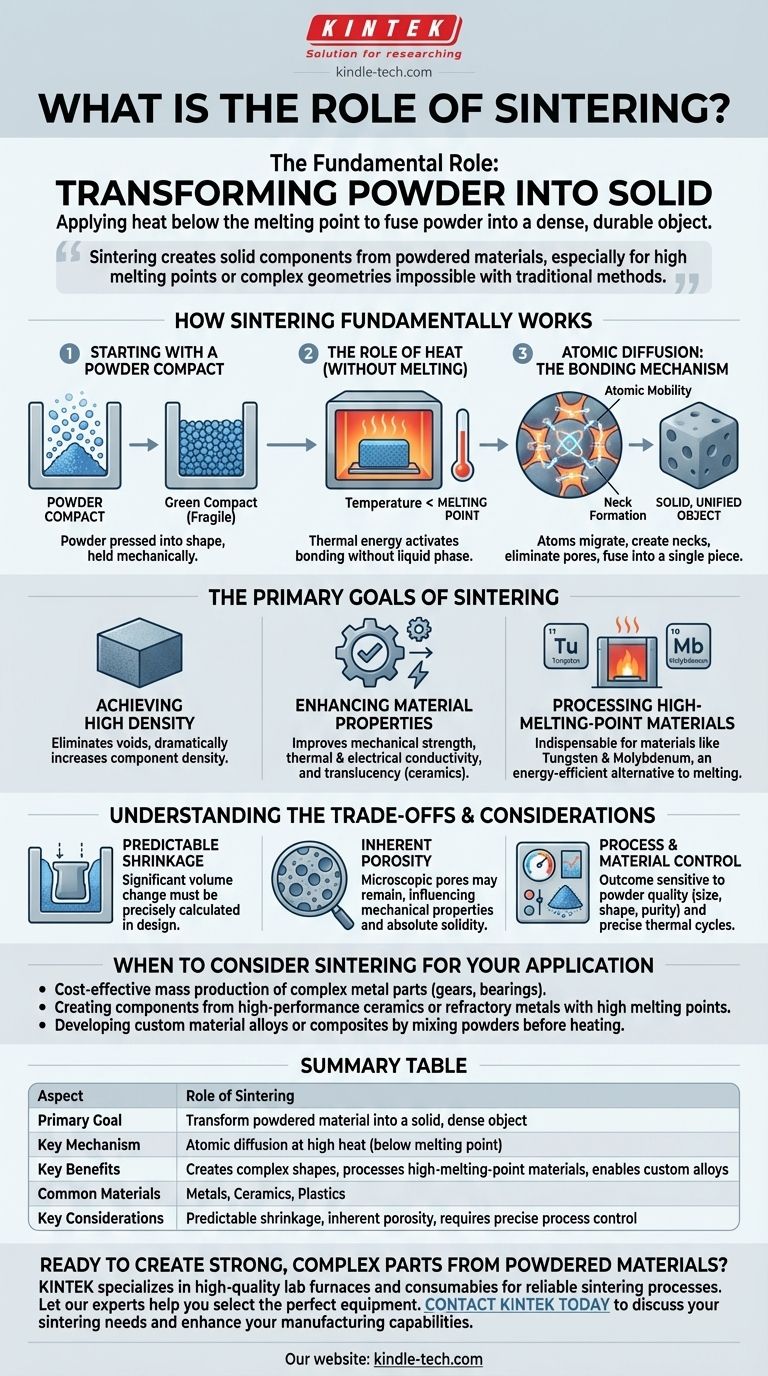
The fundamental role of sintering is to transform a mass of powder into a solid, unified object by applying heat without melting it. By holding the material at a high temperature just below its melting point, the process triggers atoms to migrate between individual particles, fusing them together into a dense and durable final part. This makes it an essential manufacturing technique for a wide range of materials, including metals, ceramics, and plastics.
Sintering provides a powerful pathway to create solid components from powdered materials, especially those with extremely high melting points or complex geometries that are difficult or inefficient to produce through traditional melting and casting.
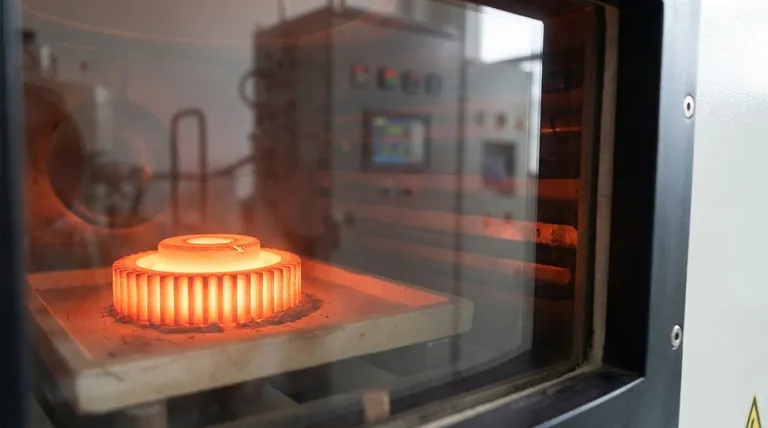

How Sintering Fundamentally Works
Sintering is not a simple melting process. It is a sophisticated thermal treatment that relies on atomic-level changes to consolidate a material.
Starting with a Powder Compact
The process begins with a material in powdered form. This powder is first compacted into a desired shape, often using high pressure in a mold. This initial form is known as a "green compact" and is fragile, with particles held together mechanically.
The Role of Heat (Without Melting)
The green compact is then placed in a specialized furnace and heated to an extreme temperature. Critically, this temperature is kept below the material's melting point. The heat provides the thermal energy necessary to activate the bonding mechanism.
Atomic Diffusion: The Bonding Mechanism
At this elevated temperature, atoms on the surfaces of adjacent powder particles become highly mobile. They begin to diffuse across the boundaries from one particle to another, creating "necks" or bridges between them. As this process continues, these necks grow, pulling the particles closer, eliminating the porous spaces between them, and fusing the entire mass into a single, solid piece.
The Primary Goals of Sintering
Engineers and manufacturers choose sintering to achieve specific outcomes that other processes cannot deliver as effectively.
Achieving High Density
The primary goal is densification. By eliminating the voids between powder particles, sintering dramatically increases the density of the final component, transforming it from a loose aggregate into a solid object.
Enhancing Material Properties
This increase in density directly leads to superior material characteristics. Sintered parts exhibit significantly improved mechanical strength, thermal and electrical conductivity, and in the case of some ceramics like zirconia, enhanced translucency.
Processing High-Melting-Point Materials
Sintering is indispensable for materials with exceptionally high melting points, such as tungsten and molybdenum. Melting and casting these materials would require immense energy and specialized equipment, making it impractical. Sintering provides an energy-efficient alternative to form them into usable parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, sintering is not without its unique challenges and characteristics that must be managed.
Predictable Shrinkage
As the voids between particles are eliminated, the entire component undergoes significant and predictable shrinkage. This change in volume, which can be substantial, must be precisely calculated and accounted for during the initial design of the mold and the green compact.
Inherent Porosity
While sintering drastically reduces empty space, achieving 100% density is often difficult. Microscopic pores may remain in the final part, which can influence its mechanical properties. For applications requiring absolute solidity, this residual porosity can be a limiting factor.
Process and Material Control
The final quality of a sintered part is highly sensitive to the initial conditions. The size, shape, and purity of the starting powder, as well as precise control over heating rates, temperature, and furnace atmosphere, are all critical variables that determine the outcome.
When to Consider Sintering for Your Application
Choosing a manufacturing process depends entirely on your material and end goal. Sintering is the superior choice in specific scenarios.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production of complex metal parts: Sintering is ideal for creating items like gears, bearings, and sprockets with intricate shapes that would be expensive to machine.
- If your primary focus is creating components from high-performance ceramics or refractory metals: Sintering is the go-to method for materials like zirconia or tungsten that have prohibitively high melting points.
- If your primary focus is developing custom material alloys or composites: Sintering allows you to mix different types of powders before heating, creating unique material blends that are impossible to achieve through melting.
Ultimately, sintering empowers engineers to create robust parts from powdered materials, unlocking performance and designs that would otherwise be out of reach.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role of Sintering |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Transform powdered material into a solid, dense object |
| Key Mechanism | Atomic diffusion at high heat (below melting point) |
| Key Benefits | Creates complex shapes, processes high-melting-point materials, enables custom alloys |
| Common Materials | Metals, Ceramics, Plastics |
| Key Considerations | Predictable shrinkage, inherent porosity, requires precise process control |
Ready to create strong, complex parts from powdered materials?
Sintering is a powerful technique, but achieving optimal results requires precise control and the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and consumables essential for reliable sintering processes, whether you're working with metals, ceramics, or developing new composites.
Let our experts help you select the perfect equipment for your application. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your sintering needs and enhance your manufacturing capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- How does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace facilitate TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Achieve 100% Dense Titanium Composites
- How does a vacuum environment system contribute to the hot pressing sintering of B4C-CeB6? Unlock Peak Ceramic Density
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Superior Density for Nanocrystalline Fe3Al
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?



















