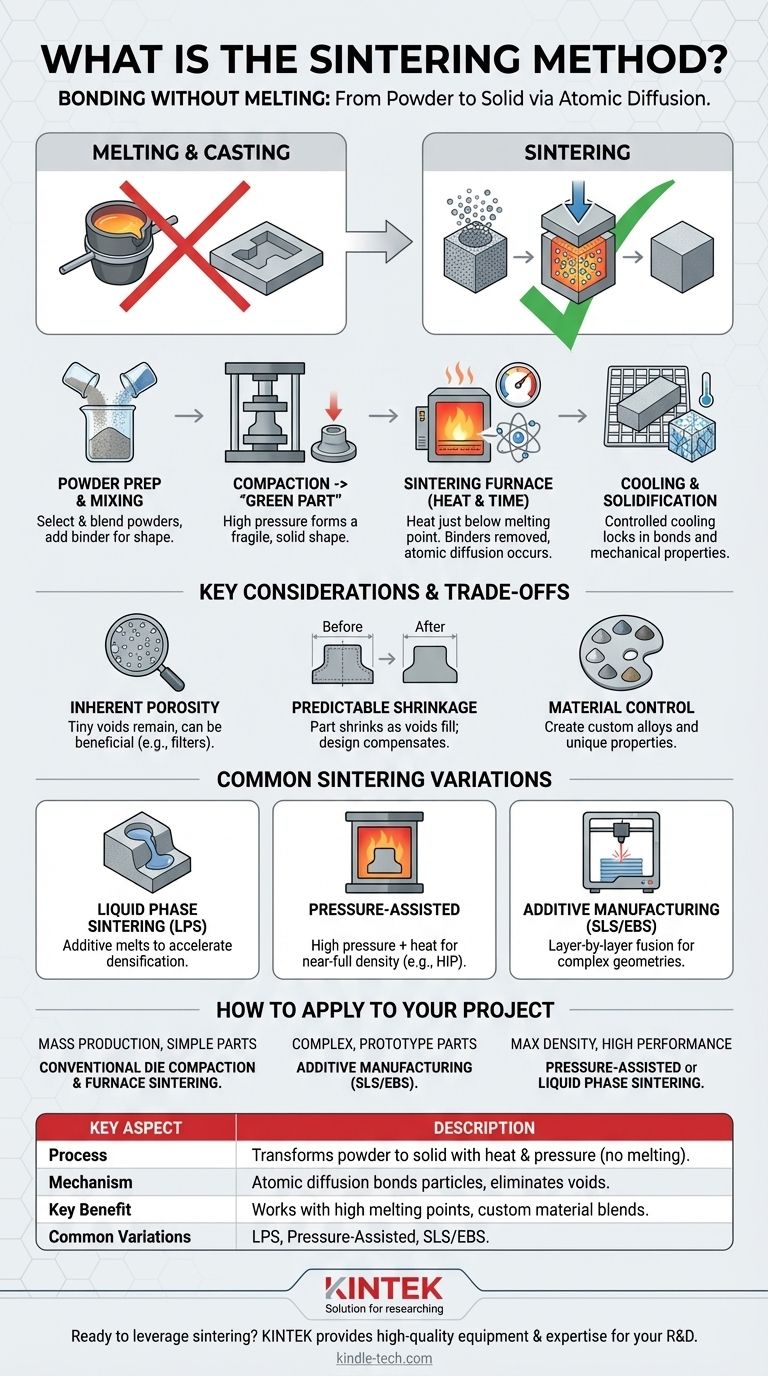
In essence, sintering is a manufacturing process that transforms a powder into a solid, dense object using heat and pressure. Crucially, this is accomplished without heating the material to its melting point, relying instead on atomic-level bonding to fuse the powder particles together.
The core problem sintering solves is how to create strong, complex parts from materials that are difficult or inefficient to melt and cast. Its solution is to use temperature to energize atoms enough to diffuse across particle boundaries, effectively welding a powder compact into a single, solid mass from the inside out.

The Fundamental Principle: Bonding Without Melting
Sintering is a cornerstone of powder metallurgy and advanced ceramics manufacturing. It operates on a principle that is distinct from casting or forging.
From Powder to Solid
The starting point for any sintered part is a fine powder. This can be a metal, a ceramic, a plastic, or a blend of different materials. The process compacts this powder and then heats it, causing the individual grains to bond and densify into a coherent piece.
The Role of Atomic Diffusion
Instead of liquefying the material, sintering heats it to a temperature where the atoms become highly mobile. This energy allows atoms to migrate across the contact points between powder particles, gradually filling the voids and forming strong, metallic or covalent bonds. The result is that the separate particles merge into a single, polycrystalline solid.
Why Not Just Melt It?
Melting and casting is not always ideal. Sintering allows for the creation of parts from materials with extremely high melting points (like tungsten or ceramics) and the manufacturing of unique alloy compositions that would be impossible to create through melting. It also provides precise control over the final part's density and porosity.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Sintering Process
While there are many variations, the conventional sintering process follows a clear, multi-stage path from loose powder to finished component.
Step 1: Powder Preparation and Mixing
The process begins by selecting and preparing the base material powder. Often, different powders are blended to create a specific alloy, or a binder (like a wax or polymer) is added. This binder temporarily holds the powder together during the initial shaping phase.
Step 2: Compaction into a "Green Part"
The powder mixture is loaded into a die or mold and subjected to high pressure. This compaction process forms the powder into the desired shape, now referred to as a "green part." This part is fragile but solid enough to be handled, with the particles held together by mechanical friction and the binder.
Step 3: The Sintering Furnace
The green part is placed in a controlled-atmosphere furnace. As the temperature rises, any binders are burned off or evaporated. The temperature is then held just below the material's melting point for a set period. It is during this "soak" that atomic diffusion occurs, bonding the particles and densifying the part.
Step 4: Cooling and Solidification
Finally, the component is cooled in a controlled manner. This allows the newly formed bonds to solidify and the desired crystalline microstructure to form, locking in the part's final mechanical properties like strength and hardness.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
Sintering is a powerful technique, but its effectiveness depends on understanding its inherent characteristics and limitations.
Inherent Porosity
Because the material is not melted, tiny voids or pores often remain in the final part. While the goal is to minimize this porosity, it is a natural characteristic of the process. In some applications, like self-lubricating bearings or filters, this porosity is actually a desired feature.
Predictable Shrinkage
As the voids between particles are eliminated during heating, the part inevitably shrinks. This shrinkage is predictable and must be precisely calculated and compensated for during the design of the initial compaction die to ensure the final part meets dimensional tolerances.
Material and Property Control
One of the greatest strengths of sintering is the ability to create custom material blends. By mixing different types of powders (e.g., iron with copper or carbon), manufacturers can engineer parts with highly specific properties that are tailored to the application.
Common Variations on the Sintering Method
Modern manufacturing employs several specialized sintering techniques to achieve different outcomes.
Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS)
In this method, a small amount of an additive with a lower melting point is mixed with the primary powder. During heating, this additive melts and flows into the pores between the solid primary particles, accelerating densification and resulting in a stronger, less porous part.
Pressure-Assisted Sintering
Techniques like Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) apply high pressure simultaneously with the heat. This external pressure helps collapse voids more effectively, leading to near-full density and superior mechanical properties.
Additive Manufacturing (SLS & EBS)
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Electron Beam Sintering (EBS) are 3D printing methods. They use a high-energy beam to sinter powder layer-by-layer, fusing the material as the object is being built. This eliminates the need for a compaction die and enables the creation of extremely complex geometries.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of sintering method depends entirely on the requirements of your component, including complexity, volume, and performance.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production of simple parts: Conventional die compaction followed by furnace sintering is the dominant and most economical method.
- If your primary focus is creating highly complex, low-volume, or prototype parts: Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and other additive manufacturing techniques offer unmatched design freedom.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and mechanical strength: Pressure-assisted methods or Liquid Phase Sintering are necessary to create high-performance, mission-critical components.
By understanding these principles, you can leverage sintering to manufacture parts that are strong, precise, and made from an exceptionally wide range of advanced materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Transforms powder into a solid object using heat (below melting point) and pressure. |
| Mechanism | Atomic diffusion bonds particles together, eliminating voids and densifying the part. |
| Key Benefit | Creates parts from materials with high melting points and allows for unique material blends. |
| Common Variations | Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS), Pressure-Assisted Sintering, Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's projects? KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced sintering processes. Whether you require a precise sintering furnace, specific metal or ceramic powders, or expert advice on method selection, our team is here to support your R&D and production goals. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you create stronger, more complex parts!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve high-density NTC ceramics with superior stability.
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Superior Density for Nanocrystalline Fe3Al
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- What are the advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity, Strength, and Performance
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics



















