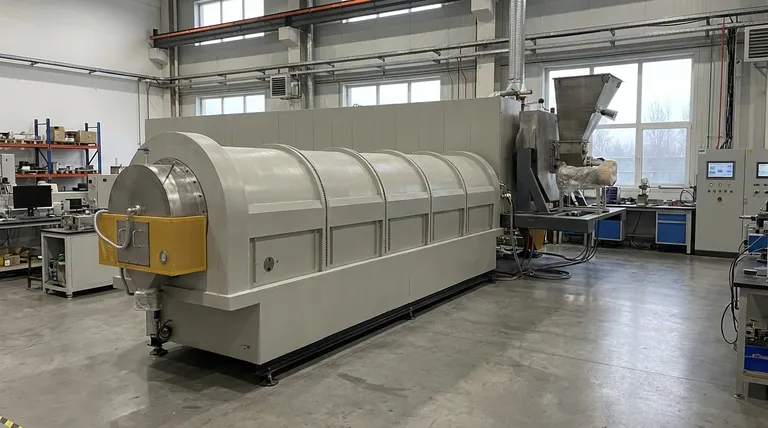
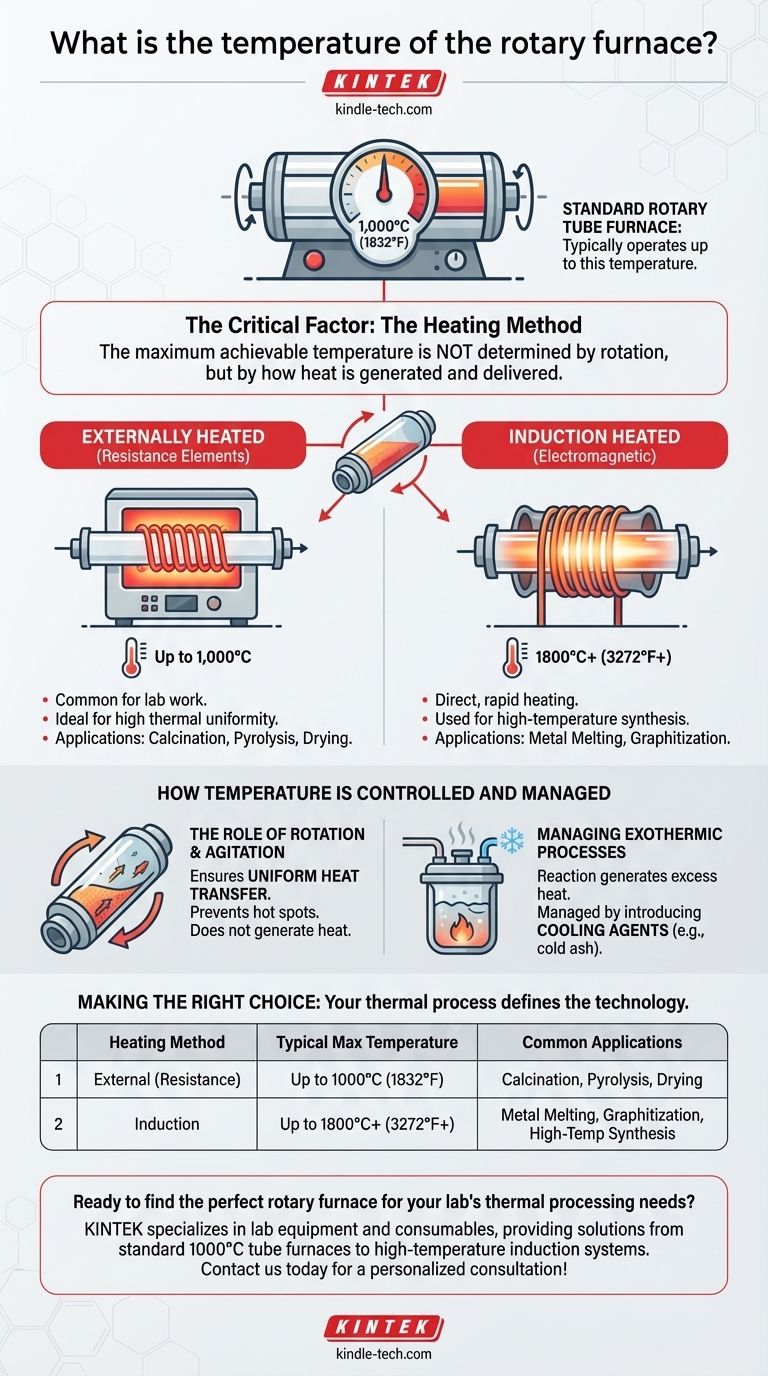
In short, a standard rotary tube furnace typically operates at temperatures up to 1,000°C (1832°F). However, this figure only tells part of the story, as the maximum achievable temperature is not determined by the furnace's rotation but by its specific heating method.
The key takeaway is that the term "rotary furnace" describes the mechanical function of rotating material, not the heating technology. The temperature capability depends entirely on whether it is heated externally by elements, by induction, or by a direct flame.

The Critical Factor: The Heating Method
The function of rotation is to tumble the material, ensuring every particle is uniformly exposed to the heat source. The actual temperature limit is set by how that heat is generated and delivered.
Externally Heated Rotary Tube Furnaces
This is the most common type for laboratory and pilot-scale work. The material moves through a rotating tube that is situated inside a larger, stationary furnace.
These are typically heated by electrical resistance elements, which is why their upper range is generally limited to around 1,000°C. They are ideal for processes requiring high thermal uniformity and controlled atmospheres, such as calcination or pyrolysis.
Induction Heated Rotary Furnaces
For much higher temperature applications, an induction coil can be used as the heat source. This method uses electromagnetic induction to directly heat the conductive material (or a conductive crucible) inside the tube.
Induction systems can achieve extreme temperatures, often reaching 1800°C (3272°F) or more. They are used for melting metals, graphitization, and other high-temperature material synthesis where direct, rapid heating is needed.
How Temperature is Controlled and Managed
Controlling the thermal environment is just as important as reaching the peak temperature. The furnace's features are designed for this purpose.
The Role of Rotation and Agitation
The rotation speed, direction (forward or reverse), and the use of internal rakes or stirrers are not for generating heat.
Instead, these mechanical actions are primary control levers for heat transfer. They ensure the material mixes properly, preventing hot spots and promoting a uniform reaction or phase change throughout the batch.
Managing Temperature in Exothermic Processes
In some applications, such as waste incineration, the reaction itself can generate heat and cause the temperature to rise too high.
In these operational scenarios, temperature is managed by introducing a cooling agent. A common method is to add cold ash or other inert material to absorb excess heat and bring the system back into its target operating range.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing temperature requirements against process needs and cost.
Rotary Tube Furnace (Externally Heated)
- Advantage: Provides excellent temperature uniformity and is well-suited for processing powders and granular materials in a controlled atmosphere.
- Limitation: Capped at approximately 1,000°C, making it unsuitable for melting most metals or for ultra-high-temperature ceramics.
Rotary Furnace (Induction Heated)
- Advantage: Capable of reaching very high temperatures (1800°C+) needed for metallurgy and advanced materials.
- Limitation: The process is dependent on the electrical conductivity of the material being heated and can be a more complex and costly setup.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace technology starts with defining your thermal processing requirements.
- If your primary focus is calcination, drying, or pyrolysis below 1000°C: A standard, externally heated rotary tube furnace provides the best combination of thermal uniformity and control.
- If your primary focus is melting metals or high-temperature synthesis above 1200°C: You must look for a rotary system specifically designed with an induction or other high-temperature heating source.
Ultimately, your material's required processing temperature is the single most important factor in determining the right furnace technology.
Summary Table:
| Heating Method | Typical Max Temperature | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| External (Resistance) | Up to 1000°C (1832°F) | Calcination, Pyrolysis, Drying |
| Induction | Up to 1800°C+ (3272°F+) | Metal Melting, Graphitization, High-Temp Synthesis |
Ready to find the perfect rotary furnace for your lab's thermal processing needs?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions from standard 1000°C tube furnaces to high-temperature induction systems. Our experts can help you select the right furnace to ensure precise temperature control, uniform heating, and optimal results for your materials.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1400℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the calcining zone in the kiln? The Key to Efficient Chemical Transformation
- What are the equipment for pyrolysis laboratory? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Research
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- How does a rotary extractor work? Master Continuous High-Volume Solid Processing



















