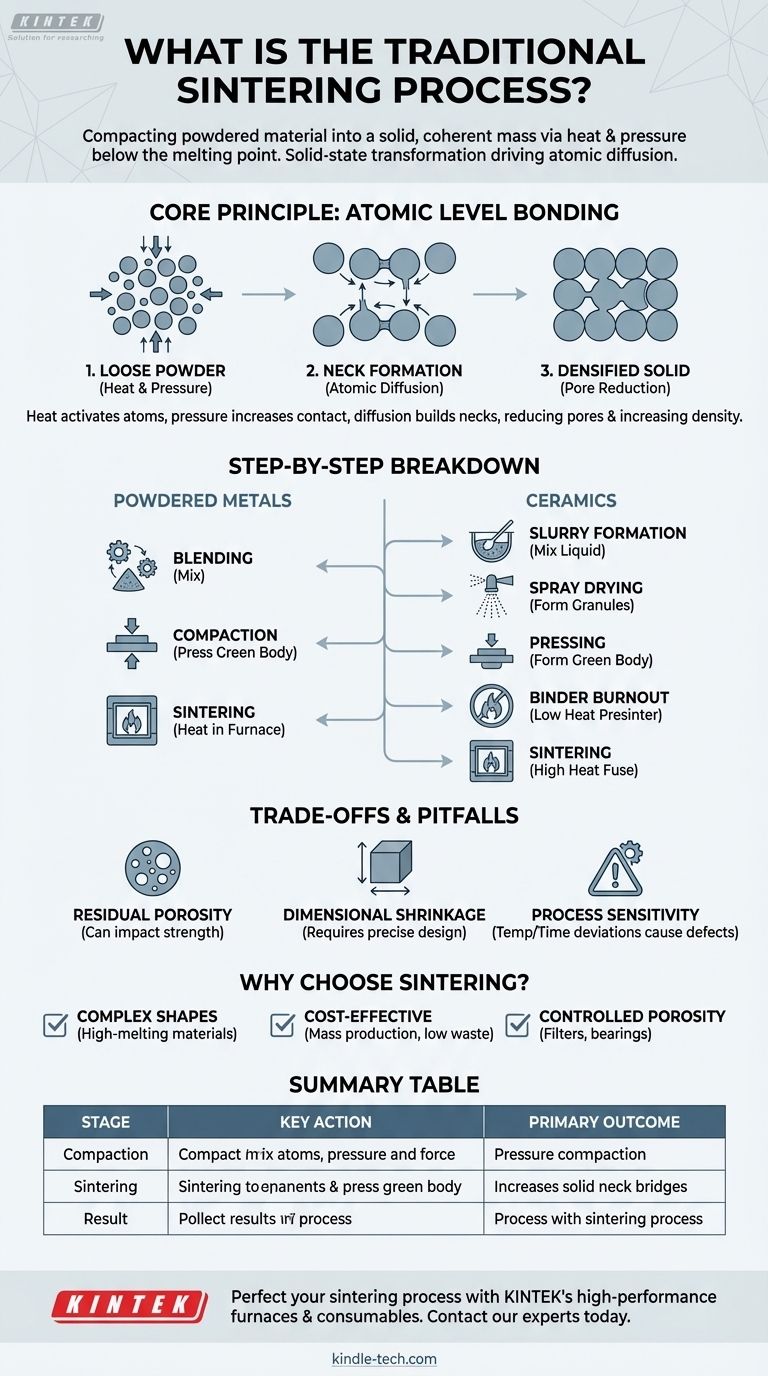
The traditional sintering process is a heat treatment method used to compact powdered material into a solid, coherent mass without melting it. By applying heat and often pressure at temperatures below the material's melting point, the process forces individual particles to bond together at an atomic level, reducing porosity and dramatically increasing the part's density and strength.
Sintering is fundamentally a solid-state transformation. It does not rely on melting and casting but instead uses thermal energy to drive atomic diffusion, creating strong metallurgical bonds between particles to form a dense and functional component from a loose powder.

The Core Principle: How Sintering Works at the Atomic Level
To understand sintering, you must look beyond the furnace and focus on the interactions between individual particles. The process is a carefully controlled exercise in materials science.
Heat Without Melting
The key is applying a temperature high enough to make the atoms within the material mobile but not so high that the material loses its solid crystalline structure. This "activated" state is crucial for the bonding process to occur.
The Role of Pressure
In many sintering methods, pressure is applied during the initial compaction stage. This step, called pressing, forms a "green body" by forcing the powder particles into intimate contact, maximizing the surface area where bonding can occur.
Atomic Diffusion and Neck Formation
At sintering temperatures, atoms from adjacent particles migrate across the points of contact. This atomic diffusion builds small bridges, or "necks," between the particles. As the process continues, these necks grow wider and stronger.
Densification and Pore Reduction
As the necks grow, they pull the particle centers closer together. This action systematically eliminates the empty spaces, or pores, between the particles. The result is a significant increase in the part's relative density and a corresponding decrease in its porosity.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process
While the core principle remains the same, the exact steps vary depending on the material. The two most common pathways are for metals and ceramics.
For Powdered Metals
The process for metals is typically straightforward and consists of three main stages:
- Blending: The base metal powder is mixed with alloying elements or additives to achieve the desired chemical composition and properties.
- Compaction: The blended powder is pressed into a mold or die under high pressure to form the part's net shape, known as a green body.
- Sintering: The green body is heated in a controlled-atmosphere furnace to the sintering temperature, allowing atomic bonding and densification to occur.
For Ceramics
The ceramic process often begins with finer powders and requires additional steps to prepare the material:
- Slurry Formation: Unfired ceramic powder is mixed with water, a binder, and other agents to create a uniform liquid slurry.
- Spray Drying: The slurry is spray-dried to form uniform, flowable granules.
- Pressing: The dried powder is pressed into a mold to form the green body.
- Binder Burnout (Presintering): The part is heated at a low temperature to slowly burn off the binder without damaging the fragile structure.
- Sintering: The part is heated to a much higher temperature to fuse the ceramic particles together and achieve final density.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Sintering is a powerful technique, but it is not without its challenges. True expertise lies in understanding its limitations and managing the critical variables.
Residual Porosity
Achieving 100% theoretical density is rare in traditional sintering. Some residual porosity almost always remains, which can impact the final mechanical properties, such as tensile strength and fatigue resistance.
Dimensional Shrinkage
As the part densifies, it shrinks. This shrinkage is substantial and must be precisely calculated and compensated for in the initial design of the compaction tools to ensure the final part meets dimensional tolerances.
Process Sensitivity
The final properties of a sintered part are highly sensitive to process variables. Minor deviations in temperature, time, or furnace atmosphere can lead to defects like undersintering (incomplete bonding), oversintering (grain growth that weakens the part), or blistering due to trapped gases.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right manufacturing process depends entirely on your objectives. Sintering excels in specific scenarios where other methods fall short.
- If your primary focus is complex shapes with high-melting-point materials: Sintering is ideal because you can form an intricate shape at room temperature before applying heat, avoiding the challenges of casting refractory metals like tungsten or molybdenum.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production: The process is highly automated and repeatable for creating millions of identical parts, such as gears and bushings, with minimal material waste compared to subtractive machining.
- If your primary focus is creating materials with controlled porosity: Sintering is one of the few methods that allows you to intentionally engineer porosity, which is essential for products like self-lubricating bearings, filters, and certain biomedical implants.
Ultimately, traditional sintering provides a precise and versatile pathway for transforming simple powders into robust, high-performance components.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Action | Primary Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Compaction | Powder is pressed into a 'green body' | Forms the part's initial shape |
| Sintering | Heat is applied below melting point | Atomic diffusion creates strong bonds |
| Result | Densification and pore reduction | Increased strength and density |
Ready to perfect your sintering process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and consumables essential for precise temperature control and consistent results in powder metallurgy and ceramic fabrication. Our expertise ensures your materials achieve optimal density and strength. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between a box furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lab Furnace for Your Application
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of sintering? A Guide to High-Performance Manufacturing
- What is the most common metal used for blacksmithing? Start with Mild Steel for Forging Success
- What is the temperature for a furnace? It Depends on Your Material and Process Goal
- What is the importance of melting process? Master the Foundation of Metal Production



















