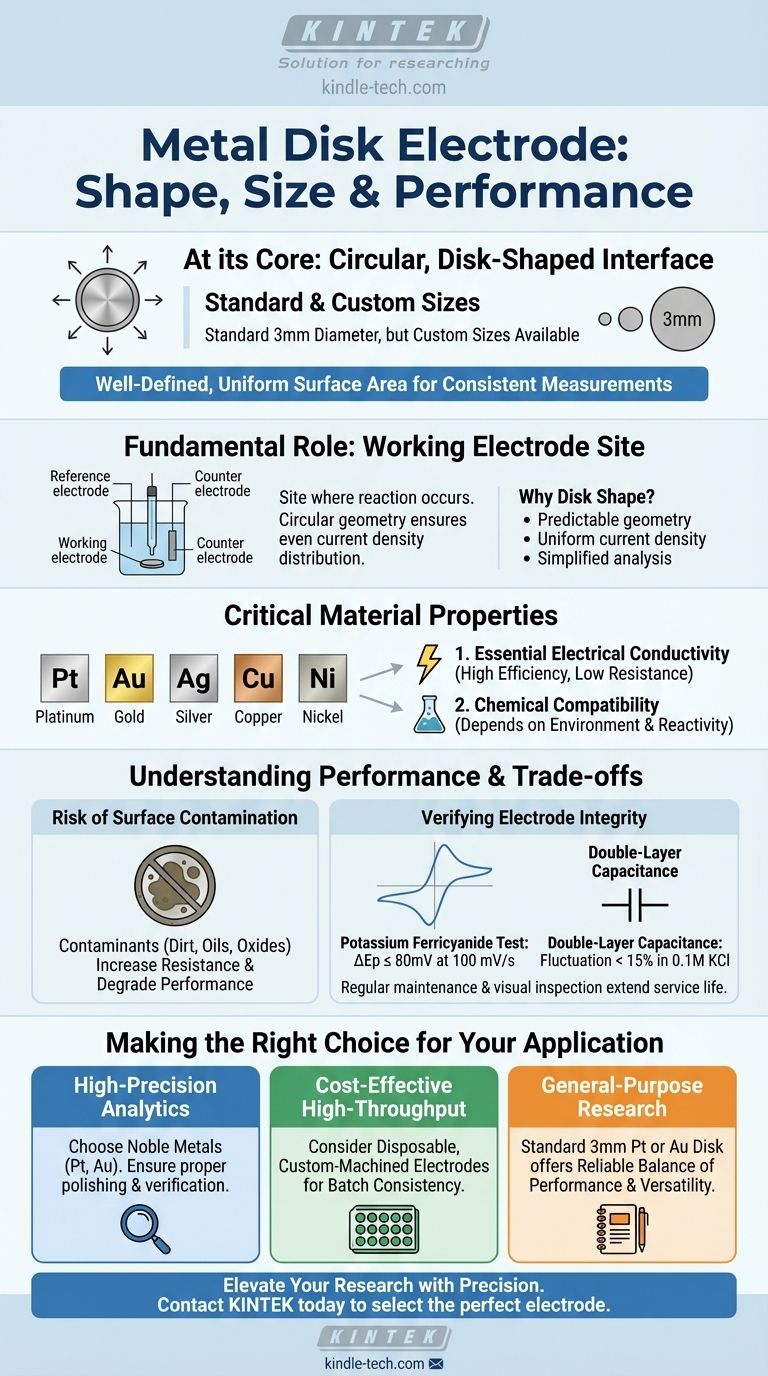
At its core, a metal disk electrode is a circular, disk-shaped component used as a primary interface in electrochemical experiments. While the standard metal diameter is a widely adopted 3mm, this dimension is not fixed; electrodes can be custom-made in various sizes to suit the specific needs of an application.
The simple, circular geometry of a metal disk electrode is not arbitrary. It is intentionally designed to provide a well-defined, uniform surface area, which is crucial for generating consistent and repeatable electrochemical measurements.

The Fundamental Role of the Disk Electrode
A metal disk electrode is one of the most common configurations for a working electrode—the site in an electrochemical cell where the reaction of interest occurs. Its physical design is directly tied to its function.
Why the Disk Shape is Standard
The circular disk shape is favored because it provides a uniform and easily calculable surface area. This predictable geometry helps ensure that the current density is evenly distributed across the electrode's face, simplifying the analysis of experimental results.
The Importance of Material and Size
Electrodes are typically constructed with a small metal disk embedded in an inert insulating sheath. While 3mm is a common diameter, they can be micromachined to much smaller sizes for specialized applications or created as cost-efficient, disposable electrodes for high-throughput testing.
Critical Material Properties
The performance of a metal disk electrode is dictated by the physical and chemical properties of its material. The choice of metal is a critical decision based on the demands of the experiment.
Essential Electrical Conductivity
A primary characteristic of any effective electrode is good electrical conductivity. This property ensures efficient current transfer between the electrode and the electrolyte solution, minimizing energy loss and signal interference.
Metals like silver and copper offer extremely high conductivity, leading to low internal resistance. This low resistance enhances the electrode's response speed and the efficiency of signal transmission.
Material Selection for Chemical Compatibility
Metal disk electrodes are available in a range of materials, including gold, platinum, silver, copper, and nickel. The selection depends entirely on the electrochemical environment, as each metal has different reactivity and stability. Platinum and gold, for example, are often chosen for their chemical inertness.
Understanding Performance and Trade-offs
An electrode's theoretical performance can be compromised by real-world conditions. Understanding these limitations is key to obtaining reliable data.
The Risk of Surface Contamination
The most common failure mode is surface contamination. A clean, pure metal surface is essential for predictable behavior. The presence of dirt, oils, or metal oxides increases the electrode's resistance, which can severely degrade performance and invalidate results.
Verifying Electrode Integrity
The performance of a metal disk electrode can be quantitatively verified. These two tests are common benchmarks for a well-functioning electrode:
- Potassium Ferricyanide Test: In a cyclic voltammetry scan at 100 mV/s, the peak potential separation (ΔEp) should be less than or equal to 80mV.
- Double-Layer Capacitance: When measured in a 0.1M KCl solution, the capacitance fluctuation should remain below 15%.
Longevity and Maintenance
When used and maintained correctly, a high-quality metal disk electrode can have a long service life. Regular maintenance involves visually inspecting the surface for damage and checking its electrical resistance. If an electrode is severely damaged and cannot be repaired, it must be replaced with a new one of the exact same model and specifications to ensure experimental consistency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of electrode depends on balancing performance requirements, chemical compatibility, and experimental constraints.
- If your primary focus is high-precision analytics: Choose a noble metal like platinum or gold known for its stability and ensure it is properly polished and electrochemically verified before each use.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-throughput screening: Consider disposable, custom-machined electrodes where consistency across a batch is more critical than the absolute performance of a single unit.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose research: A standard 3mm platinum or gold disk electrode offers a reliable balance of performance, versatility, and reusability for a wide range of experiments.
Ultimately, understanding these factors ensures your electrode is a reliable tool, not an uncontrolled variable in your experiment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Typical Specification | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Circular Disk | Provides uniform current density and easy surface area calculation. |
| Common Diameter | 3mm | A standard size for general-purpose research; other sizes are available. |
| Common Materials | Platinum, Gold, Silver, Copper, Nickel | Chosen for conductivity, chemical inertness, and application-specific needs. |
| Performance Verification | ΔEp ≤ 80mV (Ferricyanide Test) | Key metrics to ensure electrode integrity and reliable data. |
Ensure your electrochemical experiments are built on a foundation of precision and reliability.
The right metal disk electrode is critical for generating consistent, high-quality data. At KINTEK, we specialize in supplying high-performance lab equipment, including a wide range of standard and custom metal disk electrodes tailored to your specific research needs—from high-precision analytics with noble metals to cost-effective solutions for high-throughput screening.
Let our experts help you select the perfect electrode for your application. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your requirements and enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Gold Disc Electrode
People Also Ask
- What methods can be used to verify the performance of a metal disk electrode? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Results
- What is the purpose of selecting polycrystalline disc electrodes? Achieve Precision in Noble Metal Corrosion Research
- What is the expected lifespan of a metal disk electrode? Extend Its Life with Proper Care
- What is the proper post-experiment procedure for a metal disk electrode? Ensure Accurate, Reproducible Results
- How should a metal disk electrode be handled during an experiment? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements



















