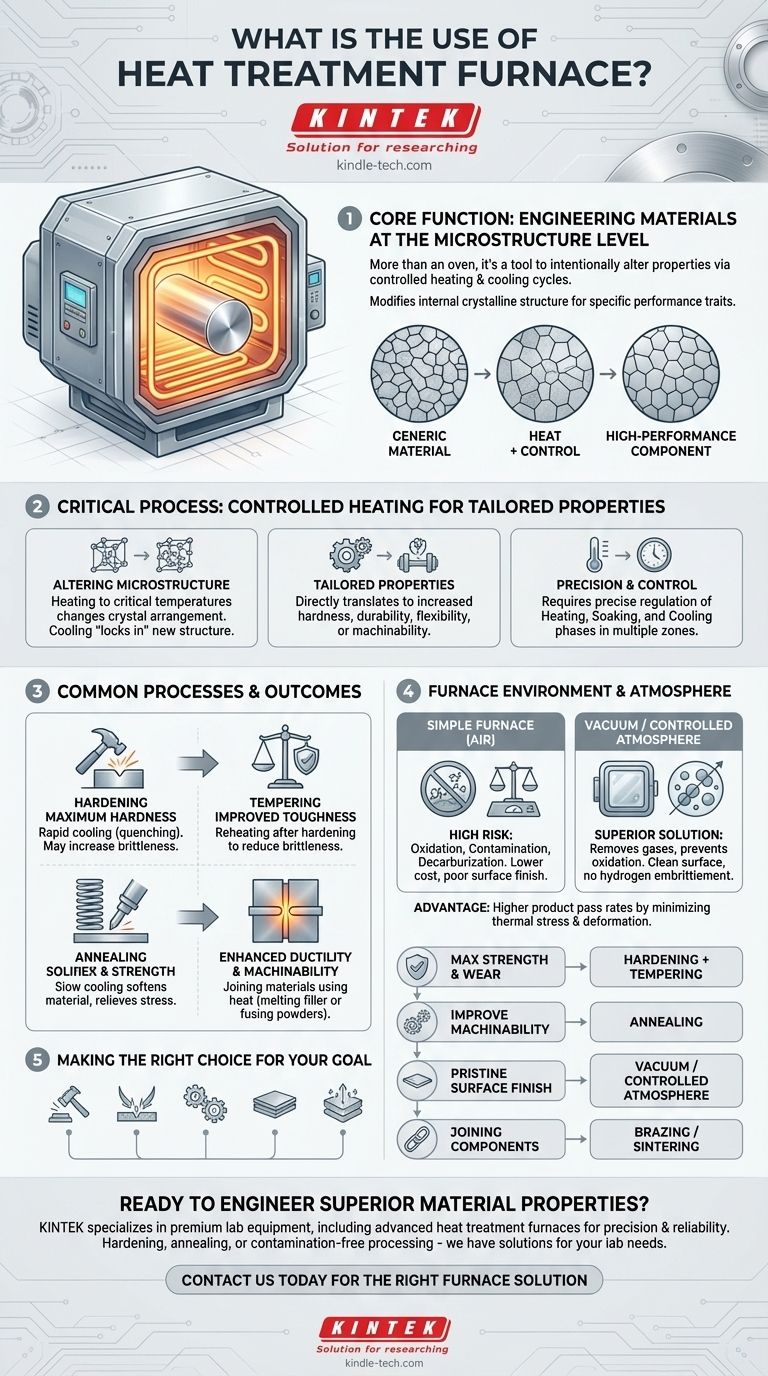
At its core, a heat treatment furnace is a specialized piece of equipment used to intentionally alter the physical, chemical, and mechanical properties of a material through precisely controlled cycles of heating and cooling. These furnaces are not simply ovens; they are advanced tools for engineering materials like metals and alloys to achieve specific performance characteristics, such as increased hardness, improved durability, or enhanced workability.
The fundamental use of a heat treatment furnace is not merely to heat a material, but to modify its internal microstructure. This controlled transformation allows you to turn a generic material into a high-performance component with specific, desirable traits that it did not possess in its raw state.

Why Controlled Heating is a Critical Engineering Process
The value of a heat treatment furnace lies in its ability to execute highly specific thermal processes. The results are determined by the temperature, the duration of heating, the cooling rate, and the atmosphere within the furnace.
Altering the Material's Microstructure
Most industrial metals have a crystalline structure. When heated to critical temperatures, the arrangement of these crystals changes. A subsequent controlled cooling "locks in" a new, more desirable structure.
The Goal: Tailored Material Properties
This change in microstructure directly translates to a change in the material's bulk properties. A component can be made significantly stronger, more resistant to wear, more flexible, or easier to machine.
The Importance of Precision and Control
A heat treatment process consists of distinct phases: a heating period, a holding or "soaking" period at a specific temperature, and a cooling period. Each phase must be precisely regulated to achieve the intended outcome and avoid damaging the material. Modern furnaces utilize multiple heat zones to ensure uniform temperature.
Common Heat Treatment Processes and Their Outcomes
Different thermal cycles achieve different results. A versatile furnace can perform a wide range of standard processes to meet diverse engineering needs.
Hardening
This process involves heating a metal to a critical temperature and then cooling it rapidly (quenching). The result is a significant increase in the material's hardness and strength, though it may also become more brittle.
Tempering
Tempering is a secondary process typically performed after hardening. The material is reheated to a lower temperature to reduce brittleness and increase its toughness, creating a better balance of hardness and durability.
Annealing
Annealing involves heating a material and then cooling it very slowly. This process softens the material, relieves internal stresses, and refines its grain structure, making it more ductile and easier to work with.
Brazing and Sintering
Heat treatment furnaces are also used for joining materials. In brazing, a filler metal is melted to join two components without melting the base parts. Sintering uses heat to fuse powdered materials together into a solid mass.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Furnace Environment
The atmosphere inside the furnace is just as critical as the temperature. The choice of furnace type often comes down to balancing cost against the need for environmental control.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
At high temperatures, most metals will react with oxygen in the air, forming an oxide layer (scale) and potentially losing carbon from their surface (decarburization). A well-sealed furnace with a controlled atmosphere prevents this.
The Advantage of Vacuum Furnaces
Vacuum furnaces are a superior solution that removes virtually all atmospheric gases. This eliminates the risk of oxidation and contamination, resulting in a clean, bright surface finish and preventing issues like hydrogen embrittlement.
Cost vs. Performance
A simple furnace exposed to air is less expensive but offers poor control over surface quality. A controlled-atmosphere or vacuum furnace provides significantly better results—improving the part's mechanical properties and service life—but represents a larger capital investment.
The Risk of Deformation
Improper or uneven heating and cooling can create internal stresses that cause the part to warp or deform. Advanced furnaces with rapid, uniform temperature control minimize this thermal stress, leading to higher product pass rates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific heat treatment process is chosen based entirely on the desired final properties of the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and wear resistance: A hardening process, often followed by tempering, is the correct path.
- If your primary focus is improving machinability or formability: An annealing process will soften the material and relieve internal stresses.
- If your primary focus is a pristine surface finish with zero contamination: A vacuum or controlled-atmosphere furnace is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is joining separate components into a single assembly: Brazing or sintering are the appropriate thermal processes.
Ultimately, a heat treatment furnace is the tool that elevates a material from a simple commodity to a component engineered for a specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Hardening | Increase Strength & Wear Resistance | Maximum Hardness |
| Tempering | Reduce Brittleness | Improved Toughness |
| Annealing | Soften Material | Enhanced Ductility & Machinability |
| Brazing/Sintering | Join Components | Solid, Fused Assemblies |
Ready to engineer superior material properties?
KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment, including advanced heat treatment furnaces designed for precision and reliability. Whether your goal is hardening, annealing, or contamination-free processing in a vacuum atmosphere, our solutions are engineered to meet your specific laboratory needs.
Contact us today to discuss how the right furnace can transform your materials and enhance your results.
Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan



















