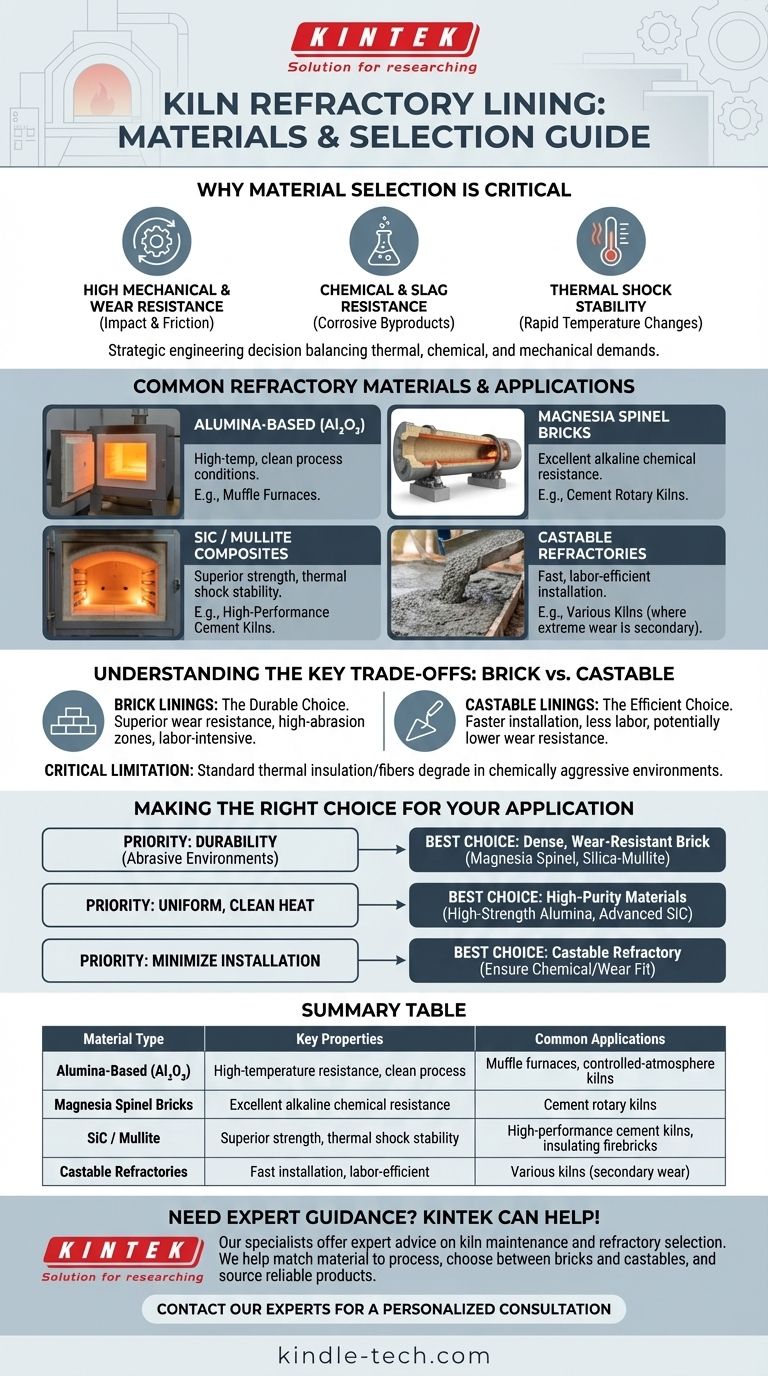
The most common refractory materials used for kiln linings are specialized bricks and castables made from compounds like high-strength alumina, magnesia spinel, silicon carbide (SiC), and silica-mullite. The specific material chosen is dictated by the kiln's operating temperature, the chemical environment, and the abrasiveness of the materials being processed.
The selection of a kiln refractory is not about finding a single "best" material, but about making a strategic engineering decision. The right choice balances thermal performance, chemical resistance, and mechanical durability against the specific demands of the kiln's application.

Why Material Selection is So Critical
A kiln's refractory lining is its primary defense against extreme operational stress. The material must be carefully chosen to withstand a unique combination of thermal, chemical, and mechanical abuse to ensure operational integrity and longevity.
High Mechanical and Wear Resistance
The movement of materials inside a kiln, especially a rotary kiln, creates significant friction and impact. The lining must possess high mechanical strength and wear resistance to prevent premature failure from this constant abrasion.
Chemical and Slag Resistance
High-temperature processes often create corrosive byproducts, such as molten slag or alkaline vapors. The refractory must be chemically inert to these substances to avoid corrosion and degradation of the lining.
Thermal Shock Stability
Kilns undergo significant temperature fluctuations during startup, operation, and shutdown. The lining material needs excellent thermal shock stability to resist cracking or spalling when exposed to these rapid temperature changes.
Common Refractory Materials and Their Applications
Different kiln types and processes require different material properties. This has led to the development of several classes of specialized refractory compounds.
Alumina-Based Materials (Al₂O₃)
High-strength alumina is a go-to material for applications requiring very high temperatures and clean, uniform process conditions. It is frequently used in the linings of muffle furnaces and other controlled-atmosphere environments.
Magnesia and Spinel Bricks
Magnesia spinel brick is a standard choice for the demanding environment of cement rotary kilns. These materials offer excellent resistance to the alkaline chemical attacks common in cement production.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Mullite Composites
Materials combining silicon carbide, mullite, and alumina are engineered for superior performance. Silica-mullite bricks are a modern, high-performance option for large cement kilns, while silicon carbide is also used in advanced insulating firebricks for its strength and thermal properties.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
The choice of refractory is not just about the chemical composition but also its physical form. The two main formats, brick and castable, offer distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Brick Linings: The Durable Choice
Refractory bricks are pre-fired blocks that are meticulously installed by skilled labor. They generally offer superior wear resistance, making them the preferred choice for high-abrasion zones in equipment like cement rotary kilns.
Castable Linings: The Efficient Choice
Castable refractories are concrete-like materials that are mixed on-site and poured or sprayed into place. This makes installation significantly faster and less labor-intensive than brick-laying, though it may not offer the same level of wear resistance as a dense, pre-fired brick.
A Critical Limitation: Chemical Erosion
It is crucial to understand that not all high-temperature materials are suitable for every kiln. Standard thermal insulation bricks and refractory fibers cannot be used in chemically aggressive environments, such as the inside of a cement kiln, as they will rapidly degrade from chemical erosion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct refractory lining is a decision based on prioritizing performance characteristics for a specific operational goal.
- If your primary focus is durability in abrasive environments (e.g., a cement rotary kiln): Your best choice is a dense, wear-resistant brick like Magnesia spinel or silica-mullite.
- If your primary focus is uniform, clean heat (e.g., a muffle furnace): Prioritize high-purity materials like high-strength alumina or advanced silicon carbide bricks.
- If your primary focus is minimizing installation time and labor: Consider a castable refractory, but ensure its chemical and wear resistance properties meet the demands of your specific process.
Ultimately, a successful kiln operation depends on a lining material perfectly matched to its unique set of challenges.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Alumina-Based (Al₂O₃) | High-temperature resistance, clean process conditions | Muffle furnaces, controlled-atmosphere kilns |
| Magnesia Spinel Bricks | Excellent alkaline chemical resistance | Cement rotary kilns |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) / Mullite | Superior strength, thermal shock stability | High-performance cement kilns, insulating firebricks |
| Castable Refractories | Fast installation, labor-efficient | Various kilns where extreme wear resistance is secondary |
Need expert guidance selecting the perfect refractory lining for your kiln?
The right material is critical for your kiln's performance, longevity, and efficiency. The specialists at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including expert advice on kiln maintenance and refractory selection for laboratory and industrial applications.
We can help you:
- Match the material to your specific process (temperature, chemical environment, abrasiveness).
- Choose between bricks and castables based on your durability and installation needs.
- Source reliable refractory products tailored to your operational goals.
Don't leave your kiln's integrity to chance. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and ensure your operation runs smoothly and efficiently.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker



















