At its core, vacuum evaporation is a process used to deposit thin films of an incredibly diverse set of materials. These range from common metals like aluminum and copper to precious metals like gold and platinum, refractory metals such as tungsten, and even complex dielectric and ceramic compounds like silicone dioxide and indium tin oxide. The specific material chosen is entirely dependent on the desired properties of the final thin film.
The selection of a material for evaporation is not arbitrary; it is a direct function of the application's requirements and the material's physical properties, especially its melting point, which determines the most suitable evaporation technique.

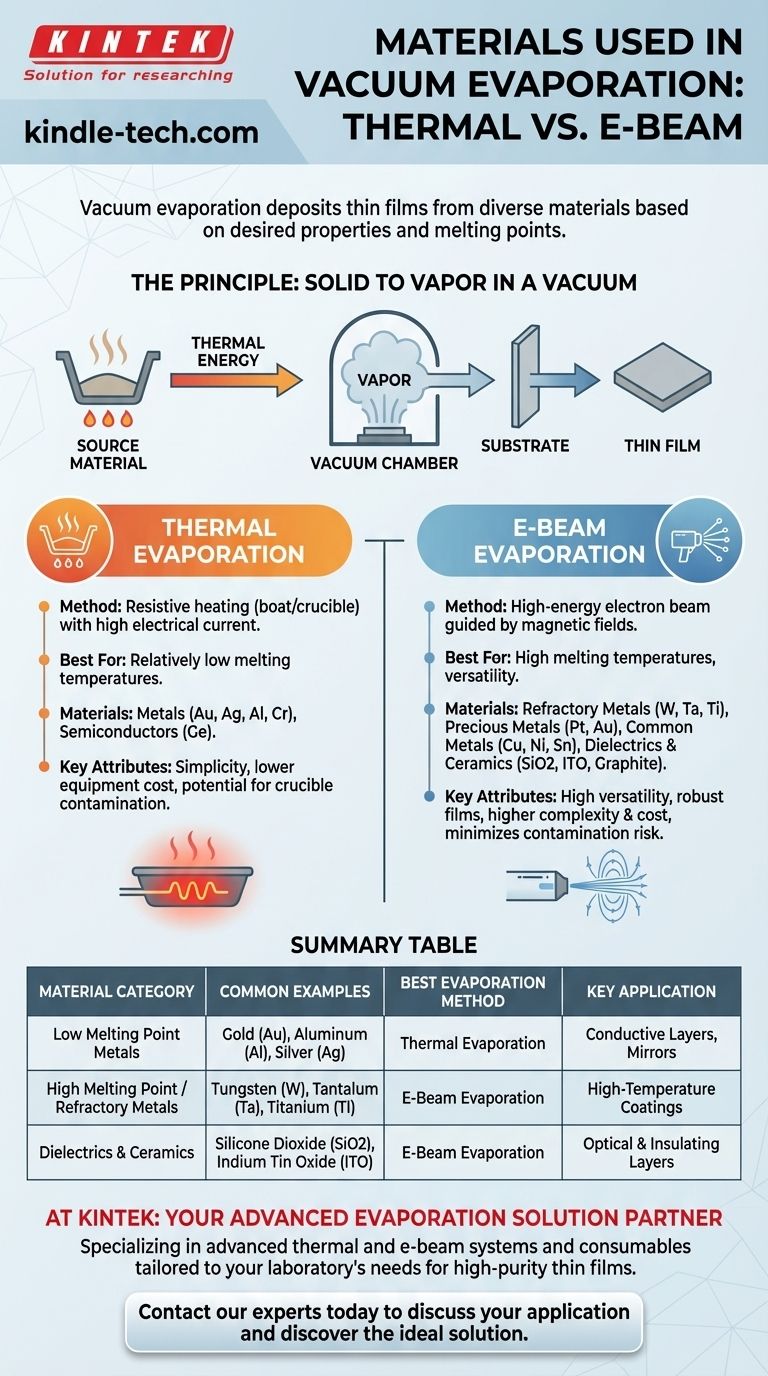
The Principle: From Solid to Vapor
Before examining specific materials, it's essential to understand the fundamental process. Evaporation works by giving a source material enough energy to transition from a solid or liquid state directly into a gaseous vapor.
Overcoming Binding Forces
Every material's atoms are held together by binding forces. The goal of any evaporation technique is to supply enough thermal energy to these atoms so they can overcome these forces and escape the surface as a vapor.
Deposition in a Vacuum
This process is conducted in a vacuum chamber. The evaporated atoms travel in a straight line until they strike a cooler surface, known as a substrate, where they condense back into a solid state, forming a thin, uniform film.
Material Selection by Evaporation Method
The method used to heat the material is the primary factor that dictates which materials can be effectively evaporated. The two most common methods are thermal evaporation and electron-beam (e-beam) evaporation.
Thermal Evaporation Materials
Thermal evaporation is the simpler of the two methods. A source material is placed in a resistive boat or crucible, which is heated by passing a high electrical current through it.
This method is best suited for materials with relatively low melting temperatures. Common examples include:
- Metals: Gold (Au), Silver (Ag), Aluminum (Al), Chromium (Cr)
- Semiconductors: Germanium (Ge)
E-Beam Evaporation Materials
E-beam evaporation uses a high-energy beam of electrons, guided by magnetic fields, to heat the source material. This technique can achieve extremely high temperatures in a very localized area.
Because of this, e-beam is the ideal choice for materials with high melting temperatures. It can deposit a much wider range of materials, including:
- Refractory Metals: Tungsten (W), Tantalum (Ta), Titanium (Ti)
- Precious Metals: Platinum (Pt), Gold (Au)
- Common Metals: Copper (Cu), Nickel (Ni), Tin (Sn)
- Dielectrics & Ceramics: Silicone Dioxide (SiO2), Indium Tin Oxide (ITO), Graphite
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material and method involves balancing technical requirements with practical limitations. No single approach is perfect for every scenario.
Thermal Evaporation: Simplicity vs. Limitation
The primary advantage of thermal evaporation is its relative simplicity and lower equipment cost. However, it is fundamentally limited to materials that can be evaporated at temperatures the crucible itself can withstand without melting or reacting.
E-Beam Evaporation: Versatility vs. Complexity
E-beam evaporation offers incredible versatility, capable of depositing robust, high-performance films from materials that are impossible to handle with thermal methods. The trade-off is higher equipment cost and greater operational complexity.
Material Purity and Contamination
In thermal evaporation, there is a risk that the heated crucible material itself can contaminate the deposited film. E-beam evaporation minimizes this risk by heating only a small portion of the source material, leaving the rest cool and contained.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the specific goal of your deposition process.
- If your primary focus is depositing conductive layers of common metals like aluminum or gold: Thermal evaporation is often a sufficient and cost-effective method.
- If your primary focus is creating durable, high-temperature, or optical coatings: E-beam evaporation is necessary to handle refractory metals and dielectric compounds.
- If your primary focus is fabricating complex semiconductor devices: You will likely need access to both methods to deposit the different conductive and insulating layers required.
Ultimately, selecting the right material and method is a strategic decision driven by the physical properties of your source and the functional requirements of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Examples | Best Evaporation Method | Key Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Melting Point Metals | Gold (Au), Aluminum (Al), Silver (Ag) | Thermal Evaporation | Conductive Layers, Mirrors |
| High Melting Point / Refractory Metals | Tungsten (W), Tantalum (Ta), Titanium (Ti) | E-Beam Evaporation | High-Temperature Coatings |
| Dielectrics & Ceramics | Silicone Dioxide (SiO2), Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) | E-Beam Evaporation | Optical & Insulating Layers |
Need to deposit a specific material for your project? The right evaporation method is critical for achieving high-purity, high-performance thin films. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced thermal and e-beam evaporation systems and consumables tailored to your laboratory's unique needs—whether you're working with common metals, refractory materials, or complex dielectric compounds.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and discover the ideal evaporation solution for your research or production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between sputtering and thermal evaporation? Choose the Right PVD Method for Your Thin Film
- What are the drawbacks of thermal evaporation? Understanding the Limitations for High-Performance Applications
- What is thermal evaporation used to deposit? A Guide to Metals, Compounds, and Key Applications
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What is the meaning of thermal evaporation? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Thin Film Coating



















