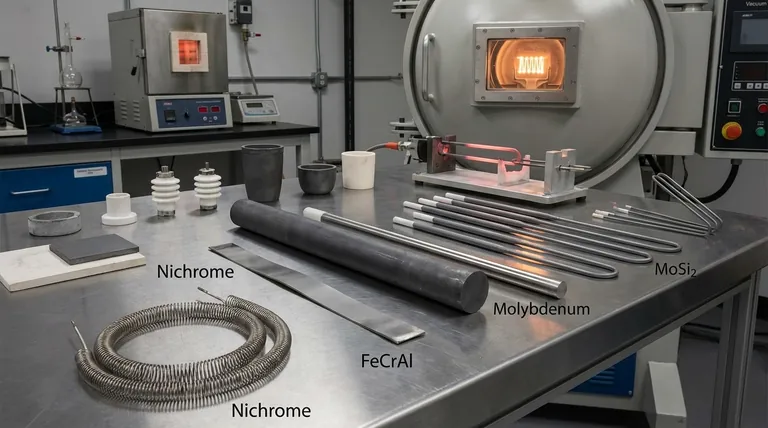
While many people believe there is a single answer, the truth is that a wide range of materials are used for heating elements. The most common and well-known is Nichrome, an alloy of nickel and chromium used in everyday appliances. However, for industrial and high-temperature applications, the choice expands significantly to include refractory metals like Molybdenum and Tungsten, as well as non-metallic materials like Graphite and Silicon Carbide.
There is no single "best" material for heating elements. The choice is a strategic decision based on the required operating temperature, the working environment (air vs. vacuum), and cost, ranging from common alloys for appliances to exotic materials for industrial furnaces.

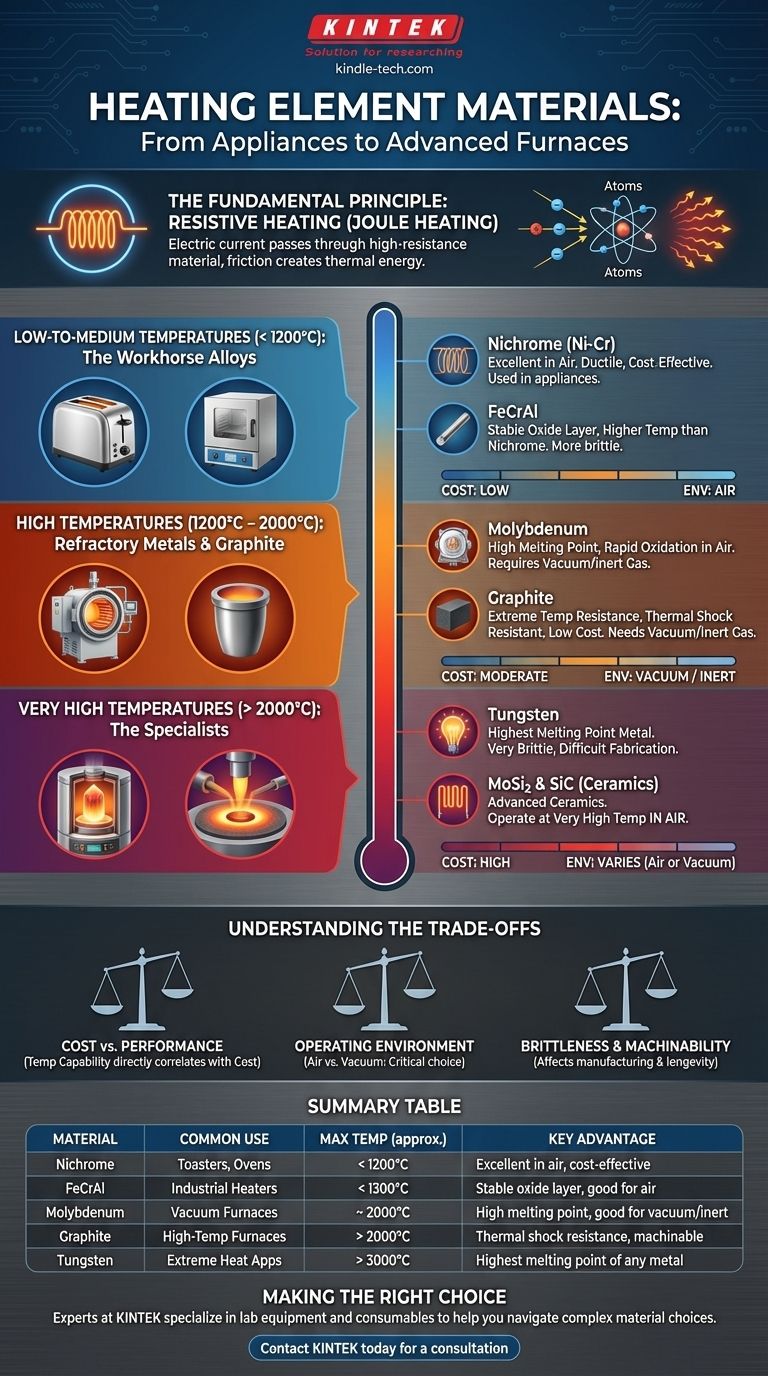
The Fundamental Principle: Resistive Heating
To understand why certain materials are chosen, we must first understand the core principle of how they work. This is known as resistive heating, or Joule heating.
How Resistance Creates Heat
When an electric current passes through a material with high electrical resistance, the flow of electrons is impeded. This friction at an atomic level converts electrical energy directly into thermal energy, causing the material to heat up.
The Critical Property: A Stable Oxide Layer
A material that simply gets hot is not enough. To be a useful heating element in open air, it must resist burning out, a process known as oxidation. Materials like Nichrome and Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl) alloys excel here because they form a thin, durable, and adherent layer of oxide on their surface that protects the metal underneath from further oxidation, even at high temperatures.
A Spectrum of Materials: From Appliances to Furnaces
The choice of heating element material is dictated almost entirely by the target operating temperature and environment. Materials are generally grouped into temperature-specific categories.
Low-to-Medium Temperatures (< 1200°C): The Workhorse Alloys
These materials are found in household appliances and common lab equipment.
- Nichrome (Nickel-Chromium): The most common choice for applications like toasters, hair dryers, and space heaters. It offers good resistance, ductility (it's easily formed into coils), and excellent performance in air.
- FeCrAl (Iron-Chromium-Aluminum): A primary alternative to Nichrome, often capable of reaching slightly higher temperatures. It forms a very stable oxide layer but can be more brittle than Nichrome.
High Temperatures (1200°C – 2000°C): Refractory Metals & Graphite
These are reserved for industrial furnaces and specialized processes that require significant heat.
- Molybdenum: A popular choice for vacuum or inert-gas furnaces. It has a very high melting point but will rapidly oxidize and fail if operated in air at high temperatures.
- Graphite: Valued for its extremely high temperature resistance, low cost, and excellent resistance to thermal shock. Like Molybdenum, it must be used in a vacuum or inert atmosphere to prevent it from burning away.
Very High Temperatures (> 2000°C): The Specialists
These materials are used in the most extreme heating applications, such as crystal growth, sintering, and advanced research.
- Tungsten: Possesses the highest melting point of any metal, making it suitable for the most demanding temperature requirements. It is, however, very brittle and difficult to work with.
- Tantalum: Another refractory metal with an extremely high melting point. It is more ductile than Tungsten but also more expensive.
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) & Silicon Carbide (SiC): These are advanced ceramic compounds, not metals. Their key advantage is the ability to operate at very high temperatures in an air atmosphere, a task that refractory metals cannot perform.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a heating element material involves balancing several key factors. The ideal choice for one application may be a catastrophic failure in another.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between temperature capability and cost. Nichrome and FeCrAl are relatively inexpensive. Molybdenum and Graphite represent a moderate cost increase. Tungsten, Tantalum, and advanced ceramics are the most expensive options, reserved for applications where their performance is non-negotiable.
Operating Environment: Air vs. Vacuum
This is the most critical trade-off. Nichrome and FeCrAl are designed to work in air. Molybdenum, Tungsten, and Graphite must be protected in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere. Specialized ceramics like MoSi2 bridge this gap, offering high-temperature performance in air.
Brittleness and Machinability
The material's physical properties affect manufacturing and element longevity. Nichrome is ductile and easily coiled. Graphite is easily machined into complex shapes. Tungsten is notoriously brittle at room temperature, making element fabrication a challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material is a matter of matching its properties to your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is consumer appliances or low-temperature ovens (<1200°C): Your choice is almost always a Nichrome or FeCrAl alloy for its excellent cost-effectiveness and stability in air.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature vacuum or inert gas furnaces (1200°C - 2000°C): Choose Molybdenum for reliable performance or Graphite for its superior thermal shock resistance and machinability.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature applications (>2000°C) or high-heat processes in open air: You must invest in a specialized material like Tungsten, Tantalum, or an advanced ceramic like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2).
Understanding these core material properties empowers you to move beyond a simple question of "what metal" and make an informed engineering decision.
Summary Table:
| Material | Common Use | Max Temp (approx.) | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nichrome (Ni-Cr) | Toasters, Ovens | < 1200°C | Excellent performance in air, cost-effective |
| FeCrAl | Industrial Heaters | < 1300°C | Stable oxide layer, good for air |
| Molybdenum | Vacuum Furnaces | ~ 2000°C | High melting point, good for vacuum/inert gas |
| Graphite | High-Temp Furnaces | > 2000°C | Excellent thermal shock resistance, machinable |
| Tungsten | Extreme Heat Applications | > 3000°C | Highest melting point of any metal |
Selecting the right heating element is critical for your process efficiency and success. The experts at KINTEK specialize in lab equipment and consumables, helping laboratories like yours navigate these complex material choices. We provide the right heating solutions for your specific temperature, atmosphere, and budget requirements.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and let our expertise ensure your lab's heating applications achieve optimal performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
People Also Ask
- How does the placement of K-type or R-type thermocouples affect temperature control? Ensure Precise Pyrolysis Results
- How do resistive heating elements work? Unlock the Science of Efficient Heat Generation
- What are the disadvantages of tungsten? Navigating its brittleness and high fabrication costs
- Is tungsten shock resistant? Uncovering the Surprising Brittleness of a Hard Metal
- Is tungsten brittle at high temperature? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Performance
- How are PTC cartridge heaters used? Self-Regulating Precision for Direct Immersion and Contact Heating
- Which heating element is the best? Choose the Right Material for Your Temperature and Budget
- What role does a specialized ceramic heating holder play during the irradiation process? Achieve Nuclear Precision











