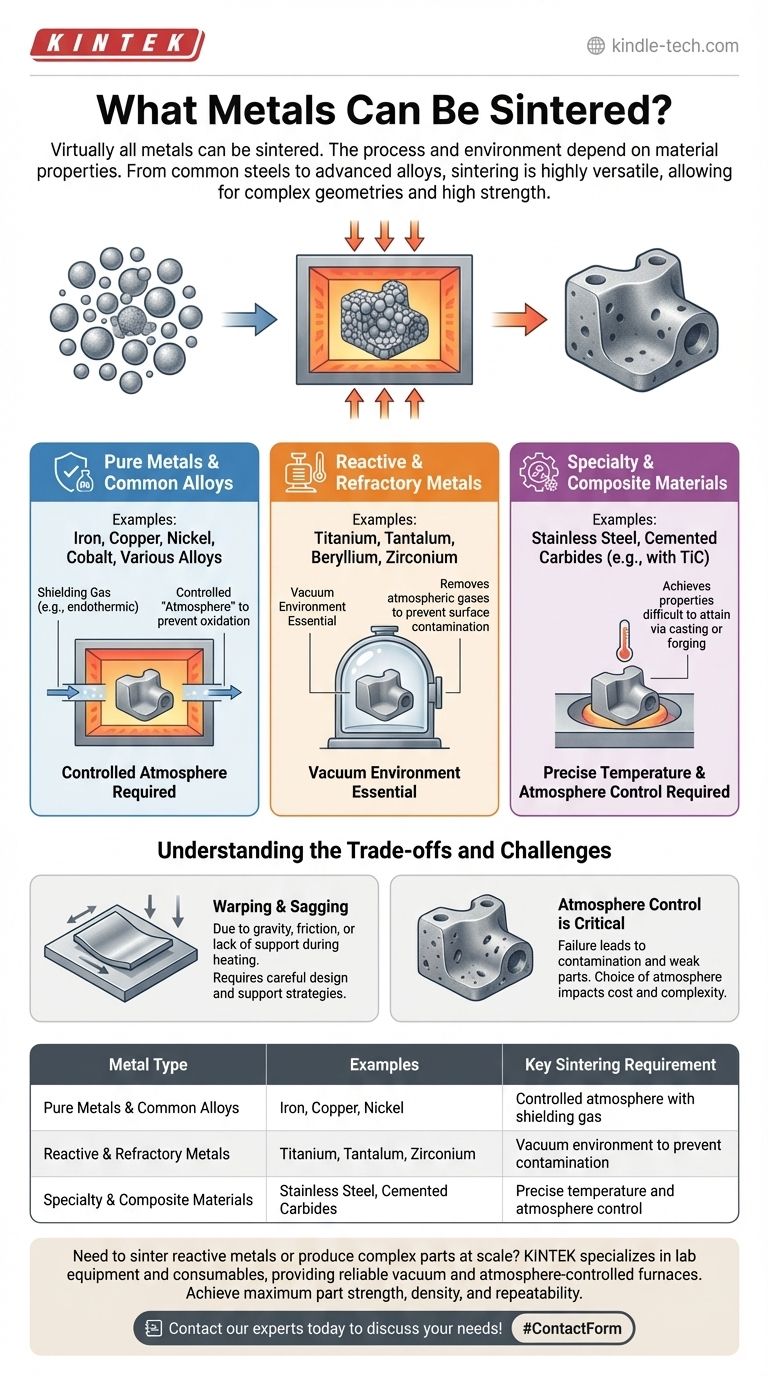
Virtually all metals can be sintered, but the specific process and required environment depend heavily on the metal's properties. Pure metals are excellent candidates, while reactive or refractory metals like titanium and tantalum require specialized conditions, such as a vacuum, to prevent surface contamination and ensure successful bonding.
Sintering is a highly versatile manufacturing process applicable to a wide range of metals, from common steels to advanced alloys. The critical factor is not if a metal can be sintered, but how it must be sintered to control its atmosphere and achieve the desired final properties.

The Principle of Metal Sintering
How It Works
Sintering is a thermal process that bonds metal powders together at a temperature below the material's melting point. By applying heat and sometimes pressure, atoms in the powder particles diffuse across the boundaries, fusing the particles into a solid, coherent piece.
This method allows for the creation of parts with complex geometries or internal features that are often difficult or impossible to produce with traditional subtractive manufacturing methods like machining.
Key Benefits of the Process
The primary advantage of sintering is its ability to create strong, durable parts with high consistency across large production volumes.
The process minimizes the porosity of an object's surface, which directly enhances its final strength and density. It is a reliable and repeatable method, making it ideal for large-scale manufacturing where uniformity is critical.
Which Metals Are Suitable for Sintering?
Pure Metals and Common Alloys
Most common metals can be sintered effectively. This includes iron, copper, nickel, cobalt, and their various alloys.
When sintering these materials at atmospheric pressure, a shielding gas (such as an endothermic gas) is typically required to prevent oxidation, which would inhibit proper bonding between the metal particles.
Reactive and Refractory Metals
Reactive metals like beryllium, titanium, and zirconium, as well as refractory metals like tantalum, are prime candidates for sintering. These materials have very high melting points or are highly susceptible to atmospheric contamination.
For these metals, vacuum sintering is essential. Performing the process in a vacuum removes atmospheric gases that would otherwise react with the metal surfaces, ensuring a clean and strong bond.
Specialty and Composite Materials
Sintering is also widely used for advanced materials. This includes various grades of stainless steel and cemented carbides, which often contain alloys like Titanium Carbide (TiC).
These materials leverage sintering to achieve properties that would be difficult to attain through casting or forging.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
The single most important process variable is the atmosphere. Failure to control it results in contamination and weak parts.
A vacuum is the ultimate protection for highly reactive metals, while a controlled gas atmosphere is sufficient for less reactive alloys. The choice directly impacts equipment cost and complexity.
Potential for Physical Defects
Despite its reliability, the process is not without challenges. Parts can suffer from warping due to gravity or friction between the part and the surface it rests on during heating.
Sagging of unsupported features can also occur, leading to dimensional inaccuracies in the final product. Careful design and support strategies are necessary to mitigate these risks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing to use sintering depends entirely on your material, the complexity of your part, and your production volume.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing with reactive or refractory metals: Vacuum sintering is the most reliable and often the only viable path to success.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of complex parts: Sintering offers exceptional repeatability and cost-effectiveness at scale compared to machining.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum material strength and density: Sintering is a proven method for creating strong, non-porous components from metal powders.
Ultimately, understanding your material's specific needs determines the correct approach to this powerful manufacturing process.
Summary Table:
| Metal Type | Examples | Key Sintering Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Pure Metals & Common Alloys | Iron, Copper, Nickel | Controlled atmosphere with shielding gas |
| Reactive & Refractory Metals | Titanium, Tantalum, Zirconium | Vacuum environment to prevent contamination |
| Specialty & Composite Materials | Stainless Steel, Cemented Carbides | Precise temperature and atmosphere control |
Need to sinter reactive metals or produce complex parts at scale? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the reliable vacuum and atmosphere-controlled furnaces essential for successful metal sintering. Our solutions help you achieve maximum part strength, density, and repeatability. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific material and production needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of sintering? A Guide to Powder-Based Manufacturing
- What are the main advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity and Performance
- What is the process of sintering a furnace? Achieve Precise Material Densification and Lining Durability
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- What are the advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity, Strength, and Performance



















