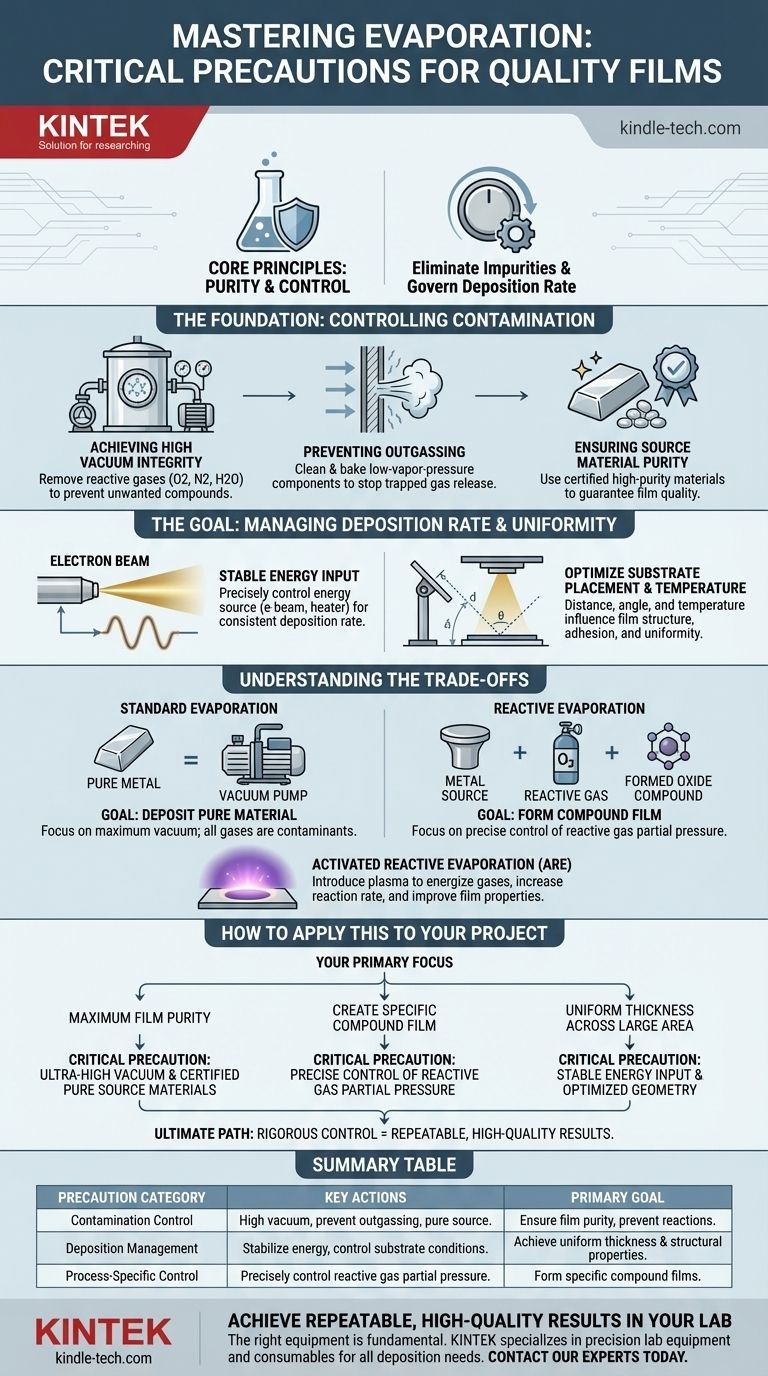
The most critical precautions in any evaporation process are centered on two principles: purity and control. This involves maintaining a high-vacuum environment to eliminate unwanted reactive gases, ensuring the source material itself is free from impurities, and precisely managing the energy input to govern the rate of deposition. Failing in any of these areas leads directly to low-quality, non-uniform films.
The core challenge of evaporation is not just turning a solid into a gas, but ensuring that only the desired atoms or molecules make the journey to the substrate. Therefore, effective precautions are less about a simple safety checklist and more about a rigorous strategy to control the entire process environment.

The Foundation: Controlling Contamination
Contamination is the primary adversary in a high-quality evaporation process. Unwanted atoms or molecules can come from the environment, the equipment, or even the source material itself, leading to films with poor chemical and structural properties.
Achieving High Vacuum Integrity
A high-vacuum or ultra-high vacuum (UHV) environment is non-negotiable. The chamber must be pumped down to remove ambient gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor.
These residual gases can react with the hot evaporant atoms mid-flight or on the substrate surface, forming unintended compounds like oxides. This directly compromises the purity of the deposited film.
Preventing Outgassing from Chamber Components
Even in a vacuum, the chamber walls and internal fixtures can be a source of contamination. When heated by the evaporation source, these components can release trapped gases, a process known as outgassing.
To prevent this, the chamber and all internal components must be made from low-vapor-pressure materials and be thoroughly cleaned and baked out before the process begins.
Ensuring Source Material Purity
The precaution of purity extends to the material you intend to evaporate. Using a low-purity source material guarantees a low-purity film.
It is critical to use source materials (pellets, wires, or powders) with the highest available purity and to handle them carefully to avoid introducing contaminants before they are placed in the crucible.
The Goal: Managing Deposition Rate and Uniformity
Once the environment is clean, the focus shifts to controlling the physical process of deposition. The goal is to deposit a film of a specific, uniform thickness across the entire substrate.
The Critical Role of Energy Input
Evaporation happens when a material is heated sufficiently to transition into a gas. The rate of this evaporation is directly tied to the temperature of the source material.
Therefore, a stable and precisely controlled energy source (like an electron beam or a resistive heater) is essential. Fluctuations in power will cause the deposition rate to vary, making it impossible to control the final film thickness accurately.
The Impact of Substrate Temperature and Placement
The substrate is not a passive observer. Its temperature affects how the arriving atoms stick and arrange themselves, influencing the film's crystal structure and adhesion.
The physical distance and angle between the source and the substrate also dictate the uniformity of the deposition. Placing the substrate too close can result in a thick center and thin edges.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Different evaporation goals require different process considerations, turning some contaminants into necessary reactants. This changes the nature of the precautions you must take.
Standard Evaporation vs. Reactive Evaporation
In standard physical vapor deposition, the goal is to deposit a pure material, so any gas is a contaminant. All precautions focus on achieving the best possible vacuum.
In Reactive Evaporation, a reactive gas (like oxygen or nitrogen) is intentionally introduced into the chamber to form a compound film (e.g., a metal oxide). The primary precaution here shifts from eliminating all gases to precisely controlling the partial pressure of the reactive gas to ensure the correct chemical composition is formed.
Activated Reactive Evaporation (ARE)
In processes like ARE, a plasma is also introduced to energize the reactive gas. This increases the reaction rate and can improve film properties.
The added precaution in this scenario is managing the plasma itself, ensuring its stability and density are optimized for the desired reaction without causing damage to the substrate or film.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your specific goal will determine which precautions demand the most attention.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum film purity: Your most critical precaution is maintaining an ultra-high vacuum (UHV) and using certified high-purity source materials.
- If your primary focus is creating a specific compound film (e.g., an oxide): Your main concern shifts to the precise control and stability of the reactive gas partial pressure.
- If your primary focus is ensuring uniform thickness across a large area: You must prioritize a stable energy input to the source and optimize the geometric relationship between the source and the substrate.
Ultimately, rigorous control over your process variables is the definitive path to repeatable, high-quality results.
Summary Table:
| Precaution Category | Key Actions | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Contamination Control | Achieve high vacuum, prevent outgassing, use pure source materials. | Ensure film purity and prevent unwanted chemical reactions. |
| Deposition Management | Stabilize energy input, control substrate temperature and placement. | Achieve uniform film thickness and desired structural properties. |
| Process-Specific Control | For reactive processes: precisely control reactive gas partial pressure. | Form specific compound films with correct chemical composition. |
Achieve repeatable, high-quality results in your lab. The right equipment is fundamental to implementing these critical evaporation precautions. KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for all your deposition needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you master contamination control, deposition uniformity, and process stability for your specific project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is sintering easier in the presence of a liquid phase? Unlock Faster, Lower-Temperature Densification
- What is sintering reaction? Transform Powders into Dense Solids Without Melting
- What is the function of a vacuum furnace? Achieve High-Purity, Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- What is the sintering process of powder metallurgy? Transform Powder into Durable Metal Parts
- Where is vacuum furnace used? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and High-Tech Manufacturing



















