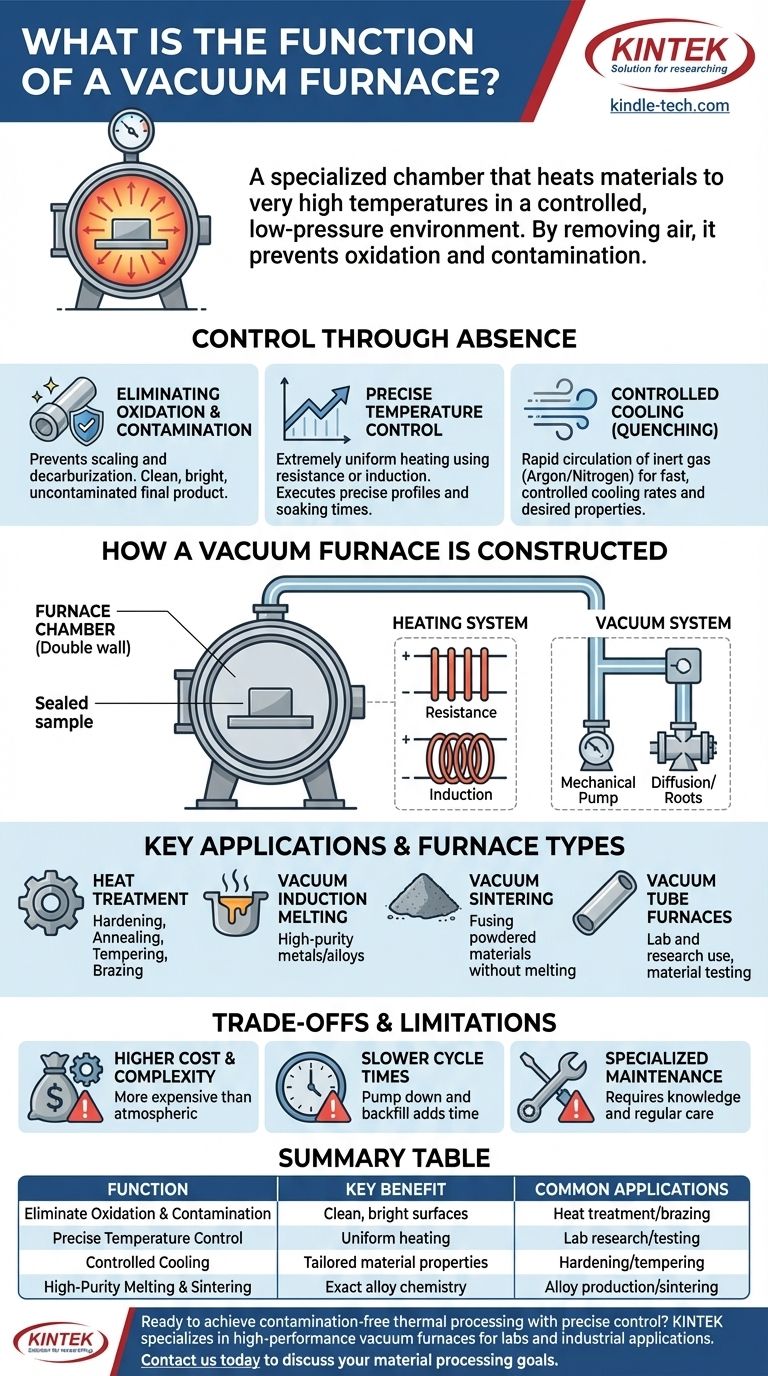
At its core, a vacuum furnace is a specialized chamber designed to heat materials to very high temperatures in a controlled, low-pressure environment. By pumping out nearly all of the air and other reactive gases, it creates a vacuum that prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation and contamination. This allows for high-purity thermal processes that are impossible to achieve in a standard atmospheric furnace.
The primary function of a vacuum furnace is not just to heat materials, but to enable precise control over the material's environment. By removing the atmosphere, you eliminate its influence, ensuring that the only changes to the material are the ones you intentionally introduce through heat and controlled cooling.

The Core Principle: Control Through Absence
The defining feature of a vacuum furnace is what it removes: the atmosphere. This absence of oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor is fundamental to its function and provides three critical advantages.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
In a normal furnace, the oxygen in the air reacts with hot metal, causing oxidation (scaling) and decarburization (loss of carbon from the surface), which can weaken the material. A vacuum environment completely prevents these reactions, resulting in a clean, bright, and uncontaminated final product.
Achieving Precise Temperature Control
The isolated vacuum environment allows for extremely uniform heating. Using elements for resistance heating or coils for electromagnetic induction heating, the furnace can execute precise temperature profiles, including specific heating rates, holding times (soaking), and cooling rates.
Enabling Controlled Cooling (Quenching)
After the heating cycle, the cooling process is just as critical. The furnace chamber is backfilled with a high-pressure stream of an inert gas, such as argon or nitrogen. This gas is circulated rapidly to absorb heat from the workpiece, allowing for a controlled and fast cooling rate (quenching) that is essential for achieving desired material properties like hardness.
How a Vacuum Furnace is Constructed
The ability to maintain a high-purity, high-temperature environment requires specialized components working in concert.
The Furnace Chamber
The main body is a robust, sealed vessel, often with a double wall for water cooling. It is built from high-quality materials capable of withstanding extreme temperatures and the pressure difference between the internal vacuum and the outside atmosphere.
The Heating System
Different applications call for different heating methods. The most common are resistance heating, where electric current passes through graphite or refractory metal elements, and induction heating, which uses magnetic fields to generate heat directly within the metal part itself.
The Vacuum System
A multi-stage system of pumps is required to create the low-pressure environment. This typically includes mechanical pumps for the initial rough vacuum and diffusion or Roots pumps to achieve the final high vacuum level, which can reach pressures as low as 7×10-3 Pa.
Key Applications and Furnace Types
Vacuum furnaces are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Their design is often specialized for a particular industrial process.
Vacuum Heat Treatment
This is a broad category that includes processes like hardening, annealing, tempering, and brazing. The precise control over heating and cooling cycles allows for superior metallurgical properties in finished parts.
Vacuum Induction Melting
Used to produce high-purity metals and alloys, a vacuum induction furnace melts metal in a crucible using electromagnetic induction. The vacuum prevents the molten metal from reacting with gases, ensuring the final chemistry of the alloy is precisely what was intended.
Vacuum Sintering
This process is used to fuse powdered materials, such as ceramics or metals, into a solid mass without melting them. The vacuum prevents oxidation of the fine powders and improves the density and performance of the final sintered product.
Vacuum Tube Furnaces
Often used in laboratory and research settings, a vacuum tube furnace is a type of "hot wall" furnace where a process tube containing the sample is heated externally. This design is versatile for small-scale experiments and material testing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not the universal solution for all heating applications. Objectivity requires acknowledging their specific challenges.
Higher Initial Cost and Complexity
The need for robust vacuum chambers, sophisticated pump systems, and advanced control instrumentation makes vacuum furnaces significantly more expensive and complex than their atmospheric counterparts.
Slower Cycle Times
Achieving a high vacuum is not instantaneous. The time required to pump down the chamber before heating and to backfill it for cooling adds to the overall process time, making it less suitable for high-volume, rapid-turnaround production.
Specialized Maintenance
The components of a vacuum system, such as pumps, seals, and sensors, require specialized knowledge and regular maintenance to ensure they operate correctly and maintain a high-quality vacuum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing technology depends entirely on the requirements of your material and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is material purity and preventing reactions: A vacuum furnace is essential, particularly an induction or sintering model for creating high-purity alloys or components from raw materials.
- If your primary focus is altering material properties through heat treatment: The precise temperature and controlled gas quenching of a vacuum heat-treating furnace provides unmatched control over hardness, strength, and durability.
- If your primary focus is processing simple parts without critical surface finish requirements: A conventional atmospheric furnace is often a more cost-effective and faster solution.
Ultimately, a vacuum furnace is the definitive tool for any thermal process where absolute control of the atmospheric environment is non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Eliminate Oxidation & Contamination | Clean, bright surfaces; no scaling or decarburization | Heat treatment, brazing |
| Precise Temperature Control | Uniform heating & exact thermal profiles | Laboratory research, material testing |
| Controlled Cooling (Gas Quenching) | Tailored material properties like hardness | Hardening, tempering of metals |
| High-Purity Melting & Sintering | Exact alloy chemistry; dense, strong sintered parts | Alloy production, ceramic sintering |
Ready to achieve contamination-free thermal processing with precise control?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance vacuum furnaces for laboratories and industrial applications. Whether you need precise heat treatment, high-purity melting, or advanced sintering, our equipment ensures superior results by eliminating oxidation and contamination.
Contact us today to discuss how a KINTEK vacuum furnace can meet your specific material processing goals and enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature in a vacuum furnace? It Depends on Your Materials and Process Needs
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- What is the structure of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components & Functions
- What does a vacuum furnace do? Achieve High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Components



















