At their core, both compression and transfer molding are designed to work with thermosetting plastics, often called thermosets. While some specialized thermoplastics can be used, the fundamental nature of these processes—applying sustained heat and pressure to induce a chemical change—is intrinsically linked to the properties of thermosets.
The choice of material is not arbitrary; it is dictated by the process itself. Compression and transfer molding are built around materials that cure, undergoing an irreversible chemical reaction to form a strong, stable final part.

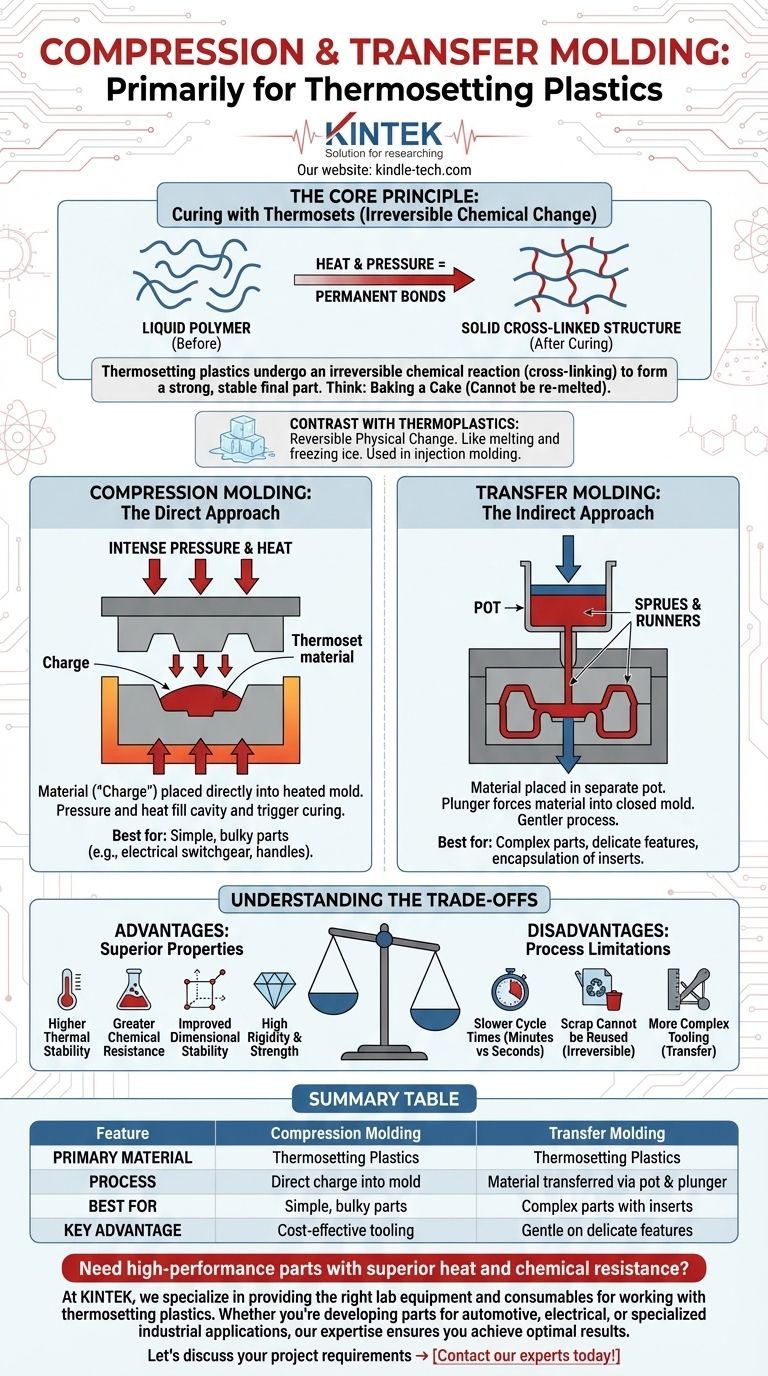
The Principle of Curing: Why Thermosets are Key
To understand why these processes use thermosets, you must first understand the fundamental difference between the two major families of plastics.
Thermosets: An Irreversible Chemical Change
Thermosetting plastics begin as pliable or liquid polymers. When subjected to heat and pressure in the mold, they undergo a chemical reaction called cross-linking.
This reaction creates powerful, permanent bonds between the polymer chains, transforming the material into a rigid, infusible solid.
Think of it like baking a cake. Once the liquid batter is baked, it becomes a solid sponge. You cannot turn it back into liquid batter by reheating it. This change is permanent. Common thermosets include phenolics, epoxies, silicones, and polyesters.
Thermoplastics: A Reversible Physical Change
In contrast, thermoplastics soften and melt when heated, and then re-harden when cooled. No chemical reaction occurs.
This process is like melting and freezing an ice cube. It's a reversible physical change. This property makes thermoplastics ideal for processes like injection molding, where rapid cycles of melting and solidification are required.
Compression vs. Transfer Molding: Two Paths to the Same Goal
Both processes use heat and pressure to cure a thermoset material, but they differ in how the material is introduced into the mold cavity.
Compression Molding: The Direct Approach
In compression molding, a pre-measured amount of thermoset material, called a "charge," is placed directly into the heated lower half of the mold cavity.
The upper half of the mold then closes, applying intense pressure and heat. This forces the material to fill the entire cavity while simultaneously triggering the curing reaction.
This method is straightforward and cost-effective, making it ideal for relatively simple, often bulky parts like electrical switchgear, utensil handles, and automotive components.
Transfer Molding: The Indirect Approach
Transfer molding adds an intermediate step. The thermoset material is placed in a separate chamber, or "pot," located above the main mold cavity.
A plunger heats and pressurizes the material in the pot, forcing it to flow through channels (known as sprues and runners) and into the closed mold cavity.
This indirect filling method is more gentle on the mold and allows for the creation of more complex parts with delicate features or the encapsulation of inserts like metal pins or electronic components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a thermoset-based process like compression or transfer molding comes with a distinct set of advantages and disadvantages compared to using thermoplastics in a process like injection molding.
The Advantage: Superior Material Properties
Thermosets are often chosen when performance is critical. Due to their cross-linked structure, they typically offer:
- Higher thermal stability and resistance to heat.
- Greater chemical resistance.
- Improved dimensional stability and resistance to creep over time.
- High rigidity and strength-to-weight ratios.
The Disadvantage: Slower and Less Forgiving
The reliance on a chemical curing process introduces limitations:
- Longer cycle times: Curing can take several minutes, compared to the seconds-long cycles of injection molding. This makes the process slower and less suited for extremely high-volume production.
- Scrap cannot be reused: Since the curing process is irreversible, any excess material (flash) or rejected parts cannot be melted down and reformed.
- More complex tooling: Transfer molds, with their pots and plunger systems, can be more complex and costly than a simple two-plate compression mold.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use compression or transfer molding is a decision to prioritize material performance over production speed.
- If your primary focus is ultimate heat resistance, chemical stability, or structural rigidity: A thermoset processed via compression or transfer molding is the correct engineering choice.
- If your part has complex geometry or requires embedded inserts: Transfer molding offers better control and a more gentle filling process than direct compression molding.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of simple consumer parts: You should investigate injection molding with thermoplastics, as it offers much faster cycle times and lower per-part costs.
Ultimately, your application's unique performance requirements will guide you to the right combination of material and manufacturing process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Compression Molding | Transfer Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Material | Thermosetting Plastics | Thermosetting Plastics |
| Process | Direct charge into mold | Material transferred via pot & plunger |
| Best For | Simple, bulky parts | Complex parts with inserts |
| Key Advantage | Cost-effective tooling | Gentle on delicate features |
Need high-performance parts with superior heat and chemical resistance?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables for working with thermosetting plastics. Whether you're developing parts for automotive, electrical, or specialized industrial applications, our expertise ensures you achieve optimal results with compression and transfer molding.
Let's discuss your project requirements → Contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of press machines? Choose the Right Heating Tech for Your Application
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- Why is it necessary to use high-precision temperature-controlled heating furnaces? Secure Natural Fiber Integrity.
- What is the hot press molding method? A Guide to Shaping Materials with Heat & Pressure
- What is the temperature range for compression molding? Optimize Your Process for Perfect Parts



















