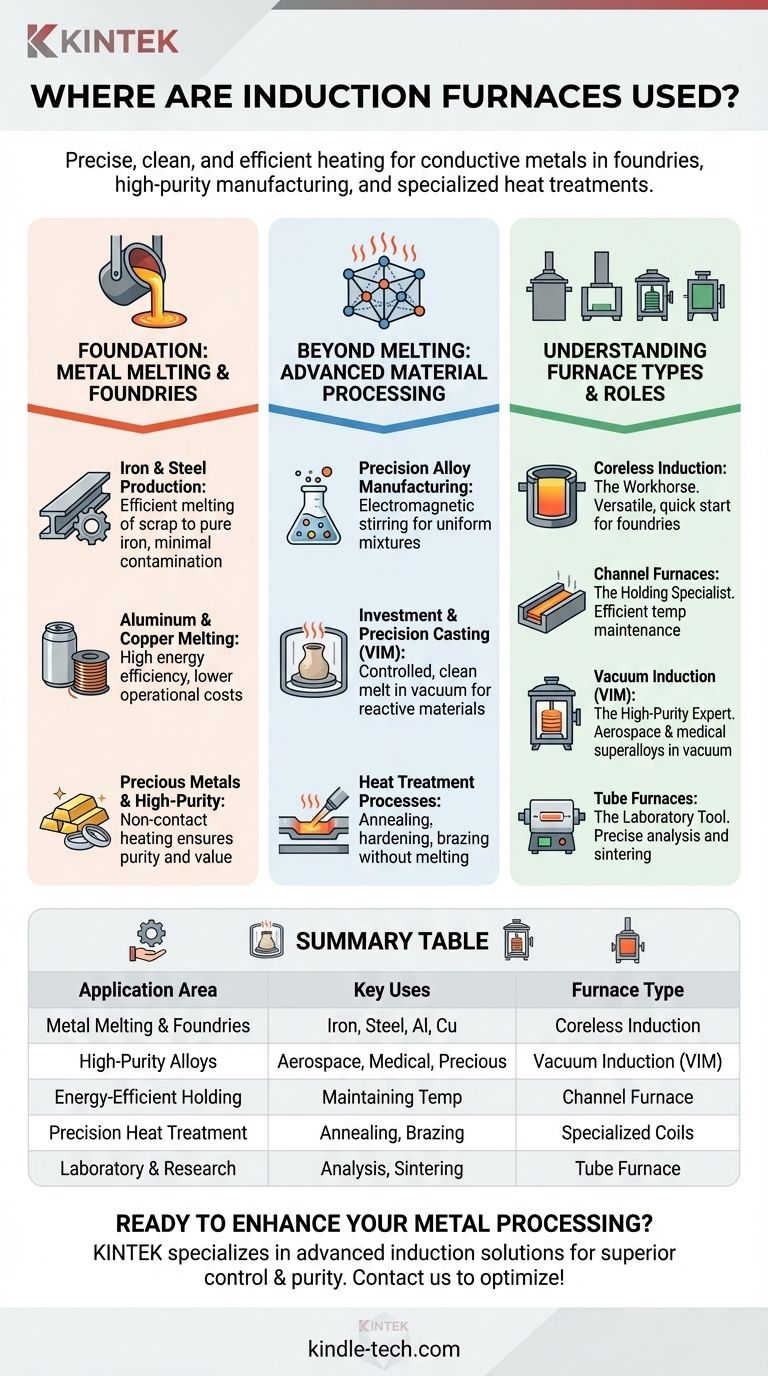
In short, induction furnaces are used anywhere precise, clean, and efficient heating of conductive metals is required. Their primary applications are in foundries for melting metals like iron, steel, and aluminum, as well as in manufacturing high-purity alloys, precision casting, and performing specialized heat treatments such as annealing and brazing.
The core reason for their widespread use isn't just that they melt metal, but how they do it. By using non-contact electromagnetic heating, induction furnaces provide a level of purity, temperature control, and material uniformity that conventional fuel-fired furnaces cannot match.
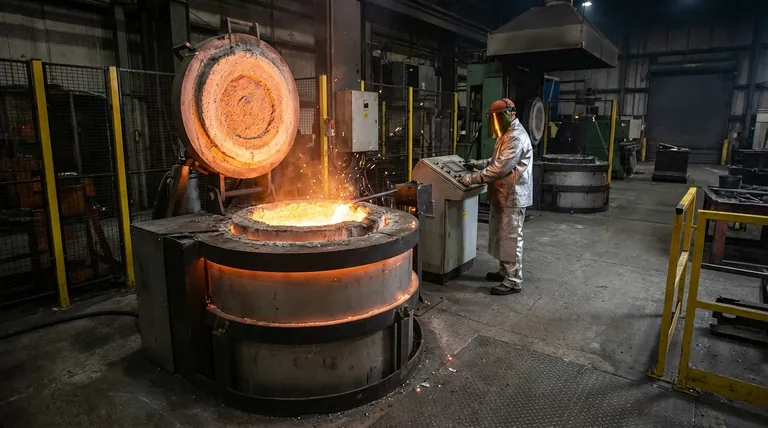

The Foundation: Metal Melting and Foundries
The most common application for induction furnaces is in the primary melting of metals. Their speed and cleanliness make them the backbone of the modern foundry industry.
Iron and Steel Production
Induction furnaces are fundamental in steel mills and iron foundries. They can efficiently melt everything from scrap metal to pure iron.
Because the heat is generated directly within the metal, there is minimal contamination from external heating elements or combustion byproducts, resulting in a cleaner final product.
Aluminum and Copper Melting
For non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper, energy efficiency is a major factor. Induction furnaces excel here, converting electrical energy into heat with very high efficiency.
This leads to lower operational costs and a smaller environmental footprint compared to traditional gas furnaces.
Precious Metals and High-Purity Applications
When melting precious metals like gold and platinum or creating ultra-pure alloys, avoiding any contamination is critical.
The non-contact heating principle of induction is ideal for these tasks, ensuring the final product maintains its intended purity and value.
Beyond Melting: Advanced Material Processing
While melting is their primary function, the precise control offered by induction furnaces makes them indispensable for a range of secondary processes.
Precision Alloy Manufacturing
Creating a high-quality alloy requires a perfectly uniform mixture of elements. The electromagnetic field in an induction furnace naturally stirs the molten metal bath.
This electromagnetic stirring ensures all components are evenly distributed, resulting in alloys with consistent, reliable properties.
Investment and Precision Casting
In investment casting, molten metal is poured into a ceramic mold. Induction furnaces provide the controlled, clean melt required for creating intricate and high-tolerance parts.
For extremely sensitive or reactive materials, this process is done in a Vacuum Induction Furnace (VIM) to prevent any atmospheric contamination.
Heat Treatment Processes
Induction technology is also used for a variety of heat treatments that alter a metal's physical properties without melting it.
These processes include annealing (softening), hardening, brazing (joining metals), and shrink-fitting, where a part is heated to expand and fit over another.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Furnace Types and Roles
Not all induction furnaces are the same. The specific design is chosen based on the intended application, creating a landscape of specialized tools.
The Workhorse: Coreless Induction Furnaces
This is the most common type used in foundries. They are versatile, can be started and stopped quickly, and are excellent for melting a wide variety of metals from a cold start.
The Holding Specialist: Channel Furnaces
Channel furnaces are extremely efficient at maintaining the temperature of already molten metal. They are often used as "holders" to store metal melted in a coreless furnace, allowing a foundry to melt during off-peak energy hours and pour during peak hours to save costs.
The High-Purity Expert: Vacuum Induction Furnaces (VIM)
When producing aerospace-grade superalloys or medical implants, even trace amounts of oxygen can ruin the material. VIMs operate in a vacuum chamber to create the purest metals and alloys possible.
The Laboratory Tool: Tube Furnaces
On a much smaller scale, induction-heated tube furnaces are used in laboratories for material analysis, sintering, and various chemical processes that require precise, programmable temperature profiles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal furnace is dictated entirely by the desired outcome. Understanding the different types allows you to select the right tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, flexible metal melting: A coreless induction furnace is the industry standard for foundries.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity, reactive, or aerospace-grade alloys: A vacuum induction furnace (VIM) is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is maintaining molten metal temperature efficiently or managing energy costs: A channel furnace is the most effective choice.
- If your primary focus is precise heat treatment or controlled laboratory analysis: A specialized induction coil or tube furnace is required.
Ultimately, the induction furnace is a versatile and powerful tool chosen for its precision, cleanliness, and control.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses | Furnace Type |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Melting & Foundries | Melting iron, steel, aluminum, copper | Coreless Induction Furnace |
| High-Purity Alloys | Aerospace, medical, precious metals | Vacuum Induction Furnace (VIM) |
| Energy-Efficient Holding | Maintaining molten metal temperature | Channel Furnace |
| Precision Heat Treatment | Annealing, brazing, hardening | Specialized Induction Coils |
| Laboratory & Research | Material analysis, sintering | Tube Furnace |
Ready to enhance your metal processing with precision and purity? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including induction furnaces tailored for foundries, alloy production, and research laboratories. Our solutions deliver superior temperature control, energy efficiency, and contamination-free heating to meet your specific needs. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can optimize your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation



















