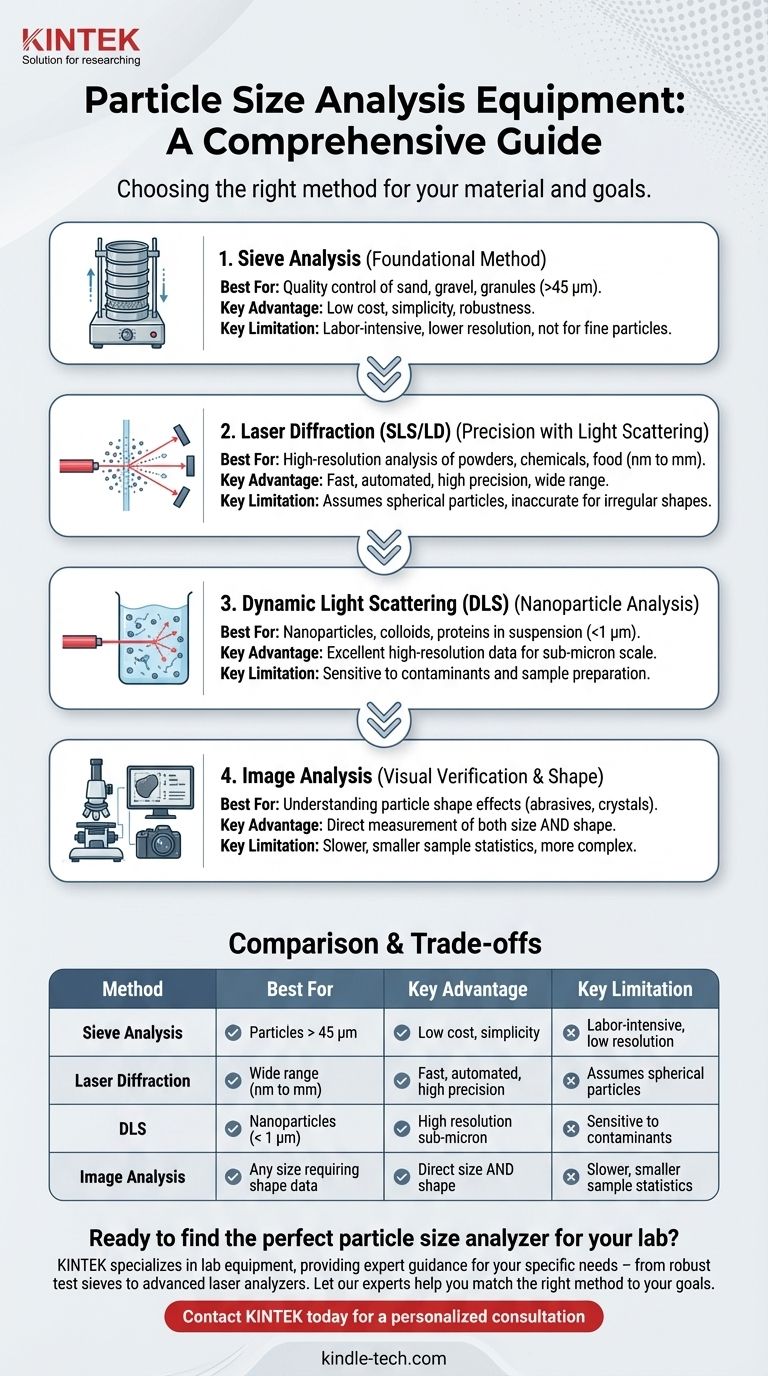
The primary equipment for particle size analysis ranges from traditional mechanical tools to highly advanced optical instruments. The most common methods involve test sieves, laser diffraction analyzers, dynamic light scattering systems, and direct image analyzers. The choice of equipment is dictated by the particle size range being measured, the nature of the material, and the required precision of the results.
Your core challenge is not simply finding equipment, but matching the right analytical method to your specific material and goals. While sieve analysis is a simple and cost-effective starting point, modern techniques like light scattering and image analysis offer far greater precision and detail for more demanding applications.

The Foundational Method: Sieve Analysis
Sieve analysis is the traditional and most widely understood method for determining particle size distribution, especially for relatively large, dry, and free-flowing materials.
The Equipment Used
The core components are a set of test sieves, which are precision-made pans with a wire mesh or perforated plate bottom of a specific, certified aperture size. For consistent and repeatable results, these sieves are typically agitated using a mechanical sieve shaker, which imparts a tapping or vibratory motion.
How It Works
A stack of sieves is arranged with the largest mesh opening at the top and the smallest at the bottom. A pre-weighed sample is placed in the top sieve, and the entire stack is agitated for a set duration. The particles are separated by size, and the weight of the material retained on each sieve is measured to calculate the distribution.
When to Choose It
This method is ideal for quality control and production environments where the particles are larger than approximately 45 micrometers. It is valued for its low cost, simplicity, and robustness.
Precision Analysis with Light Scattering
Light scattering techniques are fast, automated, and highly precise methods that have become the standard for analyzing finer particles, from the nanometer to the millimeter range.
Static Light Scattering (SLS) / Laser Diffraction (LD)
This is the most common modern technique for particle sizing. An instrument known as a laser diffraction particle size analyzer passes a laser beam through a dispersed sample. As particles pass through the beam, they scatter light at different angles—small particles scatter light at wide angles, while large particles scatter at narrow angles. Detectors measure the angular intensity of this scattered light to calculate the particle size distribution.
Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
DLS is specifically designed for measuring very small, sub-micron particles and nanoparticles (typically < 1 micrometer). A DLS system shines a laser into a liquid suspension of the particles. The instrument measures the rapid fluctuations in scattered light intensity, which are caused by the random Brownian motion of the particles. Software analyzes this data to determine particle size.
Visual Verification with Image Analysis
Image analysis offers a direct measurement approach, essentially taking high-resolution pictures of the particles and measuring them individually using sophisticated software.
The Equipment and Process
The equipment consists of a high-quality optical system—either a microscope (for static analysis) or a high-speed camera (for dynamic analysis)—coupled with powerful image analysis software. The software identifies individual particles in the image and can measure a variety of size and, crucially, shape parameters.
The Unique Advantage: Shape
Unlike light scattering, which assumes particles are spherical, image analysis directly measures the particle's true dimensions. This makes it the only method that can provide critical data on morphology, such as aspect ratio, circularity, and angularity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single method is universally superior. The choice depends on balancing cost, speed, resolution, and the type of information you need.
Sieve Analysis
Its primary advantages are low cost and simplicity. However, it is labor-intensive, has lower resolution than other methods, and is not effective for cohesive powders or particles smaller than about 45 micrometers.
Laser Diffraction (SLS/LD)
This method is extremely fast, repeatable, and covers a very wide size range. Its main limitation is that the calculation assumes spherical particles, which can lead to inaccuracies if your material contains highly irregular or elongated shapes.
Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
DLS provides excellent, high-resolution data for nanoparticles and colloids. Its effective range is limited to the sub-micron scale, and results can be highly sensitive to sample preparation and the presence of even a few large contaminants.
Image Analysis
The key benefit is obtaining direct size and shape information. The trade-off is that it can be slower and more complex than scattering methods, and may only analyze a statistically smaller number of particles per run.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your equipment based on the specific question you need to answer about your material.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control of sand, gravel, or large granules (>45 µm): Sieve analysis is the most practical and cost-effective method.
- If your primary focus is high-resolution analysis for materials like pharmaceuticals, chemicals, or food powders: A laser diffraction (SLS) analyzer provides the speed and precision required for process control and R&D.
- If your primary focus is working with nanoparticles, pigments, or colloids in a liquid suspension: A dynamic light scattering (DLS) system is the specialized tool designed for this sub-micron range.
- If your primary focus is understanding how particle shape affects performance (e.g., abrasives, crystals): An image analysis system is the only method that can provide this critical morphological data.
Choosing the right instrument is about aligning the technology's capabilities with your specific analytical needs.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sieve Analysis | Particles > 45 µm (e.g., sand, granules) | Low cost, simplicity, robustness | Labor-intensive, low resolution for fine particles |
| Laser Diffraction (SLS/LD) | Wide range (nm to mm); powders, chemicals | Fast, automated, high precision, wide range | Assumes spherical particles |
| Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) | Nanoparticles, colloids (< 1 µm) | High resolution for sub-micron particles | Sensitive to contaminants, limited size range |
| Image Analysis | Any size requiring shape data (e.g., crystals) | Direct measurement of size AND shape | Slower, smaller sample statistics |
Ready to find the perfect particle size analyzer for your lab?
Choosing the right equipment is critical for accurate results and efficient workflows. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance to help you select the ideal particle sizing solution—from robust test sieves for quality control to advanced laser diffraction analyzers for R&D precision.
We understand your laboratory needs. Let our experts help you match the right analytical method to your specific materials and goals.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and unlock the full potential of your particle analysis.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of sieving method? Achieve Accurate Particle Size Separation
- What are the principles of a sieve shaker? Achieve Accurate Particle Size Analysis
- What is the object of the sieve shaker experiment? To Determine Particle Size Distribution for Material Control
- What are the advantages of a sieving machine? Achieve Precise Particle Analysis for Quality Control
- What is the amplitude of a sieve shaker? A Guide to Optimizing Particle Separation
- What are the components of a sieving machine? Unlock the Anatomy of Precision Particle Separation
- What is a sieve shaker? Automate Your Particle Size Analysis for Accurate Results
- How does a laboratory shaker or extractor function during 133Ba adsorption? Optimize Your Kinetic Evaluation



















