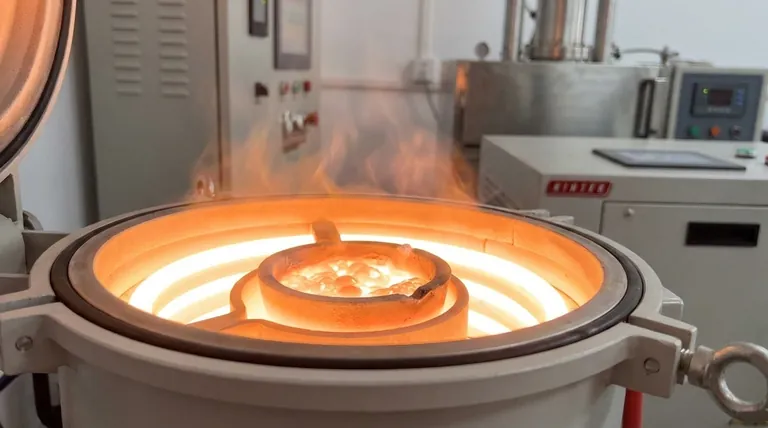
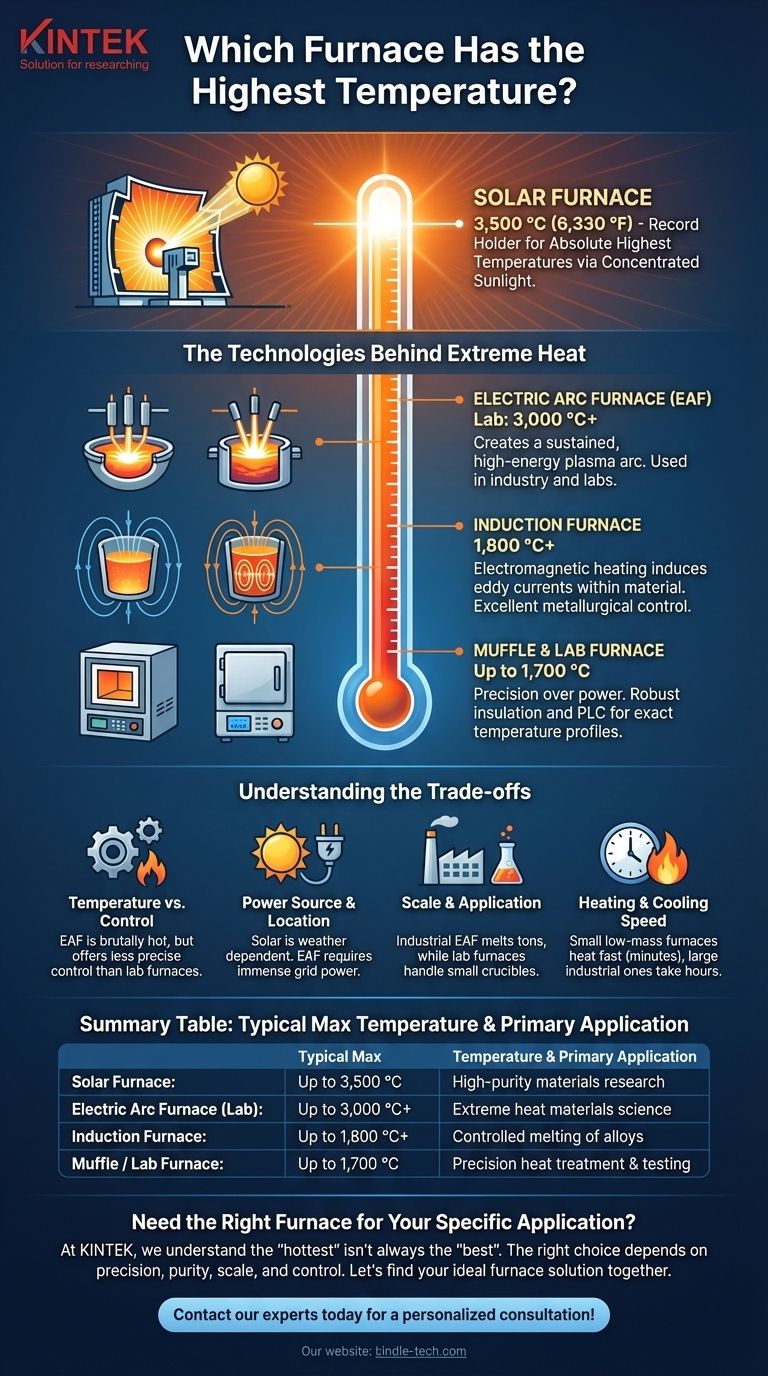
For achieving the absolute highest temperatures, the record is held by a solar furnace. Specifically, the facility in Odeillo, France, can use concentrated sunlight to reach temperatures of 3,500 °C (6,330 °F). In terms of more conventional and widely used technology, specialized laboratory electric arc furnaces can also exceed 3,000 °C, making them a top contender for creating extreme heat.
While a specific solar furnace holds the record, the broader truth is that extreme heat is generated by highly specialized technologies—not a single type of furnace. The "best" furnace is determined not by its maximum theoretical temperature, but by the specific scientific or industrial goal it is designed to achieve.

The Technologies Behind Extreme Heat
To understand which furnace is "hottest," you must first understand the different methods used to generate thermal energy. Each technology is suited for a different purpose, scale, and temperature range.
Solar Furnaces: Concentrated Sunlight
A solar furnace operates on the principle of concentrated solar power. It is conceptually similar to using a massive magnifying glass.
An array of mirrors, called heliostats, tracks the sun and reflects its light onto a larger parabolic concentrator. This concentrator then focuses all that solar energy onto a single, small point, generating immense heat without any contaminants from combustion or electric arcs.
Electric Arc Furnaces: Creating a Plasma Arc
Electric arc furnaces (EAF) are the workhorses of the steel recycling industry and a source of some of the highest man-made temperatures.
They work by passing an enormous electric current through graphite electrodes. When the electrodes are brought close to the target material (like scrap metal), the current jumps the gap, creating a sustained, high-energy plasma arc.
Industrial units for melting steel regularly operate above 1,800 °C. Highly specialized laboratory versions can push beyond 3,000 °C for materials research.
Induction Furnaces: Electromagnetic Heating
Induction furnaces do not use any external heating element or arc. Instead, they use powerful alternating currents to generate a strong magnetic field around the material to be heated.
This magnetic field induces powerful eddy currents within the conductive material itself, causing it to heat up rapidly from the inside out. While they typically operate at lower temperatures than arc furnaces, they can still reach 1,800 °C or more and offer excellent metallurgical control.
Muffle & Laboratory Furnaces: Precision Over Power
Standard laboratory furnaces, including muffle furnaces, are designed for precision and atmospheric control, not raw temperature.
These units are crucial for processes like ashing, heat-treating, and materials testing. They typically operate in a range from 100 °C up to 1,700 °C, using robust insulation and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to maintain exact temperature profiles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The furnace with the highest theoretical temperature is not always the right tool. Practicality, cost, and the specific application are far more important factors.
Temperature vs. Control
An electric arc furnace is brutally hot and effective for melting tons of steel, but it offers less precise temperature control than a PLC-driven laboratory furnace. The extreme environment of the arc is also not suitable for delicate processes.
Power Source and Location
A solar furnace is completely dependent on clear, sunny weather and can only be built in specific geographic locations. An electric arc furnace avoids this dependency but requires access to a power grid capable of delivering immense amounts of electricity.
Scale and Application
The Odeillo Solar Furnace is a massive research facility. An industrial EAF can melt over 100 tons of steel at a time. A laboratory muffle furnace might only hold a small crucible. The scale of the technology is directly tied to its intended application.
Heating and Cooling Speed
The time it takes to reach a target temperature is a critical factor. A small lab furnace with low-mass insulation might reach its peak temperature in 20 minutes. A large industrial furnace built with dense refractory brick could take several hours, representing a significant operational cost.
Matching the Furnace to the Goal
Choosing a furnace is about defining your objective. The technology you need is a direct reflection of the problem you are trying to solve.
- If your primary focus is pure materials science research at the highest possible temperatures: A solar furnace or a custom-designed laboratory arc furnace is the instrument of choice.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial melting of metals like steel: An electric arc furnace (EAF) is the industry standard for its raw power and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is clean, controlled melting of non-ferrous or specialty alloys: An induction furnace provides excellent control and avoids contamination from an electric arc.
- If your primary focus is precise, repeatable heat treatment or sample analysis in a lab: A muffle furnace or a programmable box furnace is the correct tool, even with its lower maximum temperature.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace is a matter of matching the specific heating technology to your precise engineering or scientific objective.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Max Temperature | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Furnace | Up to 3,500 °C (6,330 °F) | High-purity materials research |
| Electric Arc Furnace (Lab) | Up to 3,000 °C+ | Extreme heat materials science |
| Induction Furnace | Up to 1,800 °C+ | Controlled melting of alloys |
| Muffle / Lab Furnace | Up to 1,700 °C | Precision heat treatment & testing |
Need the Right Furnace for Your Specific Application?
At KINTEK, we understand that the 'hottest' furnace isn't always the best furnace. The right choice depends entirely on your goals: precision, purity, scale, and control.
We specialize in providing laboratory equipment and consumables tailored to your unique needs. Whether you're processing materials at extreme temperatures or require precise, repeatable heat treatment, our experts can help you select the perfect solution to enhance your lab's efficiency and research outcomes.
Let's find your ideal furnace solution together. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the most commonly used metals in a vacuum furnace's hot zone? Discover the Key to High-Purity Processing
- Can an arc happen in a vacuum? Yes, and here's how to prevent it in your high-voltage design.
- What happens to heat generated in a vacuum? Mastering Thermal Control for Superior Materials
- Does platinum evaporate? Understanding High-Temperature Stability and Material Loss
- At what temperature does molybdenum evaporate? Understanding Its High-Temperature Limits



















