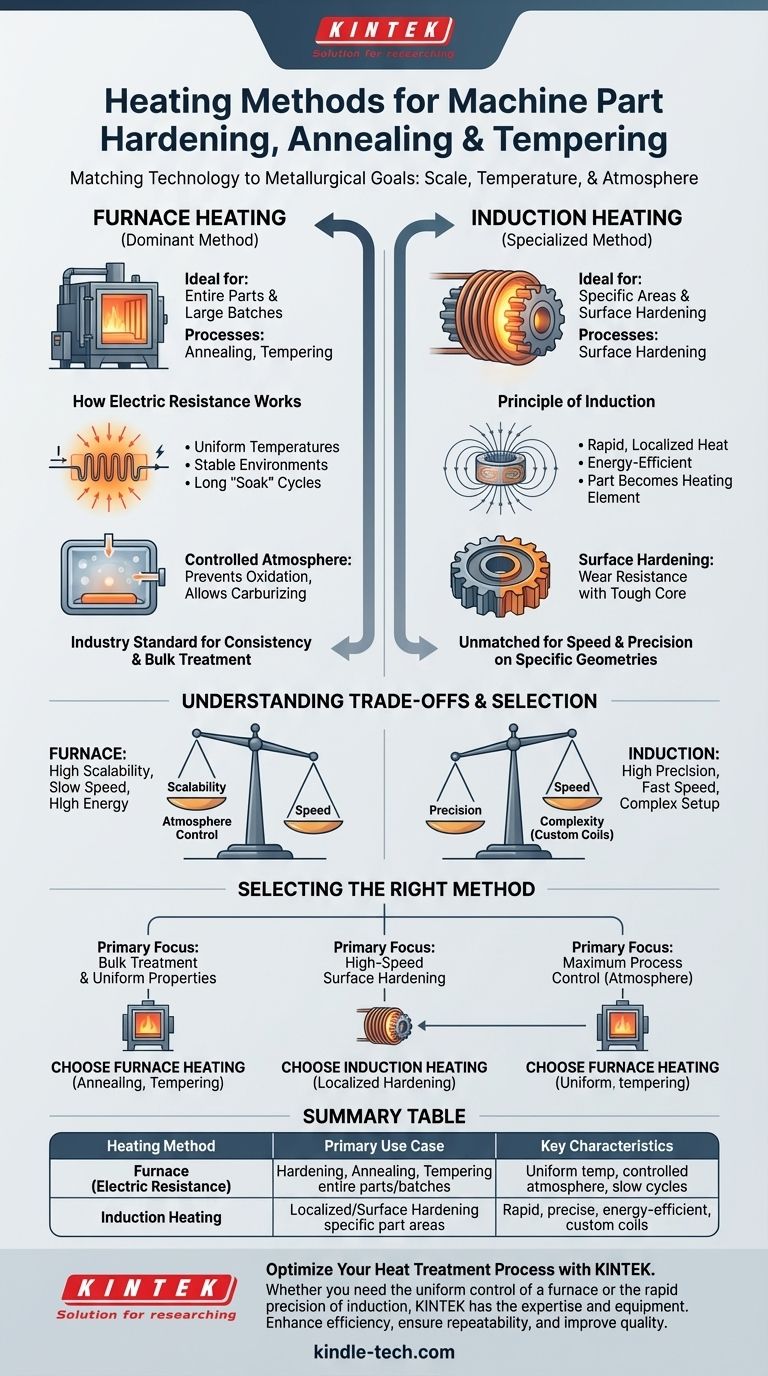
For most industrial applications, the heat treatment processes of hardening, annealing, and tempering rely on electric resistance heating inside a controlled-atmosphere furnace. This method provides the uniform temperatures and stable environments necessary for treating entire machine parts. For applications requiring treatment of only a specific area, induction heating is a common and highly effective alternative.
The choice of heating technology is not about finding one superior method, but about matching the technology to the metallurgical goal. The decision is driven by the required temperature, the scale of the treatment (the entire part vs. a specific area), and the need for atmospheric control.

The Dominant Method: Furnace Heating
For treating entire components or large batches of parts, furnaces are the industry standard. They provide the stable, uniform heat essential for most heat treatment processes.
How Electric Resistance Furnaces Work
These furnaces operate on a straightforward principle: high electrical current is passed through highly resistive heating elements. These elements, which can be made of materials like nickel-chromium alloys, silicon carbide, or molybdenum, glow hot and heat the furnace chamber through radiation and convection.
The part or parts inside the chamber absorb this energy, allowing their temperature to be raised and held with high precision.
Why Furnaces Excel at Annealing and Tempering
Annealing and tempering are defined by the need for precise temperature control over extended periods. Annealing, for example, often requires a long "soak" at a specific temperature followed by very slow, controlled cooling to achieve maximum softness and ductility.
A furnace is the ideal environment for this, as its thermal mass and controlled heating elements provide stability and uniformity across the entire workpiece.
The Critical Role of a Controlled Atmosphere
Many hardening processes require a specific atmosphere to prevent undesirable chemical reactions, like oxidation (scaling), or to intentionally introduce elements into the part's surface (like in carburizing).
Furnaces can be sealed and filled with inert gases, reactive gases, or placed under a vacuum. This control is critical for achieving the desired final surface properties and is a primary advantage of furnace-based treatments.
The Specialized Method: Induction Heating
When only a portion of a machine part needs to be hardened—such as the teeth on a gear or the surface of a shaft—induction heating is the preferred method.
The Principle of Induction
Induction heating uses a powerful, high-frequency alternating magnetic field generated by a copper coil. When a conductive part (like steel) is placed inside this field, the magnetic field induces electrical currents, known as eddy currents, directly within the part.
The part's own resistance to the flow of these currents generates intense, rapid, and localized heat. The part itself becomes the heating element.
Key Applications for Hardening
This technique is unmatched for surface hardening. It can heat the surface layer of a steel component above its transformation temperature in a matter of seconds. When the part is then immediately quenched, only this thin surface layer becomes hard, while the core remains softer and tougher.
This creates a component that is highly resistant to wear on the surface but can still withstand shock and impact without fracturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single heating method is perfect for every scenario. The choice involves clear trade-offs between speed, cost, precision, and volume.
Furnace Heating: Scalability vs. Speed
A furnace's main advantage is its ability to process large, complex parts or entire batches of smaller parts simultaneously. However, heating the entire furnace chamber is a slow process that consumes significant energy. It is ideal for processes that require long, slow cycles.
Induction Heating: Precision vs. Complexity
Induction is incredibly fast and energy-efficient because it only heats the necessary part of the workpiece. Its primary drawback is that it requires a custom-designed induction coil for each specific part geometry, making the initial setup more complex and costly.
Selecting the Right Heating Method
Your final choice depends entirely on the desired outcome for the machine part.
- If your primary focus is bulk treatment and uniform properties: Furnace heating is the industry standard for its consistency and ability to handle large batches for annealing and tempering.
- If your primary focus is high-speed surface hardening: Induction heating offers unmatched speed, precision, and energy efficiency for treating specific, localized areas of a part.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum process control: Both methods offer high precision, but furnace heating provides superior control over the part's atmosphere, which is critical for many advanced hardening techniques.
Understanding these core principles allows you to select a heating strategy that precisely engineers the desired mechanical properties for your application.
Summary Table:
| Heating Method | Primary Use Case | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace (Electric Resistance) | Hardening, Annealing, Tempering entire parts/batches | Uniform temperature, controlled atmosphere, ideal for slow cycles |
| Induction Heating | Localized/Surface Hardening specific part areas | Rapid, precise, energy-efficient, requires custom coil design |
Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right heating technology is critical for achieving the precise mechanical properties your machine parts require. Whether you need the uniform, controlled environment of a furnace for annealing and tempering, or the rapid, localized power of induction for surface hardening, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your laboratory and production needs.
As a specialist in lab equipment and consumables, we provide reliable solutions that enhance efficiency, ensure repeatability, and improve your final product quality.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover the ideal heating solution for your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation



















