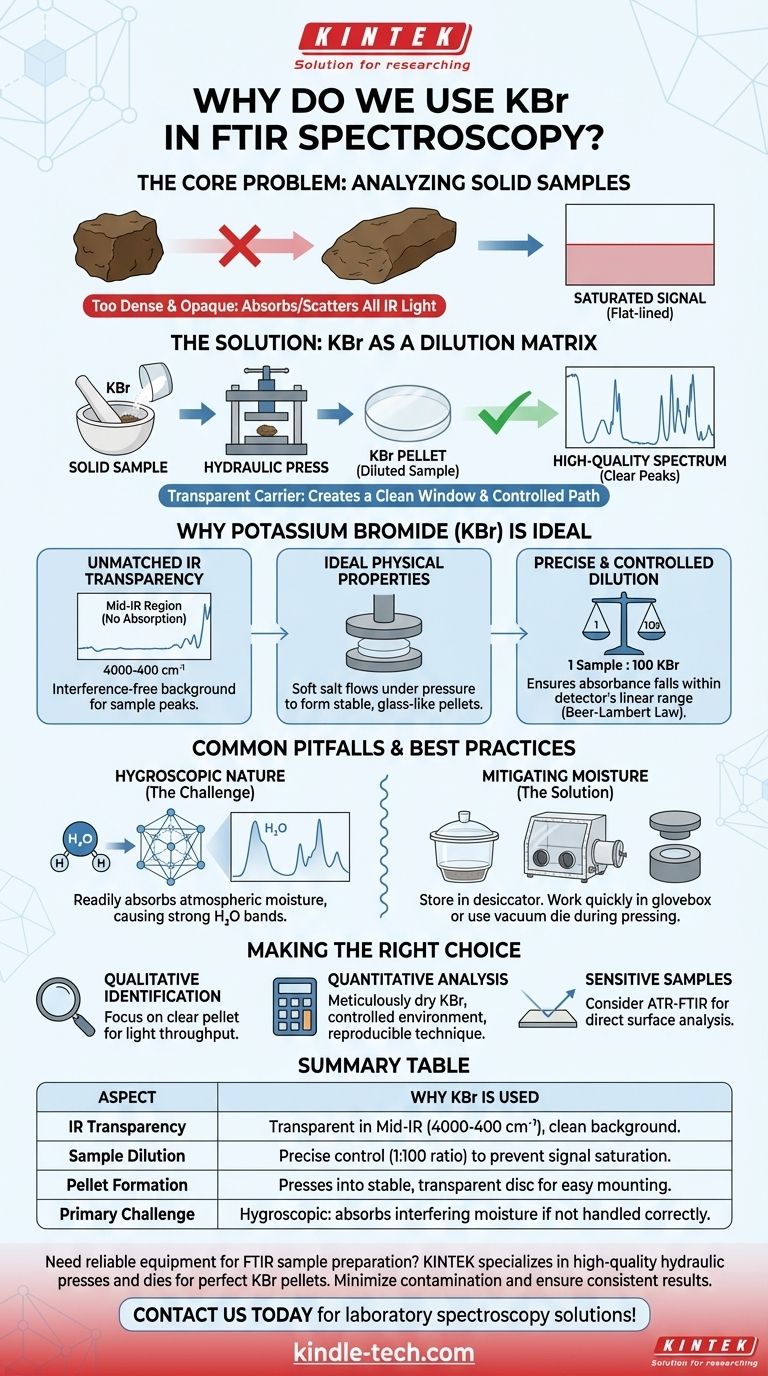
In Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, potassium bromide (KBr) is used because it is almost perfectly transparent to infrared radiation and acts as an ideal solid-state matrix. By mixing a tiny amount of a solid sample with KBr and pressing it into a thin pellet, the sample is diluted to a concentration that allows infrared light to pass through, enabling the instrument to measure a clear, high-quality spectrum.
The core challenge in analyzing solid samples with FTIR is controlling their concentration in the infrared beam. KBr solves this by creating a transparent, solid dilution that holds the sample uniformly in the light path, preventing signal saturation and ensuring an accurate analysis.

The Core Problem: Analyzing Solid Samples
The Challenge of Concentration
A pure solid sample is typically too dense and opaque for FTIR analysis. If you place a chunk of a solid material directly in the instrument's beam path, it will absorb or scatter nearly all the infrared light.
This results in a saturated or "flat-lined" spectrum, where no meaningful peaks can be distinguished, making molecular identification impossible.
The Need for a Dilution Matrix
To get a useful spectrum, the sample must be diluted and distributed evenly. Much like dissolving a substance in a solvent for liquid analysis, a solid sample needs a carrier or matrix.
This matrix must hold the sample in the beam path without contributing its own spectral features, acting as a clean "window" through which the sample can be observed.
Why Potassium Bromide is the Ideal Solution
Unmatched Infrared Transparency
The primary reason for using KBr is its lack of absorption in the mid-infrared region (4000-400 cm⁻¹). This is the "fingerprint" region where most organic and inorganic molecules exhibit their characteristic vibrational absorptions.
Because KBr is transparent here, it provides a clean, interference-free background, ensuring that every peak observed in the spectrum comes from the sample, not the matrix.
Ideal Physical Properties
KBr is a soft, crystalline salt that flows well under high pressure. When the finely ground KBr/sample mixture is compressed in a hydraulic press, the KBr particles fuse together.
This process forms a stable, semi-transparent, glass-like disc or pellet that is easy to handle and mount in the spectrometer's sample holder.
Precise and Controlled Dilution
The KBr pellet technique allows for precise control over the sample concentration. The typical ratio is around 100 parts KBr to 1 part sample by weight.
This high level of dilution ensures that the sample's absorbance falls within the linear range of the instrument's detector. This is critical for obtaining a spectrum where peak intensities are proportional to concentration, a principle foundational to the Beer-Lambert law.
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
The Hygroscopic Nature of KBr
The most significant drawback of KBr is that it is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere.
Water (H₂O) has very strong and broad infrared absorption bands (a broad peak around 3400 cm⁻¹ and another near 1640 cm⁻¹). If the KBr is contaminated with moisture, these large water peaks can obscure important sample peaks, compromising the analysis.
Mitigating Moisture Contamination
To avoid water contamination, KBr powder should always be stored in a desiccator or a drying oven.
During pellet preparation, it is crucial to work quickly. In humid environments, performing the grinding and pressing inside a glovebox with a dry atmosphere or using a specialized vacuum die that removes air and moisture is highly recommended.
Ensuring a Uniform Mixture
For a high-quality spectrum, the sample must be distributed perfectly evenly throughout the KBr. This requires thoroughly grinding the sample and KBr together, typically with an agate mortar and pestle.
An uneven mixture will lead to a sloping baseline and distorted peak shapes, as different parts of the pellet will absorb light differently.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the best results, your preparation technique should align with your analytical needs.
- If your primary focus is qualitative identification: Your goal is a clear, transparent pellet that maximizes light throughput, even if minor water peaks are present.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis: You must meticulously dry the KBr, work in a controlled environment, and use a consistent pressing technique to ensure repeatability and minimize water interference.
- If your sample is sensitive to moisture or pressure: Consider an alternative method like Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR-FTIR), which analyzes the surface of a sample directly with minimal preparation.
Ultimately, the KBr pellet method is a powerful technique that transforms an otherwise opaque solid into a measurable sample, unlocking detailed molecular information.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Why KBr is Used |
|---|---|
| Infrared Transparency | Transparent in the mid-IR region (4000-400 cm⁻¹), providing a clean background. |
| Sample Dilution | Allows precise control of sample concentration (typically 1:100 ratio) to prevent signal saturation. |
| Pellet Formation | Presses into a stable, transparent disc that is easy to mount in the spectrometer. |
| Primary Challenge | Hygroscopic—absorbs moisture, which can interfere with the spectrum if not handled properly. |
Need reliable equipment for your FTIR sample preparation? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including hydraulic presses and dies for creating perfect KBr pellets. Our products help you achieve accurate, reproducible results by minimizing contamination and ensuring consistent pellet quality. Contact us today (#ContactForm) to find the right solution for your laboratory's spectroscopy needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- kbr pellet press 2t
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System



















