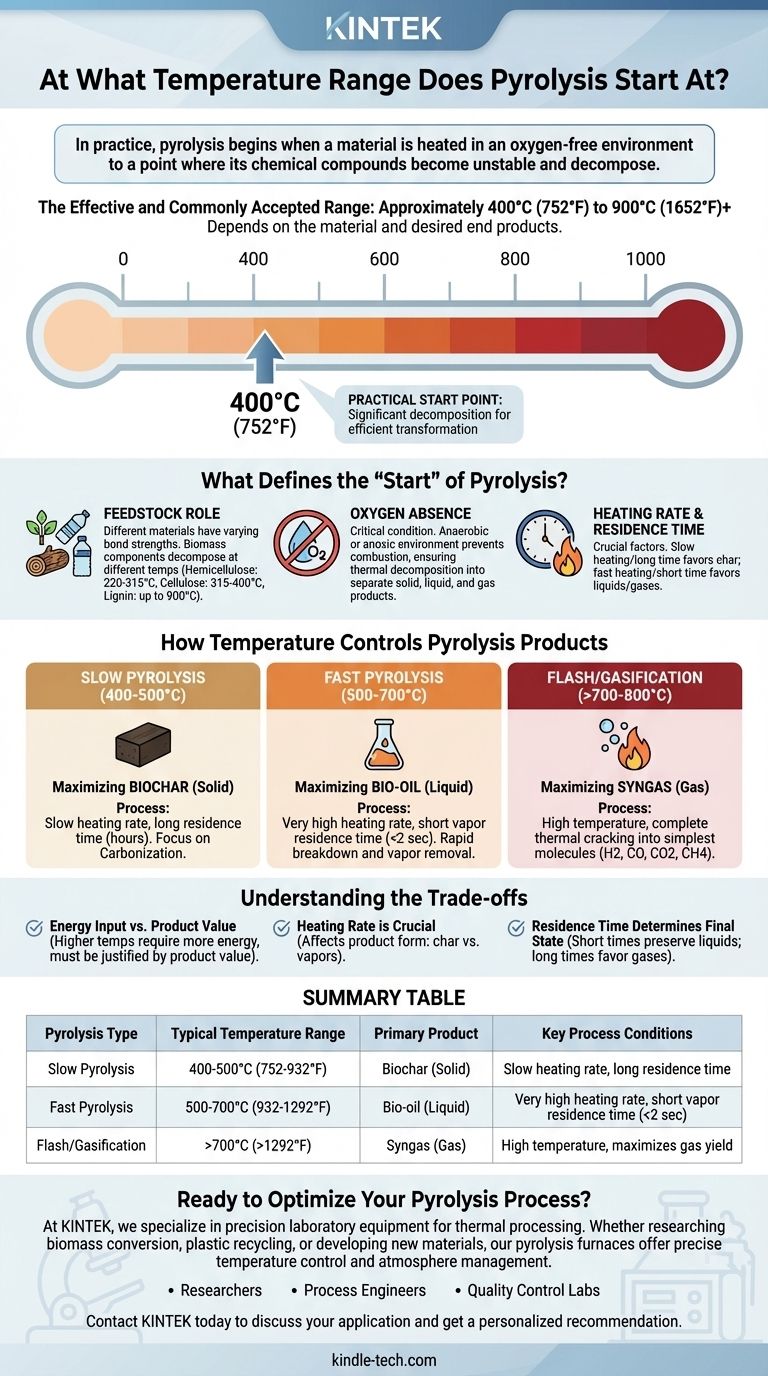
In practice, pyrolysis begins when a material is heated in an oxygen-free environment to a point where its chemical compounds become unstable and decompose. While minor thermal degradation can occur at lower temperatures, the effective and commonly accepted range for pyrolysis starts at approximately 400°C (752°F) and can extend up to 900°C (1652°F) or higher, depending entirely on the material being processed and the desired end products.
The question is not just "at what temperature does pyrolysis start," but rather "what temperature do I need for my desired outcome?" The specific temperature is a control lever that determines whether the process yields primarily solid biochar, liquid bio-oil, or combustible syngas.
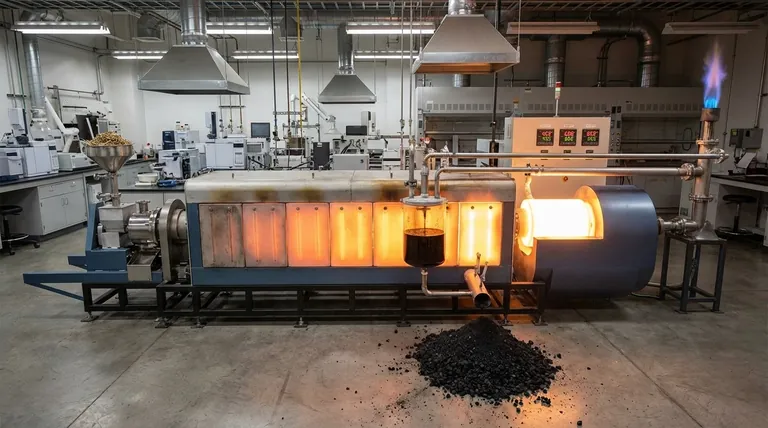

What Defines the "Start" of Pyrolysis?
Pyrolysis isn't a simple on/off switch that activates at a single temperature. It's a complex process of thermal decomposition, and its "start" depends on both the material and the goal of the process.
Thermal Decomposition vs. Practical Application
Technically, the weakest chemical bonds in a material can begin to break at temperatures as low as 200-300°C. However, in an industrial or laboratory context, "pyrolysis" refers to a more significant and rapid conversion.
This practical range, starting around 400°C, is where the decomposition rate becomes substantial enough to efficiently transform the bulk of the material into new products.
The Critical Role of Feedstock
Different materials are made of different molecules with varying bond strengths. This is the single most important factor influencing the required temperature.
For example, in biomass, hemicellulose decomposes first (220-315°C), followed by cellulose (315-400°C), and finally lignin, which requires higher temperatures (up to 900°C) for complete breakdown. Plastics have their own distinct decomposition profiles based on their polymer structure.
The Absence of Oxygen
It is critical to understand that pyrolysis is defined by heating in an anaerobic (oxygen-free) or anoxic (low-oxygen) environment. If significant oxygen were present, the material would simply burn (combust) rather than thermally decompose into separate solid, liquid, and gas products.
How Temperature Controls Pyrolysis Products
The final temperature you choose is the primary tool for steering the chemical reactions toward a specific output. This is often categorized into three main types of pyrolysis.
Slow Pyrolysis (Low Temperature): Maximizing Biochar
Operating at lower temperatures, typically 400-500°C, with a slow heating rate and long residence time (hours), favors the production of a solid carbon-rich product.
This process, known as carbonization, minimizes the formation of liquids and gases, making it ideal for producing biochar for agricultural use or activated carbon.
Fast Pyrolysis (Medium Temperature): Maximizing Bio-oil
To produce the maximum amount of liquid product (bio-oil), a medium temperature range of around 500-700°C is used.
Crucially, this process requires a very high heating rate and a short vapor residence time (typically less than 2 seconds). This quickly breaks down the material and removes the vapors from the hot zone before they can further decompose into gas.
Flash Pyrolysis & Gasification (High Temperature): Maximizing Syngas
At very high temperatures, generally above 700-800°C, the process favors breaking down all components into the simplest possible molecules.
This maximizes the yield of non-condensable gases, collectively known as syngas (a mixture of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and methane). This gas can be used as fuel or as a chemical precursor.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a temperature is an engineering decision with clear consequences. You must consider more than just the final temperature itself.
Heating Rate is Crucial
How quickly the material reaches the target temperature is just as important as the temperature itself. A slow heating rate allows for char formation, while a very fast heating rate cracks molecules into vapors, favoring liquid and gas production.
Residence Time Determines Final State
Residence time—how long the material or its resulting vapors are held at the peak temperature—is the other key variable. Short residence times preserve liquid intermediates, while long residence times allow those liquids to further break down into gases.
Energy Input vs. Product Value
Higher temperatures require significantly more energy input. A process designed to run at 900°C is far more energy-intensive than one at 450°C. This operational cost must be justified by the higher value or specific application of the resulting syngas compared to biochar or bio-oil.
Selecting the Right Temperature for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge effectively, you must first define your objective. The optimal temperature is a direct function of the product you want to create.
- If your primary focus is solid biochar production: Operate in the lower range (400-500°C) using a slow heating rate and a long residence time to maximize solid yield.
- If your primary focus is liquid bio-oil: Use fast pyrolysis in the medium range (500-700°C) with very rapid heating and short vapor residence times.
- If your primary focus is producing syngas: Operate at high temperatures (above 700°C) to ensure the complete thermal cracking of all components into gaseous products.
Ultimately, the correct pyrolysis temperature is determined not by a textbook definition, but by the specific outcome you need to achieve.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Type | Typical Temperature Range | Primary Product | Key Process Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Pyrolysis | 400-500°C (752-932°F) | Biochar (Solid) | Slow heating rate, long residence time |
| Fast Pyrolysis | 500-700°C (932-1292°F) | Bio-oil (Liquid) | Very high heating rate, short vapor residence time (<2 sec) |
| Flash/Gasification | >700°C (>1292°F) | Syngas (Gas) | High temperature, maximizes gas yield |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision laboratory equipment for thermal processing. Whether you're researching biomass conversion, plastic recycling, or developing new materials, our pyrolysis furnaces offer the precise temperature control and atmosphere management you need to achieve your target yields.
We provide solutions for:
- Researchers needing reproducible results for biochar, bio-oil, or syngas production.
- Process Engineers scaling up from lab to pilot plant.
- Quality Control Labs analyzing feedstock behavior.
Let our experts help you select the right equipment for your specific temperature and output goals. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy



















