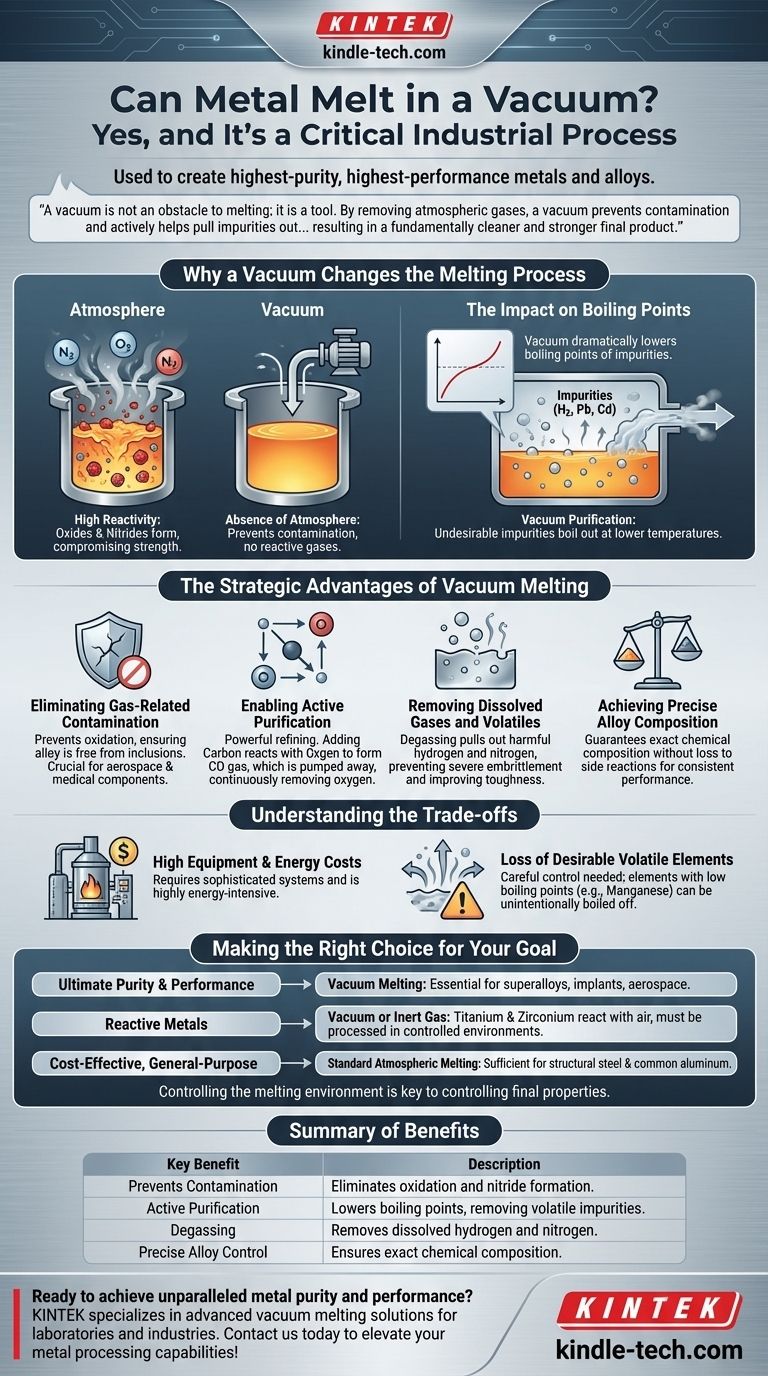
Yes, metal can absolutely melt in a vacuum. In fact, it is a critical industrial process used to create the highest-purity, highest-performance metals and alloys for demanding applications. The absence of air fundamentally changes the environment, preventing unwanted chemical reactions and allowing for a level of purification that is impossible in a normal atmosphere.
The core principle to understand is that a vacuum is not an obstacle to melting; it is a tool. By removing atmospheric gases, a vacuum prevents contamination and actively helps pull impurities out of the molten metal, resulting in a fundamentally cleaner and stronger final product.
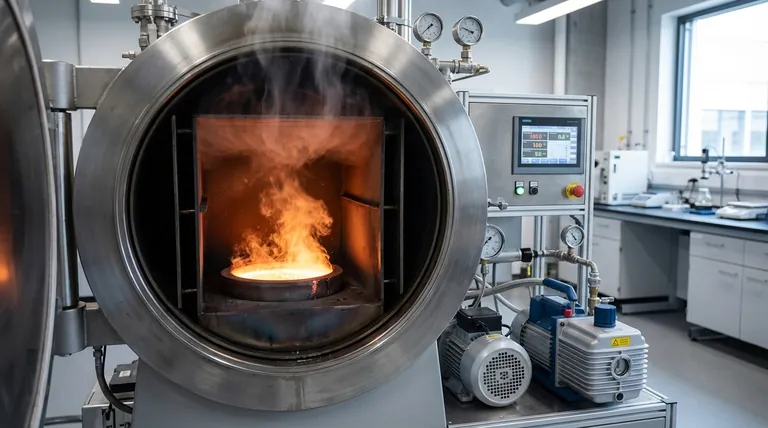

Why a Vacuum Changes the Melting Process
Melting a metal is about adding enough thermal energy to break its crystalline structure. A vacuum's primary influence is not on the melting point itself, but on the chemical environment in which the melting occurs.
The Absence of an Atmosphere
In a normal atmosphere, air is roughly 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen. At high temperatures, these gases are highly reactive with molten metal, leading to the formation of oxides and nitrides.
These compounds are impurities that can become trapped in the metal as it cools, creating microscopic weak points that compromise the material's strength, ductility, and fatigue resistance. A vacuum removes these reactive gases, preventing this contamination from ever occurring.
The Impact on Boiling Points
While the pressure of a vacuum has a negligible effect on a substance's melting point, it dramatically lowers its boiling point. This physical principle is the key to vacuum purification.
Many undesirable impurities, including dissolved gases (like hydrogen) and certain volatile metals (like lead or cadmium), have lower boiling points than the primary metal. In a vacuum, these impurities can be made to boil out of the molten bath at temperatures far below their normal boiling point, allowing them to be pumped away as vapor.
The Strategic Advantages of Vacuum Melting
Engineers and metallurgists use vacuum melting not just to avoid problems but to achieve specific enhancements to the material's properties.
Eliminating Gas-Related Contamination
The most immediate benefit is the prevention of oxidation. This ensures the final alloy is free from oxide inclusions that can initiate cracks under stress, which is a critical factor for components in aerospace or medical applications.
Enabling Active Purification
A vacuum enables powerful refining techniques. For example, carbon can be added to the molten metal to react with any remaining oxygen, forming carbon monoxide (CO) gas.
In a normal atmosphere, this reaction would reach equilibrium. In a vacuum, the CO gas is continuously pumped away, forcing the reaction to continue until virtually all oxygen is removed from the melt.
Removing Dissolved Gases and Volatiles
Harmful dissolved gases, particularly hydrogen and nitrogen, can cause severe embrittlement in many metals. A vacuum effectively pulls these dissolved gases out of the liquid metal, a process known as degassing. This dramatically improves the material's toughness and reliability.
Achieving Precise Alloy Composition
When creating advanced alloys, metallurgists add precise amounts of different elements. In a vacuum, these carefully measured additions are not lost to oxidation or other side reactions. This guarantees the final chemical composition is exactly what was intended, ensuring consistent and predictable performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the benefits are significant, vacuum melting is a specialized process with clear trade-offs. It is not the default choice for all metal production.
High Equipment and Energy Costs
Creating and maintaining an industrial-scale high vacuum requires sophisticated, expensive furnace systems and powerful pumps. The process is also highly energy-intensive, making it significantly more costly than melting in a standard furnace.
Loss of Desirable Volatile Elements
The same principle that removes unwanted volatile impurities can also remove desired alloying elements if they have a low boiling point. The process must be carefully controlled when producing alloys containing elements like manganese, which can be unintentionally boiled off under a vacuum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use vacuum melting is driven entirely by the performance requirements of the final product.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and performance: Vacuum melting is essential for creating superalloys, medical implants, and aerospace components where material failure is not an option.
- If your primary focus is working with reactive metals: Metals like titanium and zirconium are so reactive with air that they can only be effectively melted and processed in a vacuum or inert gas environment.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, general-purpose metal: For applications like structural steel or common aluminum products, standard atmospheric melting provides the necessary properties at a much lower cost.
Ultimately, controlling the melting environment is the key to controlling the final properties of the metal.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Prevents Contamination | Eliminates oxidation and nitride formation by removing reactive gases. |
| Active Purification | Lowers boiling points of impurities, allowing volatile elements to be removed. |
| Degassing | Removes dissolved hydrogen and nitrogen to prevent embrittlement. |
| Precise Alloy Control | Ensures exact chemical composition without loss to side reactions. |
Ready to achieve unparalleled metal purity and performance? KINTEK specializes in advanced vacuum melting solutions for laboratories and industries requiring the highest-quality metals and alloys. Whether you're developing aerospace components, medical implants, or high-performance alloys, our expertise ensures your materials meet the most demanding standards. Contact us today to discuss how our lab equipment can elevate your metal processing capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the leak rate for a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Purity and Repeatability
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost



















