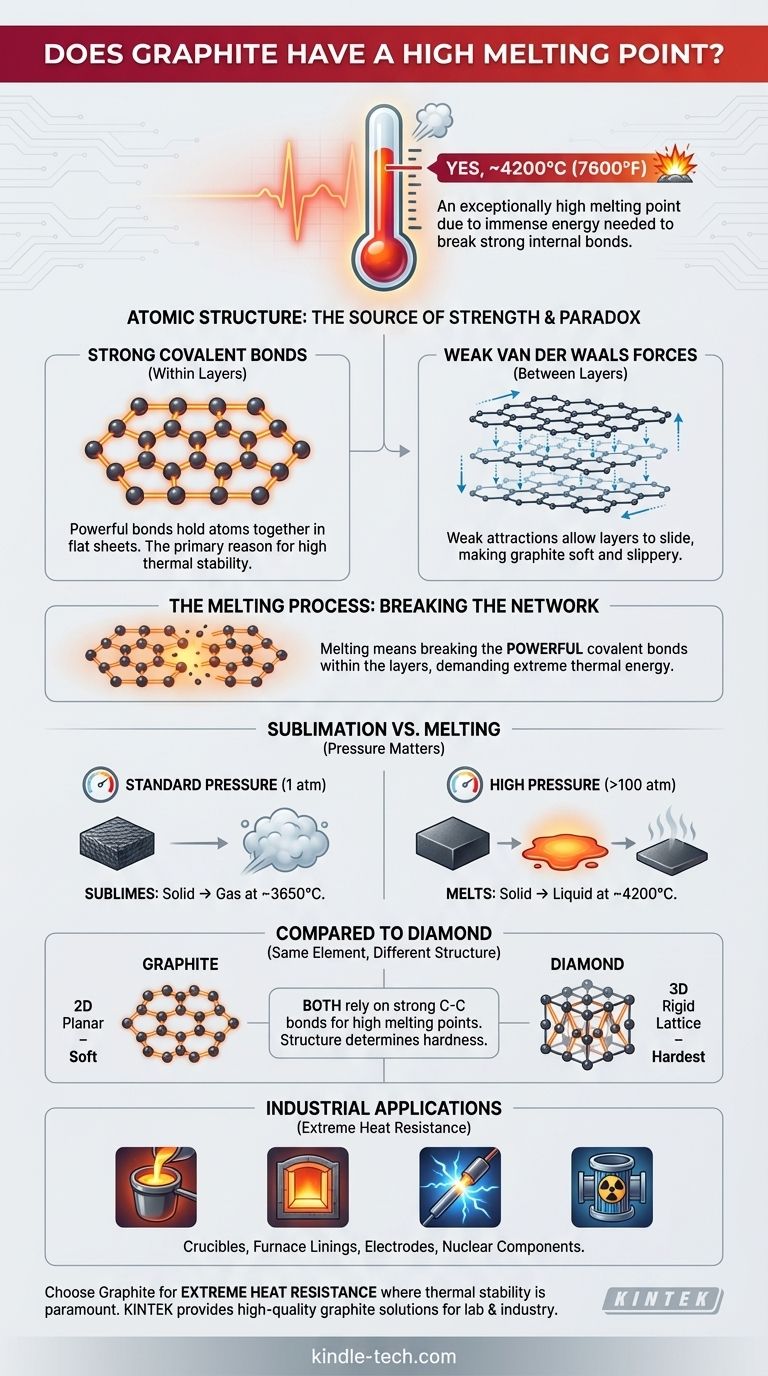
Yes, graphite has an exceptionally high melting point. This property is a direct consequence of its atomic structure, which requires an immense amount of energy to break apart. While its exact melting point can vary with pressure, it is often cited as being around 4200°C (7600°F).
Graphite's high melting point is not due to the weak forces between its layers (which make it soft), but to the incredibly strong covalent bonds holding the carbon atoms together within each layer. To melt graphite, you must break these powerful internal bonds, a process that demands extreme temperatures.

The Source of Graphite's Strength: Atomic Bonding
The reason for graphite's seemingly contradictory nature—being both soft and having a high melting point—lies in two different types of chemical forces working at once.
Strong Covalent Bonds Within Layers
Graphite is composed of carbon atoms arranged in flat, hexagonal sheets, much like a honeycomb. Within each sheet, every carbon atom is linked to three others by strong covalent bonds.
These bonds are among the most stable and powerful chemical bonds in nature. They are the primary source of graphite's thermal stability and high melting point.
Weak van der Waals Forces Between Layers
While the atoms within a sheet are bonded tightly, the sheets themselves are stacked on top of each other and held together by much weaker forces called van der Waals forces.
These weak attractions are easily overcome, allowing the layers to slide past one another. This is what gives graphite its characteristic softness, slipperiness, and usefulness as a lubricant.
What "Melting" Actually Means for Graphite
Understanding the melting process is key to resolving the paradox of graphite's properties.
Breaking the Covalent Network
Melting a substance involves giving its atoms enough energy to break free from their fixed positions. For graphite, this doesn't mean separating the layers—it means breaking the strong covalent bonds within the layers themselves.
Overcoming the strength of these C-C bonds requires a massive input of thermal energy, which is why the temperature must be so incredibly high.
Sublimation vs. Melting
It is important to note that under standard atmospheric pressure, graphite doesn't truly melt. Instead, it sublimes—turning directly from a solid into a gas—at around 3650°C.
Achieving a true liquid state for carbon typically requires applying high pressure (over 100 atmospheres) to prevent the atoms from immediately flying apart into a gas.
Understanding the Context and Trade-offs
Graphite's properties are best understood when compared to other materials, especially its famous allotrope, diamond.
The Diamond Comparison
Both diamond and graphite are made purely of carbon, and both have extremely high melting/sublimation points. This is because both rely on the strength of carbon-carbon covalent bonds.
The difference in their hardness comes from the bonds' arrangement. Diamond has a rigid 3D lattice of covalent bonds, making it the hardest natural material. Graphite has a 2D planar structure with weak forces between layers, making it soft.
The key takeaway is that melting point is determined by bond strength, while physical hardness is determined by bond structure and arrangement.
Practical Implications
Graphite's high melting point makes it an indispensable industrial material. It is used to make:
- Crucibles for holding and melting metals.
- Linings for high-temperature furnaces.
- Electrodes in electric arc furnaces that can reach thousands of degrees.
- Components in nuclear reactors that must withstand extreme heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this property allows you to select and use materials based on their fundamental structure.
- If your primary focus is extreme heat resistance: Graphite is a prime candidate, as its strong internal covalent bonds provide immense thermal stability.
- If your primary focus is solid lubrication: Graphite's layered structure is ideal, but know that its lubricating properties are backed by a structure that won't melt or degrade under high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is understanding material science: Always distinguish between properties derived from atomic bonds (like melting point) and those derived from bulk structure (like softness or hardness).
Ultimately, graphite's dual nature as both soft and supremely heat-resistant is a direct result of the two distinct types of bonds that define its structure.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | ~4200°C (7600°F) (under high pressure) |
| Sublimation Point | ~3650°C (at standard pressure) |
| Key Structural Feature | Strong covalent bonds within 2D carbon layers |
| Industrial Applications | Crucibles, furnace linings, electrodes, nuclear reactor components |
Need a reliable partner for high-temperature applications?
Graphite's exceptional thermal stability makes it ideal for demanding lab and industrial processes. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including graphite-based solutions like crucibles and furnace components, designed to withstand extreme conditions.
Let our experts help you select the right materials for your specific needs. Contact KINTEK today to enhance your laboratory's capabilities and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why do we use sputter coating? For Superior Thin Film Uniformity and Adhesion
- What is the difference between AC and DC sputtering? Choose the Right Method for Your Material
- What is plasma magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Performance Thin-Film Deposition
- What happens to metal powders during sintering? Transform Powder into Durable, Complex Metal Parts
- How long does fast pyrolysis take? Achieve High Bio-Oil Yields in Under 2 Seconds
- Is pyrolysis oil a biofuel? Understanding Its Potential as a Renewable Energy Source
- What is a lab oven used for? A Guide to Precise Heating, Sterilization & Drying
- What is high temperature sintering of ceramics? Transform Powder into Dense, High-Performance Components



















