Yes, metal absolutely evaporates in a vacuum. In fact, creating a vacuum is the essential step that makes it possible to evaporate metals and other materials in a controlled, useful way. This process, known as vacuum evaporation or thermal evaporation, is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing for everything from computer chips to optical lenses.
The critical insight is that a vacuum doesn't cause evaporation, but it dramatically lowers the temperature and energy required for it to occur. It clears the path for evaporated atoms to travel, enabling the creation of precise, ultra-thin films.
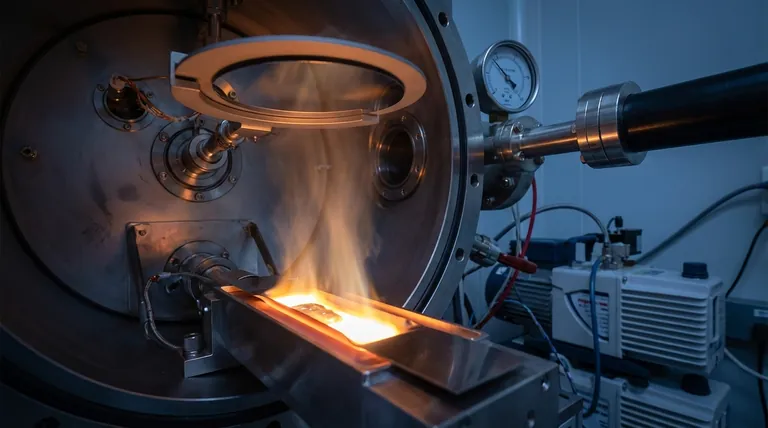

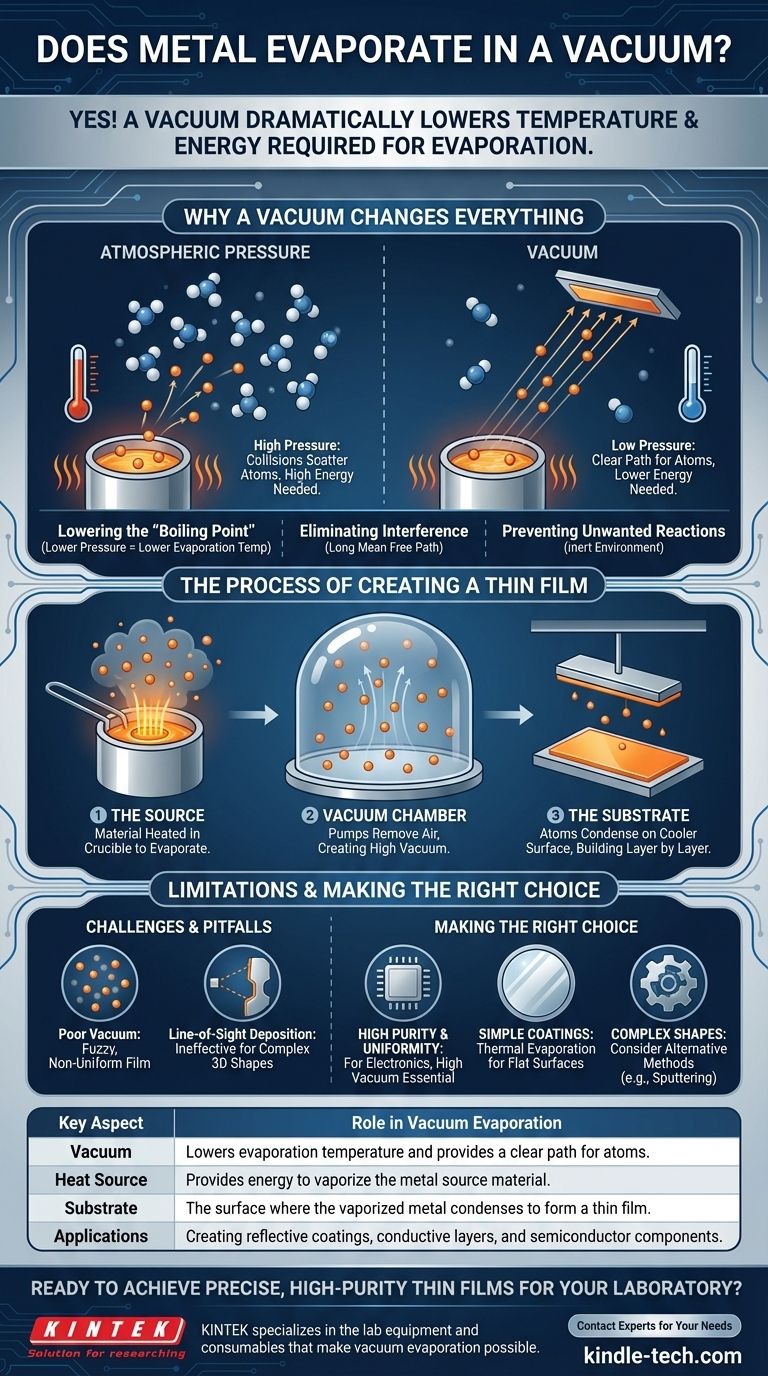
Why a Vacuum Changes Everything for Evaporation
To understand the process, we must first understand the role of pressure. Evaporation is the transition of a substance from a solid or liquid state to a gas. A vacuum is simply a space with extremely low pressure and very few air particles.
Lowering the "Boiling Point"
Every material has a temperature at which its atoms have enough energy to escape its surface. At normal atmospheric pressure, this temperature is very high for metals.
A vacuum drastically reduces the pressure pushing down on the material's surface. With this opposing force removed, metal atoms need far less thermal energy to break free and enter the gaseous phase. This effectively lowers the material's evaporation temperature, similar to how water boils at a lower temperature at high altitudes.
Eliminating Interference
Under normal atmospheric conditions, an evaporated metal atom would almost instantly collide with billions of air molecules (like oxygen and nitrogen). These collisions would scatter the metal atoms, preventing them from traveling in a predictable direction.
In a high vacuum, the path is clear. The evaporated metal atoms can travel in a straight line from the source to their target without interference. This is called a long mean free path.
Preventing Unwanted Reactions
Many metals are highly reactive at their evaporation temperatures. If exposed to air, they would immediately oxidize or form other compounds, contaminating the final product.
A vacuum provides an inert environment, ensuring the evaporated material remains pure as it travels from the source to the target surface.
The Process of Creating a Thin Film
Vacuum evaporation is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) method used to apply a thin film of material onto a surface, called a substrate.
The Three Key Components
- The Source: The material to be deposited (e.g., aluminum, gold, chromium) is placed in a container called a crucible. It's then heated, typically by passing a large electrical current through a resistant filament, until it begins to evaporate.
- The Vacuum Chamber: This entire process takes place inside a sealed chamber where pumps have removed nearly all the air, creating a high-vacuum environment.
- The Substrate: This is the object to be coated (e.g., a silicon wafer, a piece of glass, a plastic part). It is positioned above the source so that it is in the direct path of the evaporating atoms.
As the metal atoms travel through the vacuum, they eventually strike the cooler surface of the substrate. Upon impact, they lose their energy, condense back into a solid state, and build up layer by layer to form a smooth, uniform, and extremely thin film.
Understanding the Limitations and Pitfalls
While powerful, vacuum evaporation is not without its challenges. The quality of the outcome depends entirely on controlling the variables.
The Importance of High Vacuum
The level of the vacuum is paramount. A poor vacuum means too many residual gas molecules remain in the chamber. This leads to collisions that scatter the metal atoms, resulting in a non-uniform or "fuzzy" film that lacks the desired properties.
Line-of-Sight Deposition
Because the evaporated atoms travel in straight lines, this method can only coat surfaces that are in its direct line of sight. It is not effective for coating complex 3D shapes with undercuts or hidden surfaces.
Material Compatibility
Not all materials are suitable for thermal evaporation. Some compounds may decompose when heated instead of evaporating cleanly, while materials with extremely high boiling points can be difficult and energy-intensive to process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the principles of vacuum evaporation allows you to apply it correctly for specific technical goals.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity, uniform films for electronics: A high-quality vacuum is non-negotiable to ensure a clean process and excellent film adhesion.
- If your primary focus is applying a simple reflective or conductive coating: Thermal evaporation is an efficient and cost-effective method for coating flat or gently curved surfaces.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex, three-dimensional object: You should consider alternative deposition methods, such as sputtering, which do not have the same line-of-sight limitations.
By controlling pressure, you gain precise control over the fundamental state of matter, turning a raw material into an engineered surface.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Role in Vacuum Evaporation |
|---|---|
| Vacuum | Lowers evaporation temperature and provides a clear path for atoms. |
| Heat Source | Provides energy to vaporize the metal source material. |
| Substrate | The surface where the vaporized metal condenses to form a thin film. |
| Applications | Creating reflective coatings, conductive layers, and semiconductor components. |
Ready to achieve precise, high-purity thin films for your laboratory?
KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables that make vacuum evaporation possible. Whether you are developing advanced electronics, optical coatings, or specialized materials, our expertise ensures your process is efficient and reliable.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs and elevate your research and production capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
People Also Ask
- Why is temperature important in casting? Master the Thermal Balance for Defect-Free Parts
- How does a high-temperature annealing furnace facilitate the homogenization of high-entropy alloys and stainless steels?
- What is the primary function of high-temperature furnaces in mechanical characterization? Simulating Extreme Reality
- What conditions does a vacuum annealing furnace provide for Ti41.5Zr41.5Ni17 films? Optimize Quasicrystal Stability
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering aluminum composites? Achieve Superior Bonding & Density
- What happens if sintering temperature is too high? Avoid Irreversible Damage to Your Parts
- At what temperature is sintering done? Find the Thermal Sweet Spot for Your Material
- Which heat treatment process is a softening process? Understand Annealing for Superior Metal Workability



















