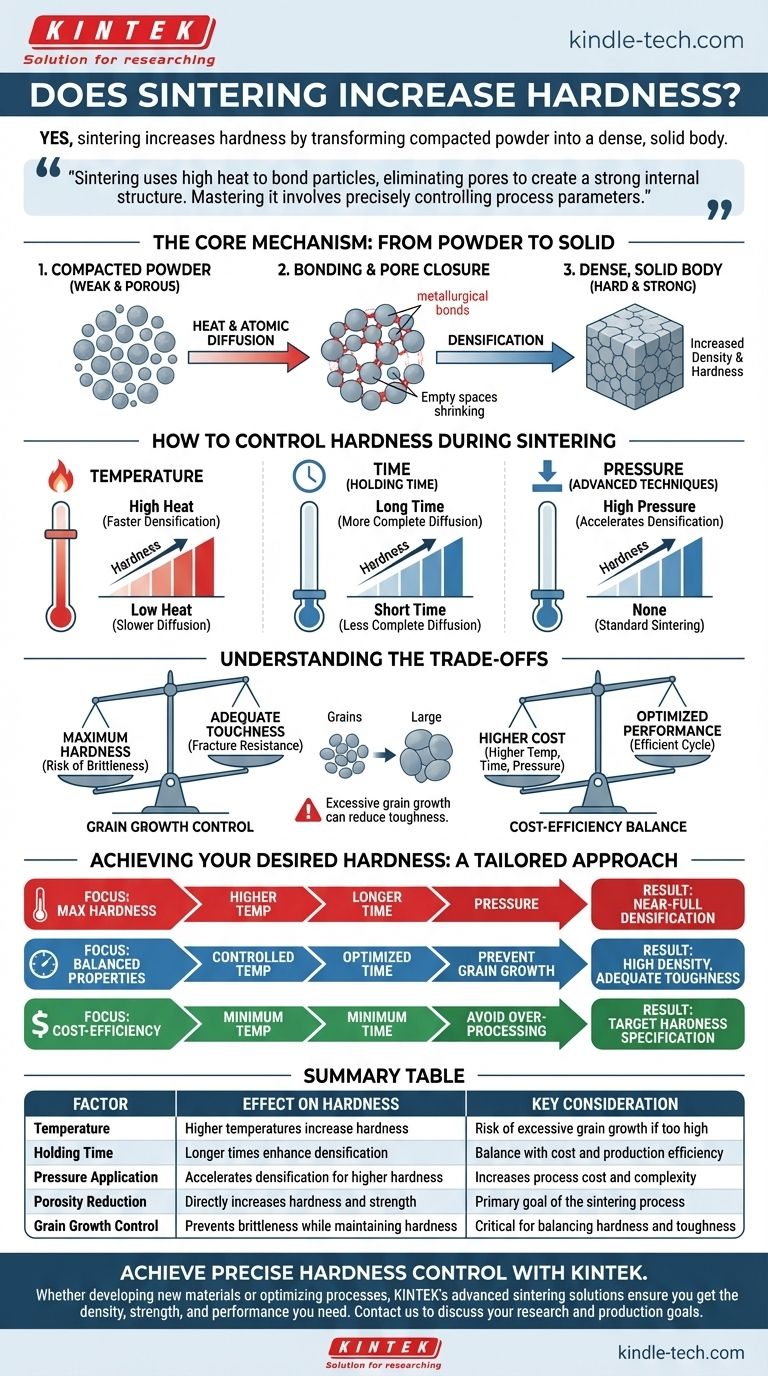
Yes, fundamentally, the process of sintering is designed to increase hardness and strength. It achieves this by transforming a compacted object made of loose powder into a dense, solid body. This transformation occurs at a microscopic level, creating a strong internal structure where one did not previously exist.
Sintering increases hardness by using high heat to bond individual material particles together, systematically eliminating the empty spaces (pores) between them. The key to mastering this process is not just achieving hardness, but precisely controlling it by managing the process parameters to shape the material's final microstructure.

The Core Mechanism: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is a thermal treatment that fundamentally changes a material's internal structure. A part pressed from powder has mechanical integrity but is weak and porous. Sintering provides the hardness and strength required for performance.
Bonding Particles Together
At temperatures below the material's melting point, atoms become highly mobile. They migrate across the contact points between individual powder particles, forming strong, continuous metallurgical bonds, much like welding on a microscopic scale.
Eliminating Porosity
As atoms diffuse and bonds form, the empty spaces, or pores, between the original particles begin to shrink and close. Since pores are points of weakness, their elimination directly results in a harder, stronger, and denser material.
Achieving Densification
The collective result of particle bonding and pore elimination is densification. The part shrinks in volume as its internal voids are removed, leading to a significant increase in its overall density. This increase in density is directly correlated with the increase in hardness.
How to Control Hardness During Sintering
The final hardness of a sintered part is not an accident; it is a direct result of carefully controlled process parameters. These variables give you precise levers to achieve a target specification.
The Role of Temperature
Temperature is the primary driver of sintering. Higher temperatures accelerate the rate of atomic diffusion, leading to faster and more complete densification. This results in a harder final product.
The Impact of Time
The duration the part is held at the peak sintering temperature, known as holding time, is also critical. A longer holding time allows the diffusion process more time to complete, further reducing porosity and increasing hardness.
The Function of Pressure
In some advanced techniques like Hot Pressing or Spark Plasma Sintering, external pressure is applied. This pressure physically forces particles together, dramatically accelerating densification and making it possible to achieve high hardness at lower temperatures or in shorter times.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Simply maximizing hardness is rarely the goal. Effective sintering involves balancing competing factors to achieve the optimal properties for a specific application.
The Risk of Grain Growth
If the temperature is too high or the time too long, a phenomenon called grain growth can occur. Small crystalline grains within the material begin to merge into larger ones. While the part may be fully dense, excessively large grains can sometimes reduce other important properties like toughness, making the material more brittle.
Hardness vs. Toughness
The hardest possible material is often not the best. Extreme hardness can be associated with brittleness, meaning the part could fracture under sudden impact. The ideal process finds the sweet spot that delivers the required hardness while maintaining adequate toughness.
Balancing Cost and Performance
Higher temperatures, longer furnace times, and the use of external pressure all increase the cost of production. The goal is to design a sintering cycle that achieves the necessary hardness and performance characteristics in the most cost-effective manner possible.
Achieving Your Desired Hardness
Use the principles of sintering to tailor the material properties to your specific engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness: Utilize higher sintering temperatures and longer holding times, and consider pressure-assisted methods to achieve near-full densification.
- If your primary focus is balanced properties (e.g., hardness and toughness): Carefully control the temperature and time to achieve high density while actively preventing excessive grain growth.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency: Optimize the sintering cycle to use the minimum temperature and time required to meet your target hardness specification, avoiding the expense of over-processing.
By understanding these levers, you can use sintering as a precise tool to engineer materials with predictable and reliable mechanical properties.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Hardness | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Higher temperatures increase hardness | Risk of excessive grain growth if too high |
| Holding Time | Longer times enhance densification | Balance with cost and production efficiency |
| Pressure Application | Accelerates densification for higher hardness | Increases process cost and complexity |
| Porosity Reduction | Directly increases hardness and strength | Primary goal of the sintering process |
| Grain Growth Control | Prevents brittleness while maintaining hardness | Critical for balancing hardness and toughness |
Achieve precise hardness control in your lab with KINTEK's advanced sintering solutions. Whether you're developing new materials or optimizing existing processes, our expertise in lab equipment ensures you get the density, strength, and performance you need. Contact us today to discuss how our sintering furnaces and consumables can enhance your research and production outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the effect of heating rate on sintering? Achieve Uniform Density and Avoid Defects
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic
- What is the thermal resistance of SiC? Understanding Its High Thermal Conductivity for Superior Performance
- How do sintering and grinding ensure Silicon Carbide heat exchanger performance? Achieve Extreme Corrosion Resistance
- Why is porcelain heat resistant? The Science of High-Temperature Resilience Explained
- What is the pressureless sintering method? A Guide to Cost-Effective Material Densification
- What are the seven classifications of ceramic materials? A Guide to Selecting the Right Material
- What are the advantages of ceramic? Unlock Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications



















