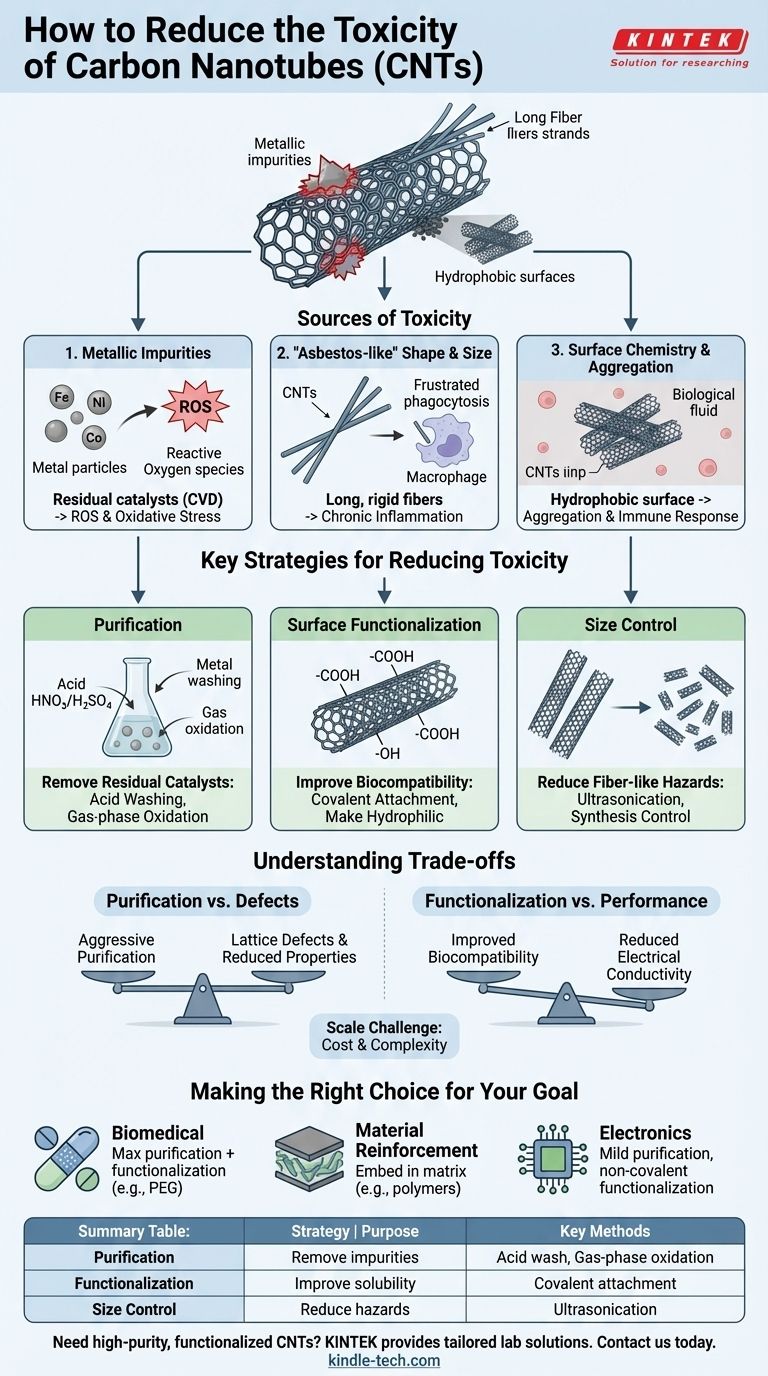
To reduce the toxicity of carbon nanotubes (CNTs), you must address the three primary sources of their adverse biological effects: metallic impurities from manufacturing, their physical shape and size, and their surface chemistry. The most effective strategies involve post-production purification to remove metal catalysts and surface functionalization to improve their solubility and change how they interact with cells.
The core issue is that CNT toxicity is not a single, fixed property but a complex outcome of its physical and chemical characteristics. Therefore, making CNTs safer isn't about finding a single "fix," but about systematically controlling impurities, shape, and surface properties to align with a specific biological or environmental context.

The Sources of CNT Toxicity: More Than Just Carbon
Understanding why CNTs can be toxic is the first step toward mitigating the risk. The toxicity is rarely caused by the carbon lattice itself but by associated impurities and physical properties.
Metallic Impurities: The Hidden Culprits
The dominant method for producing CNTs, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), relies on metal nanoparticles (e.g., iron, nickel, cobalt) as catalysts.
Inevitably, some of these metallic impurities remain embedded in the final CNT material. These residual metals can leach out and generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), causing oxidative stress and damage to cells.
The "Asbestos-like" Effect: Shape and Size Matter
The physical form of CNTs is a major determinant of their toxicity. Long, straight, and rigid multi-walled CNTs can behave like asbestos fibers.
If inhaled, these structures are too large for the body's macrophages to engulf and clear, leading to chronic inflammation and physical damage to tissues like the lungs. This is known as frustrated phagocytosis.
Surface Chemistry and Aggregation
Pristine, unmodified CNTs are highly hydrophobic (water-repelling). As a result, they tend to clump together into large aggregates in biological fluids.
These aggregates can cause blockages in biological pathways and create localized zones of high concentration, amplifying their toxic effects. Their pristine surface can also trigger an immune response.
Key Strategies for Reducing Toxicity
Based on the sources of toxicity, a multi-step approach is required to engineer safer CNTs.
Purification: Removing Residual Catalysts
The most crucial first step is to remove the metallic impurities left over from synthesis. This is typically achieved through aggressive purification methods.
Common techniques include gas-phase oxidation to burn off amorphous carbon and liquid-phase acid washing (using nitric or sulfuric acid) to dissolve and remove the metal particles.
Surface Functionalization: Improving Biocompatibility
This is the most powerful strategy for reducing CNT toxicity. Functionalization involves chemically attaching new molecules or functional groups to the surface of the CNT.
Covalently adding groups like carboxyl (-COOH) or hydroxyl (-OH) makes the CNTs hydrophilic (water-soluble). This dramatically reduces aggregation and improves dispersion in biological systems, making them "stealthier" and less likely to trigger a harsh immune response.
Controlling Physical Dimensions
Controlling the length of CNTs is another effective strategy. Shorter CNTs are generally less toxic because they are small enough for immune cells to clear from the body.
Length can be controlled during the synthesis process or by post-processing steps like ultrasonication, which can break longer tubes into smaller fragments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Reducing toxicity is not without its costs, and it's essential to understand the compromises involved.
The Purification Dilemma
While necessary, aggressive purification methods like strong acid treatments can introduce defects into the carbon lattice of the CNTs.
This damage can negatively impact the very properties—such as electrical conductivity or mechanical strength—that made the CNTs desirable in the first place.
Functionalization vs. Performance
Surface functionalization fundamentally alters the CNT's surface. This change, which improves biocompatibility, also disrupts the delocalized pi-electron system of the carbon structure.
As a result, functionalization almost always reduces electrical conductivity. There is a direct trade-off between maximizing biocompatibility and preserving the pristine electronic properties of the CNT.
The Challenge of Manufacturing Scale
Advanced purification and functionalization add significant cost and complexity to CNT production.
Achieving consistent, well-characterized, and low-toxicity CNTs at an industrial scale remains a significant engineering and financial challenge, limiting their use in many potential applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The appropriate strategy for reducing toxicity depends entirely on the intended application.
- If your primary focus is biomedical applications (e.g., drug delivery, imaging): Prioritize multi-step purification and surface functionalization with biocompatible molecules like polyethylene glycol (PEG) to ensure maximum safety and stability in the body.
- If your primary focus is material reinforcement (e.g., composites): Focus on securely embedding the CNTs within a matrix material (like a polymer) to prevent them from becoming airborne and to minimize worker exposure and end-of-life environmental release.
- If your primary focus is electronics: Use the mildest purification methods possible to preserve electrical conductivity and explore non-covalent functionalization, which coats the CNT without damaging its structure.
Ultimately, proactively managing the physicochemical properties of carbon nanotubes is the key to safely unlocking their transformative potential.
Summary Table:
| Strategy | Purpose | Key Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Purification | Remove metallic impurities | Acid washing, Gas-phase oxidation |
| Surface Functionalization | Improve solubility & biocompatibility | Covalent attachment (e.g., -COOH, -OH) |
| Size Control | Reduce fiber-like hazards | Ultrasonication, Synthesis control |
Need high-purity, functionalized carbon nanotubes for your research or application? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions tailored to your laboratory's needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your work with reliable, safer CNT materials!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Measuring Cylinder 10/50/100ml
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum drying oven preferred for ZnO nanopowders? Preserve Particle Size and Prevent Agglomeration
- How do you remove solvent by evaporation? Master the Techniques for Safe and Efficient Sample Preparation
- What is direct current magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the main safety concern from radiofrequency RF energy? Understanding the Real Risk of Tissue Heating
- How does the refrigeration system of an Ultra Freezer work? The Two-Stage Cascade Cooling Explained
- Is KBr hazardous? Understand the Risks and Safe Handling of Potassium Bromide
- What are the four heat treatment methods to enhance the properties of steel? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, and Tempering
- What are the factors affecting selective laser sintering? Master Energy, Material & Temperature Control



















