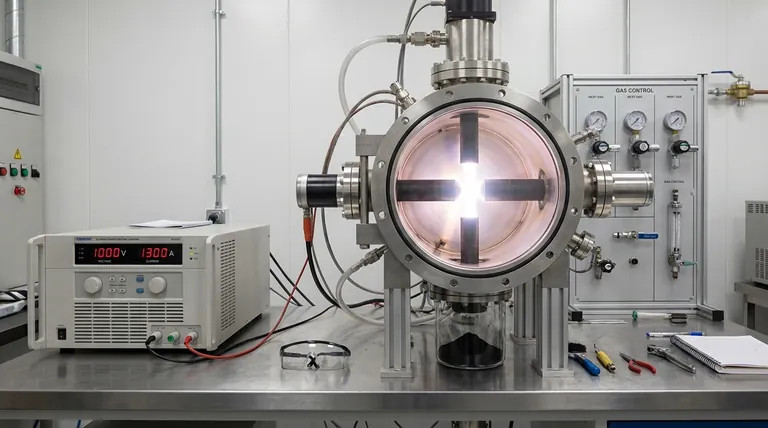
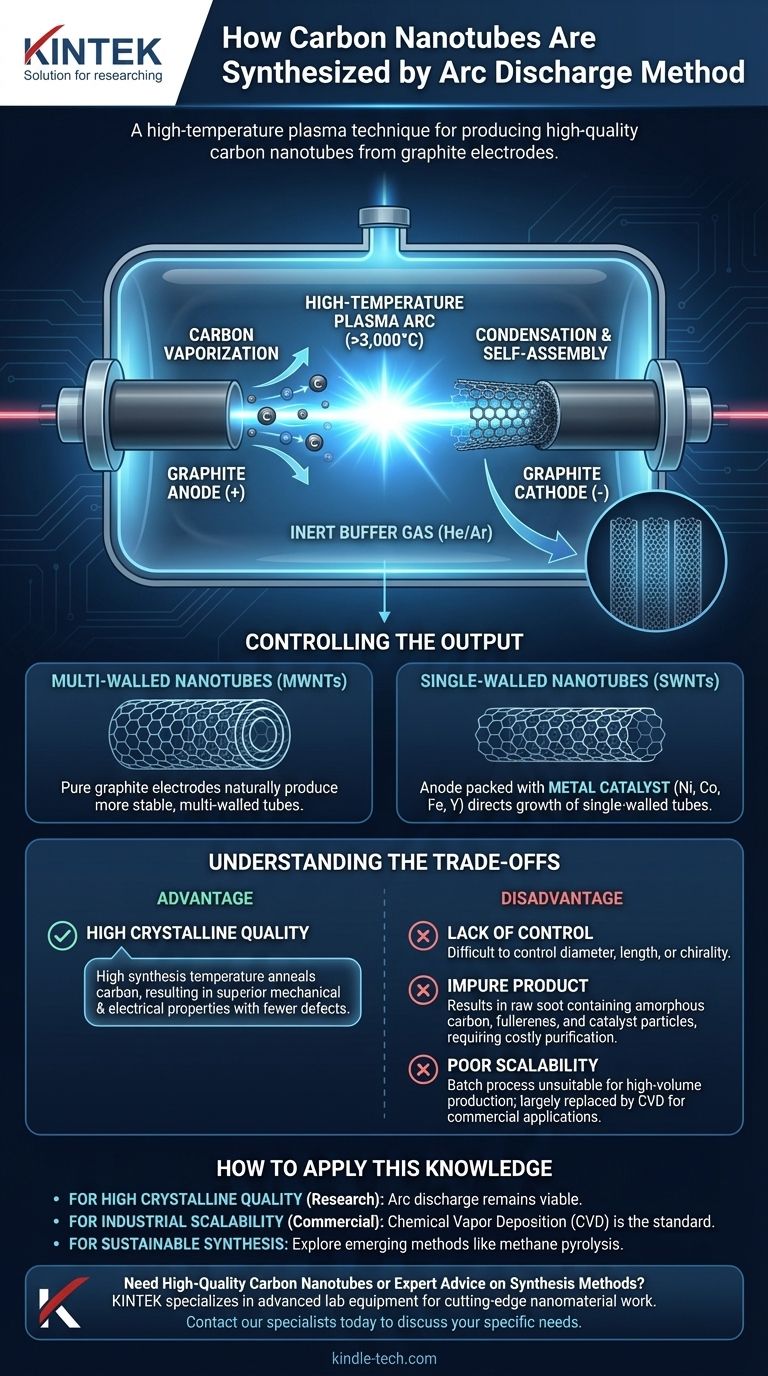
The arc discharge method synthesizes carbon nanotubes by generating a high-temperature plasma arc between two carbon electrodes in an inert atmosphere. This intense heat vaporizes carbon from the positive electrode (anode), which then travels and condenses on the cooler negative electrode (cathode), self-assembling into nanotube structures.
The arc discharge method is a historically significant, high-temperature technique for producing high-quality carbon nanotubes. However, its lack of precise control over the final product has led to its replacement by more scalable methods for most commercial applications.

The Fundamental Mechanism: From Carbon Rods to Nanotubes
To understand arc discharge, it's best to visualize it as a controlled, miniature lightning strike designed to break down and then rebuild carbon at the nanoscale.
The Core Apparatus
The setup consists of a sealed chamber filled with an inert buffer gas, typically helium or argon, at low pressure. Inside are two high-purity graphite electrodes (an anode and a cathode) separated by a small gap and connected to a high-current DC power supply.
Initiating the Plasma Arc
A high voltage is applied across the electrodes, creating a sustained electrical arc that jumps the gap. This arc generates a plasma—an ionized gas—with an extremely high temperature, often exceeding 3,000°C.
Carbon Vaporization
The intense heat from the plasma is focused on the anode, causing the solid graphite to rapidly sublimate and vaporize. This creates a dense plume of carbon atoms and ions within the plasma stream.
Condensation and Self-Assembly
This hot carbon vapor is driven from the anode towards the relatively cooler cathode. As the carbon atoms cool, they condense and self-assemble into more stable structures, primarily forming carbon nanotubes on the surface of the cathode.
Controlling the Output: Single-Walled vs. Multi-Walled CNTs
The type of nanotube produced is directly influenced by the composition of the anode.
Multi-Walled Nanotubes (MWNTs)
When both electrodes are made of pure graphite, the process naturally produces multi-walled carbon nanotubes. These are concentric cylinders of graphene sheets, which are the default and more stable form under these conditions.
Single-Walled Nanotubes (SWNTs)
To produce the more delicate single-walled carbon nanotubes, the anode must be drilled and packed with a metal catalyst. Common catalysts include mixtures of nickel, cobalt, iron, or yttrium. These metal particles become part of the plasma and act as nucleation sites, guiding the growth of single-walled tubes.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Arc Discharge
While foundational, the arc discharge method has distinct advantages and critical limitations that have defined its role in nanotechnology.
Advantage: High Crystalline Quality
The extremely high synthesis temperature anneals the carbon as it forms. This process results in nanotubes with a high degree of crystalline perfection and fewer structural defects, leading to superior mechanical and electrical properties.
Disadvantage: Lack of Control
The process is inherently chaotic. It is extremely difficult to control the diameter, length, or chirality (the angle of the atomic lattice) of the nanotubes being formed. The output is a highly varied mixture.
Disadvantage: Impure Product
The resulting material, a raw soot, is a heterogeneous mixture. It contains the desired nanotubes alongside undesirable byproducts like amorphous carbon, fullerenes, and catalyst nanoparticles. This necessitates costly and intensive post-processing for purification.
Disadvantage: Poor Scalability
The arc discharge method is essentially a batch process that produces very small quantities. It is not easily scaled for the continuous, high-volume production required for most industrial applications, which is why Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) became the dominant commercial process.
How to Apply This Knowledge
Your choice of a synthesis method depends entirely on the intended application and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is producing small batches of highly crystalline nanotubes for fundamental research: The arc discharge method remains a viable option due to the superior structural integrity of its output.
- If your primary focus is industrial-scale production with control over nanotube properties: A modern technique like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the definitive industry standard for its scalability and control.
- If your primary focus is exploring sustainable synthesis routes: Investigate emerging methods like methane pyrolysis or CO2 electrolysis, which aim to reduce cost and environmental impact.
Ultimately, understanding the principles of arc discharge provides a crucial foundation for appreciating the evolution and challenges of nanomaterial synthesis.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | High-current arc vaporizes carbon anode in inert gas. |
| Temperature | Exceeds 3,000°C. |
| Primary Output | Multi-Walled Nanotubes (MWNTs); SWNTs with metal catalyst. |
| Key Advantage | Produces high-crystalline-quality nanotubes. |
| Key Limitation | Lack of control over nanotube type, length, and chirality. |
Need High-Quality Carbon Nanotubes or Expert Advice on Synthesis Methods?
Understanding the nuances of synthesis methods like arc discharge is crucial for successful research and development. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for cutting-edge nanomaterial work. Whether you are exploring synthesis techniques or require materials for your application, our experts can help you navigate the options to achieve your goals.
Contact our specialists today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's specific needs in nanotechnology and beyond.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings



















