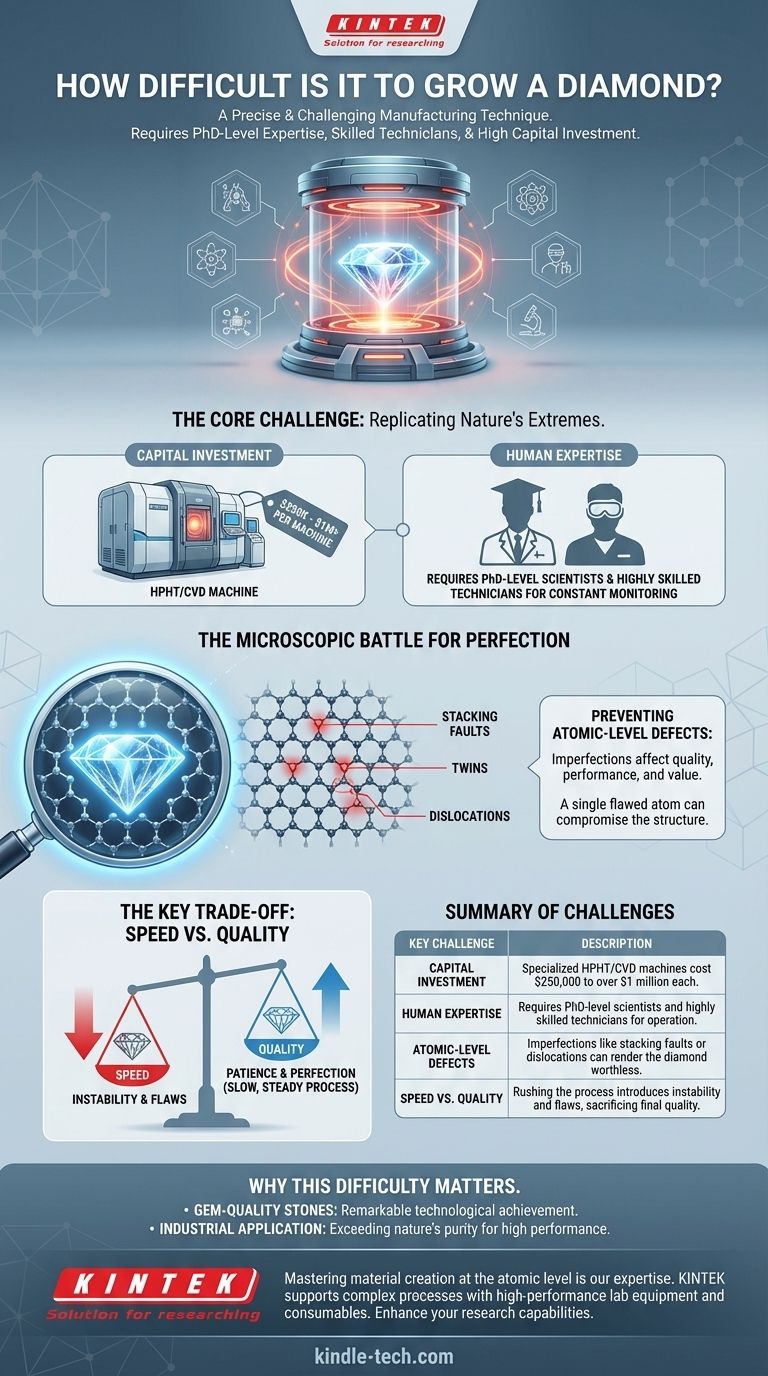
Growing a diamond is exceptionally difficult. It is widely considered one of the most precise and challenging manufacturing techniques ever developed. The process demands PhD-level scientific expertise to manage, highly skilled technicians to operate the complex machinery, and a significant capital investment for each growth chamber.
The core difficulty in growing a diamond lies not just in recreating the immense heat and pressure found deep within the Earth, but in maintaining perfect atomic-level stability over weeks to prevent microscopic defects that would render the final crystal worthless.
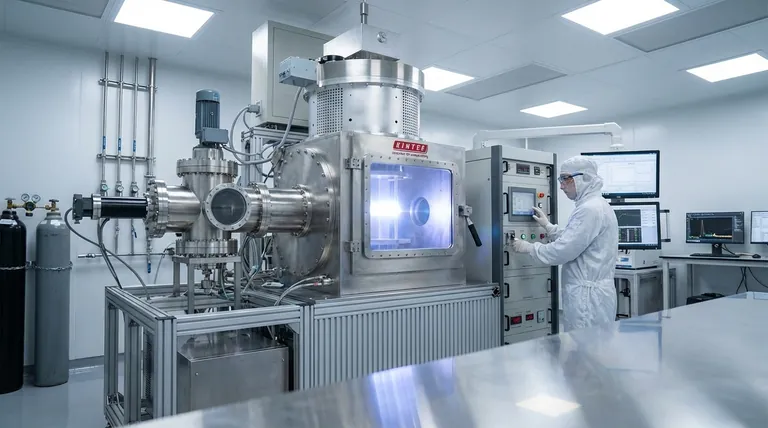

The Core Challenge: Replicating Nature's Extremes
Creating a diamond in a lab is a process of forcing carbon atoms to arrange themselves into a perfect crystalline structure. This requires an environment that is both incredibly intense and flawlessly stable, presenting immense barriers to entry.
The Barrier of Capital Investment
The specialized equipment required for diamond growth is a major hurdle. Each production machine, whether for High Pressure/High Temperature (HPHT) or Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) methods, represents a massive financial commitment.
These machines can cost anywhere from $250,000 to over $1 million apiece, placing this technology far outside the realm of casual or small-scale operations.
The Requirement of Human Expertise
This is not a "set it and forget it" manufacturing process. Diamond growth chambers are highly sensitive instruments that require constant monitoring and maintenance.
Operating this equipment effectively demands a deep, scientific understanding of physics and chemistry. This is why operations are overseen by PhDs and executed by highly skilled technicians who can interpret data and make micro-adjustments to the growth process.
The Microscopic Battle for Perfection
Beyond the high-level challenges of cost and knowledge, the true difficulty is revealed at the atomic level. The goal is to build a perfect crystal lattice, atom by atom, and even the slightest imperfection can cascade into a critical flaw.
Preventing Atomic-Level Defects
As the diamond crystal forms, it is vulnerable to numerous types of growth defects. These are not visible flaws like cracks, but rather imperfections in the atomic arrangement.
Common defects include stacking faults, twins, and dislocations. Think of this as building a perfect wall of bricks; a single brick placed at the wrong angle (a dislocation) can compromise the integrity of the entire structure.
The Challenge of Junctions
This problem is magnified in advanced techniques like "mosaic growth," where multiple small diamond seeds are grown together to create one larger diamond.
The junction regions where these individual crystals meet are extremely prone to forming defects. Ensuring a seamless, flawless transition between adjacent seeds is a significant and ongoing technical challenge.
The Impact on Quality
These microscopic defects have a macroscopic impact. In a gemstone, they can affect clarity and brilliance.
For high-tech applications, such as diamond semiconductors or precision cutting tools, these flaws can catastrophically affect the material's performance, rendering the entire diamond unusable for its intended purpose.
Understanding the Key Trade-off: Speed vs. Quality
Every diamond grower must navigate a fundamental conflict that defines the process. Rushing the growth cycle is the surest way to create a flawed, low-quality stone.
The Temptation of Speed
There is immense economic pressure to produce diamonds faster. However, accelerating the growth process invariably introduces instability into the system.
This instability dramatically increases the likelihood of forming the atomic-level defects mentioned earlier, resulting in a less valuable or even worthless final product.
The Necessity of Patience
The highest-quality diamonds are almost always the result of a slow, steady, and meticulously controlled process.
This requires maintaining perfect environmental conditions—temperature, pressure, and gas purity—for days or even weeks on end. The ultimate trade-off is sacrificing production speed to achieve the atomic perfection that gives a diamond its value.
Why This Difficulty Matters
Understanding the immense challenge of diamond growth provides crucial context for its value, whether it's used in jewelry or industry.
- If your primary focus is gem-quality stones: The difficulty and precision required are what ensure that even a lab-grown diamond is a product of remarkable technological achievement.
- If your primary focus is industrial application: The challenge is in achieving a level of structural purity that exceeds nature, as even the tiniest defect can cause failure in a high-performance semiconductor or optical lens.
Ultimately, the difficulty of growing a diamond is a testament to the incredible fusion of science and engineering required to master the creation of matter at its most fundamental level.
Summary Table:
| Key Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Specialized HPHT/CVD machines cost $250,000 to over $1 million each. |
| Human Expertise | Requires PhD-level scientists and highly skilled technicians for operation. |
| Atomic-Level Defects | Imperfections like stacking faults or dislocations can render the diamond worthless. |
| Speed vs. Quality | Rushing the process introduces instability and flaws, sacrificing final quality. |
Mastering material creation at the atomic level is our expertise. The challenges of growing flawless diamonds—from managing extreme pressure and heat to preventing microscopic defects—are similar to the precision required in advanced laboratory research and manufacturing. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-performance lab equipment and consumables necessary to support such complex processes. Whether you are developing new materials or require reliable tools for precise experimentation, our solutions are designed to meet the demanding needs of modern laboratories. Enhance your research capabilities—contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the primary advantages of the CVD method for growing diamonds? Engineering High-Purity Gems and Components
- How does MPCVD work? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Quality Film Deposition
- What is MPCVD? Unlock Atom-by-Atom Precision for High-Purity Materials
- What are the advantages of microwave plasma? Faster, Purer Processing for Demanding Applications
- What is MPCVD method? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond Synthesis



















