In short, microwave plasma works by using focused microwave energy inside a vacuum to excite a gas to the point where its atoms are broken apart. This process strips electrons from the atoms, creating an energized, highly reactive cloud of ions, electrons, and molecular fragments known as plasma, which can then be used for advanced material processing like growing diamonds.
The critical concept to grasp is that microwave plasma is not about simple heating. It's a precise method for creating a unique chemical environment—an "energetic soup"—where reactions that are normally impossible can occur efficiently and at relatively low overall temperatures.

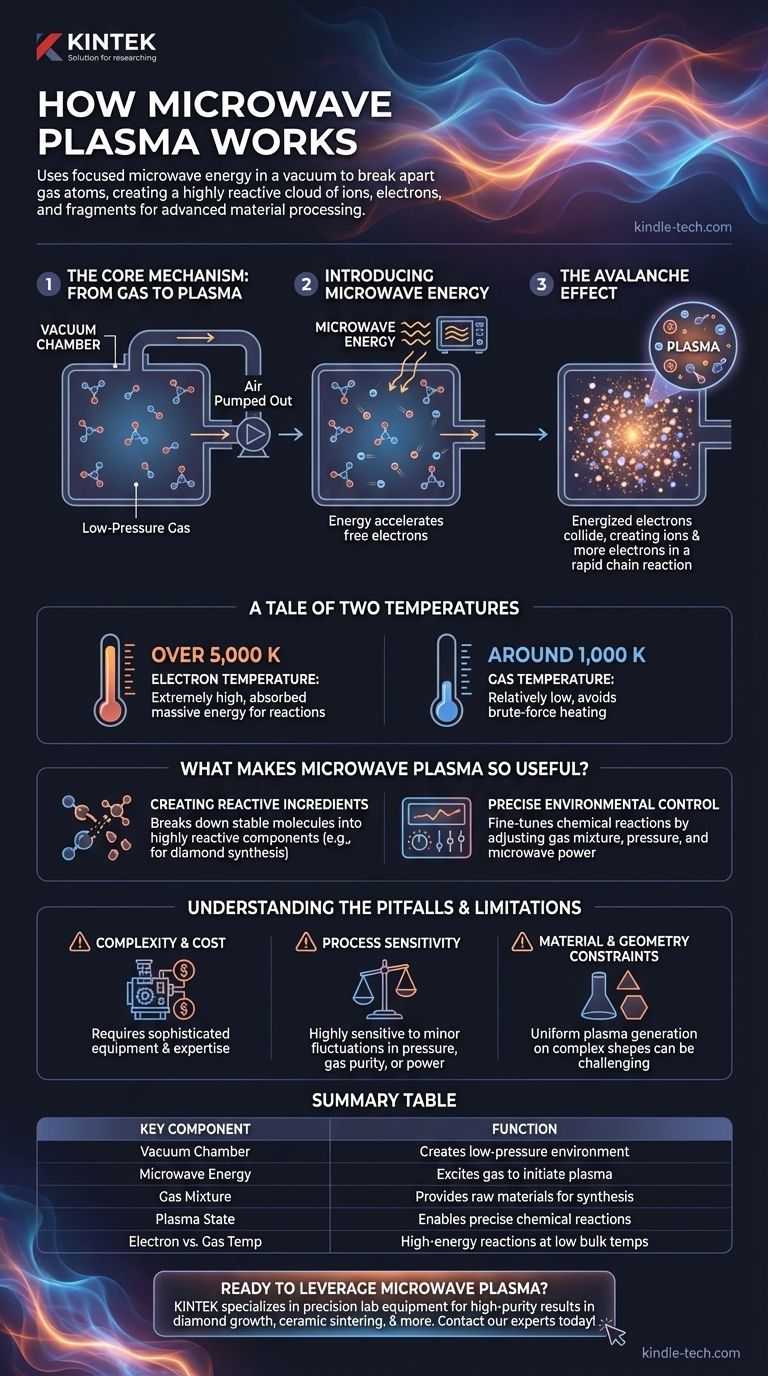
The Core Mechanism: From Gas to Plasma
To understand how microwave plasma is generated, it's best to think of it as a controlled, step-by-step process where each component plays a critical role.
The Role of the Vacuum Chamber
First, the process begins in a sealed chamber where the air is pumped out to create a vacuum or a very low-pressure environment.
This low pressure is essential because it reduces the density of the gas molecules, allowing the microwave energy to interact with them more effectively and controllably.
Introducing Microwave Energy
Next, a specific gas or a mixture of gases (like methane and hydrogen for diamond growth) is introduced into the chamber.
Microwave radiation is then beamed into the chamber. This energy doesn't heat the gas in a conventional way; instead, it rapidly accelerates the few free-floating electrons that are naturally present in the gas.
The Avalanche Effect
These newly energized electrons zip through the low-pressure gas, colliding with neutral gas atoms with tremendous force.
Each collision is energetic enough to knock another electron off a gas atom, creating a positively charged ion and another free electron. This process repeats in a rapid chain reaction, quickly creating a dense, self-sustaining cloud of charged particles—the plasma.
A Tale of Two Temperatures
A key feature of microwave plasma is the vast difference between two temperatures within the system.
The electron temperature can be extremely high (over 5,000 K), as the electrons have absorbed massive amounts of energy from the microwaves.
However, the overall gas temperature remains much lower (around 1,000 K). This is because the energy is precisely targeted at the electrons to drive chemical reactions, rather than being wasted on brute-force heating of the entire chamber.
What Makes Microwave Plasma So Useful?
The unique properties of this plasma state are what make it a powerful tool for advanced manufacturing and material science.
Creating Reactive Ingredients
The intense energy within the plasma breaks down stable molecules into highly reactive components.
For example, in diamond synthesis, stable methane (CH4) and hydrogen (H2) gases are transformed into the specific reactive carbon species and atomic hydrogen required to build a diamond crystal lattice layer by layer.
Precise Environmental Control
The plasma environment is highly controllable. By carefully adjusting the gas mixture, pressure, and microwave power, engineers can precisely tune the chemical reactions taking place.
This level of control allows for the creation of high-purity materials and complex structures that would be difficult or impossible to produce with traditional high-temperature furnaces.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Limitations
While powerful, microwave plasma technology is not a universal solution and comes with its own set of challenges that require expert management.
Complexity and Cost
Microwave plasma systems are complex and expensive. They require sophisticated vacuum pumps, precision gas flow controllers, and specialized microwave generators and waveguides, all of which demand significant investment and expertise.
Process Sensitivity
The process is highly sensitive to minor fluctuations. Small changes in pressure, gas purity, or power output can dramatically alter the plasma's characteristics and affect the quality of the final product. Consistent results require rigorous process control.
Material and Geometry Constraints
The effectiveness of the process can depend on the shape and electrical properties of the material being processed (the substrate). Uniform plasma generation over large or complex shapes can be challenging and often requires custom-designed reactor chambers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these principles allows you to identify when microwave plasma is the right tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material synthesis: Microwave plasma is ideal because it creates an ultra-clean, highly reactive environment without the extreme bulk temperatures that can introduce impurities.
- If your primary focus is creating novel material structures: The unique, non-equilibrium energy state allows for the deposition and crystallization of materials in ways that conventional heating cannot replicate.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: For certain applications like ceramic sintering, the direct and targeted energy of microwaves can lead to significantly faster processing times compared to radiant heating in a conventional furnace.
By viewing microwave plasma as a tool for precision chemical engineering, you can leverage its unique capabilities to create the next generation of advanced materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Chamber | Creates low-pressure environment for controlled plasma generation |
| Microwave Energy | Excites gas molecules to initiate and sustain the plasma state |
| Gas Mixture (e.g., CH₄, H₂) | Provides raw materials broken down into reactive species for synthesis |
| Plasma State | Energized cloud of ions and electrons enabling precise chemical reactions |
| Electron vs. Gas Temperature | Enables high-energy reactions at relatively low bulk temperatures |
Ready to leverage microwave plasma for your advanced material synthesis? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, providing the tools and expertise to help you achieve high-purity results in diamond growth, ceramic sintering, and other complex processes. Our solutions are designed for laboratories focused on innovation and efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your research and manufacturing goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- What are the limitations of diamonds? Beyond the Myth of Perfection
- How plasma is used in diamond coating films? Unlock the Power of MPCVD for Superior Coatings
- What are the advantages of microwave plasma? Faster, Purer Processing for Demanding Applications
- What is the difference between MPCVD and HFCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- What is MPCVD method? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond Synthesis



















