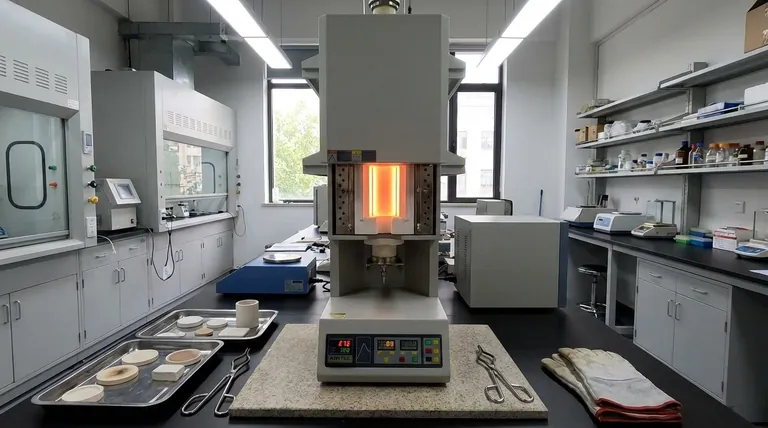
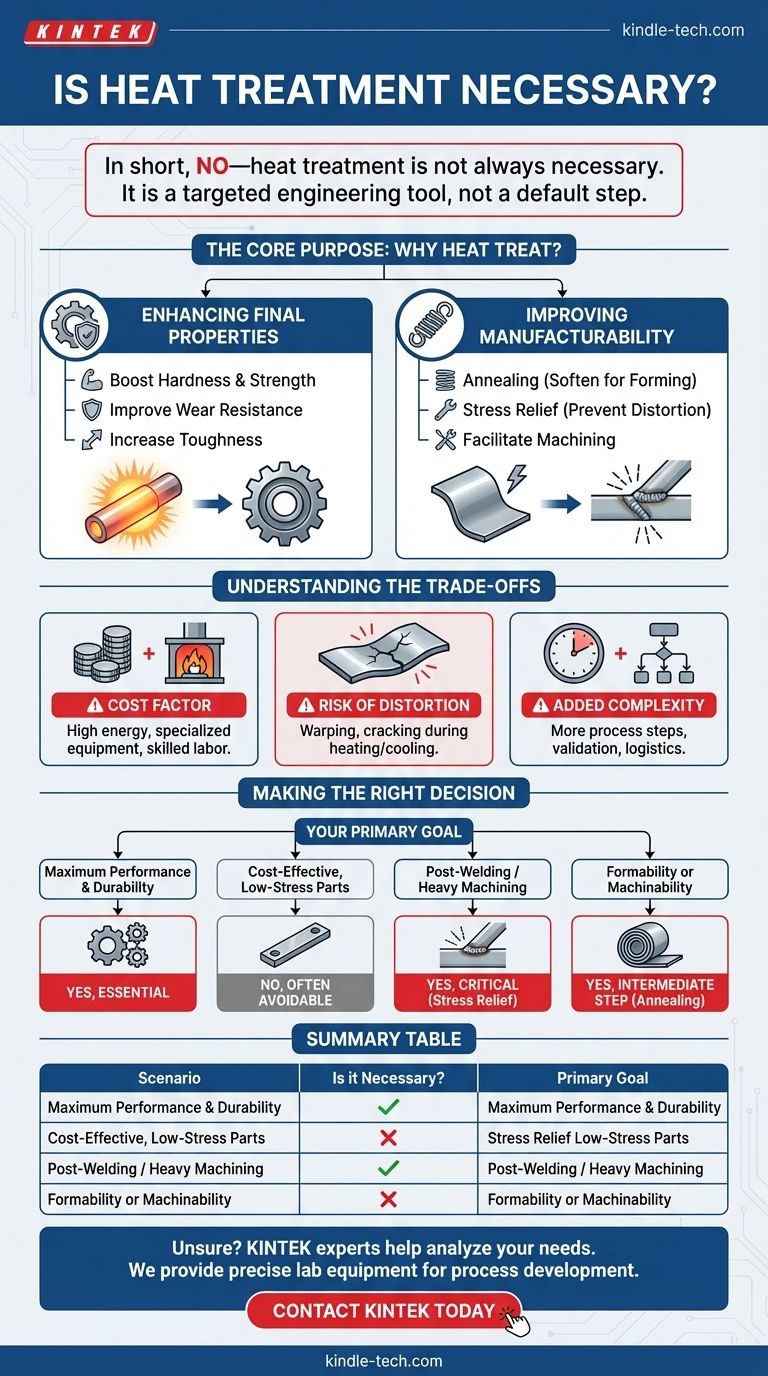
In short, no—heat treatment is not always necessary. It is a specific engineering process applied only when the desired properties of a component cannot be achieved through material selection alone. The decision to heat treat is driven by the performance requirements of the final part or the practical needs of the manufacturing process itself.
Heat treatment should be viewed as a targeted tool, not a default step. Its necessity is determined by a clear engineering goal: either to achieve final mechanical properties like hardness and strength, or to facilitate the manufacturing process by improving a material's machinability or formability.

The Core Purpose of Heat Treatment
Understanding why you would heat treat a metal is the key to determining if it's necessary. The goals typically fall into one of two categories: enhancing final properties or improving manufacturability.
Enhancing Final Mechanical Properties
This is the most common reason for heat treatment. By carefully controlling heating and cooling cycles, you can fundamentally change the internal microstructure of the metal.
This allows you to precisely engineer properties like hardness, strength, toughness, and wear resistance to levels far beyond what the base material can offer. Applications like gears, bearings, and cutting tools depend on this enhancement.
Improving Manufacturability
Sometimes, heat treatment is an intermediate step used to make a part easier to manufacture. This process is not about the final properties, but about making the material workable.
For example, a metal alloy might be delivered in a state that is too hard to machine or bend. A process like annealing can be used to soften the material, making it easy to form.
Similarly, processes like welding or heavy machining introduce significant internal stresses into a part. A subsequent stress-relief heat treatment is necessary to relax these stresses, preventing distortion or cracking later in the part's life.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Specifying heat treatment is not a "free" upgrade. It introduces costs, risks, and complexity that must be weighed against its benefits.
The Cost Factor
Heat treatment requires specialized furnaces, precise controls, energy, and skilled labor. This adds a significant and direct cost to the final price of a component.
The Risk of Distortion
Heating and cooling metal, especially in complex shapes, can cause it to warp or distort. Managing this risk requires careful planning, proper fixturing, and often leaves extra material for final machining after treatment. In worst-case scenarios, improper heat treatment can cause the part to crack, rendering it scrap.
Added Process Complexity
Introducing a heat treatment step adds time and logistical complexity to your production workflow. It becomes another critical process that must be managed, validated, and inspected to ensure quality and consistency.
Making the Right Decision for Your Application
Use your specific goal to determine if heat treatment is the correct and necessary choice for your project.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and durability: Heat treatment is likely essential to achieve the required hardness, strength, and wear resistance for demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective manufacturing for low-stress parts: You can likely avoid heat treatment by selecting a material that meets all requirements in its as-supplied or "as-fabricated" state.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability after welding or heavy machining: A stress-relief heat treatment is a critical step to prevent long-term distortion or premature failure.
- If your primary focus is formability or machinability: An intermediate annealing treatment may be a necessary manufacturing step to make an otherwise unworkable material pliable.
By treating it as a precise engineering choice rather than a default step, you ensure optimal performance without unnecessary cost.
Summary Table:
| Scenario | Is Heat Treatment Necessary? | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Performance (Gears, Bearings) | Yes, Essential | Achieve final hardness, strength, wear resistance |
| Low-Stress, Cost-Effective Parts | No, Often Avoidable | Use material in as-supplied state |
| Post-Welding or Heavy Machining | Yes, Critical | Stress relief to prevent distortion/failure |
| Improving Machinability/Formability | Yes, as an Intermediate Step | Annealing to soften material for manufacturing |
Unsure if your project requires heat treatment?
Choosing the right path is critical for balancing performance, cost, and risk. The experts at KINTEK can help you analyze your specific application and material needs.
We specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables necessary for developing and validating heat treatment processes. Whether you're optimizing for ultimate strength or cost-effective manufacturing, our solutions support your R&D and quality control.
Contact KINTALK today to discuss your project and ensure you make the most efficient and effective decision for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control



















