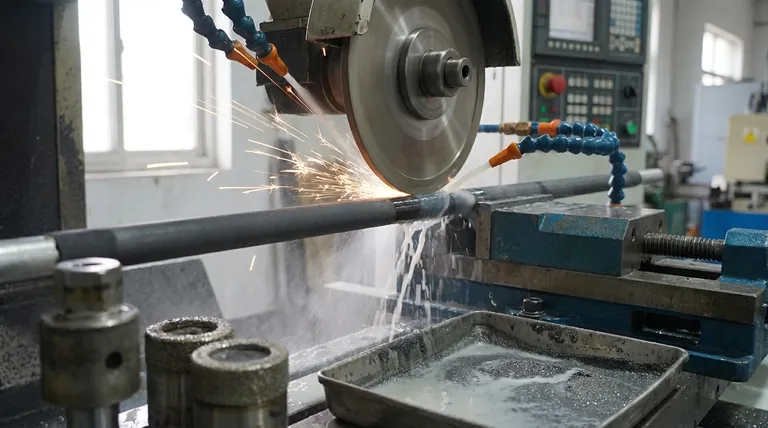
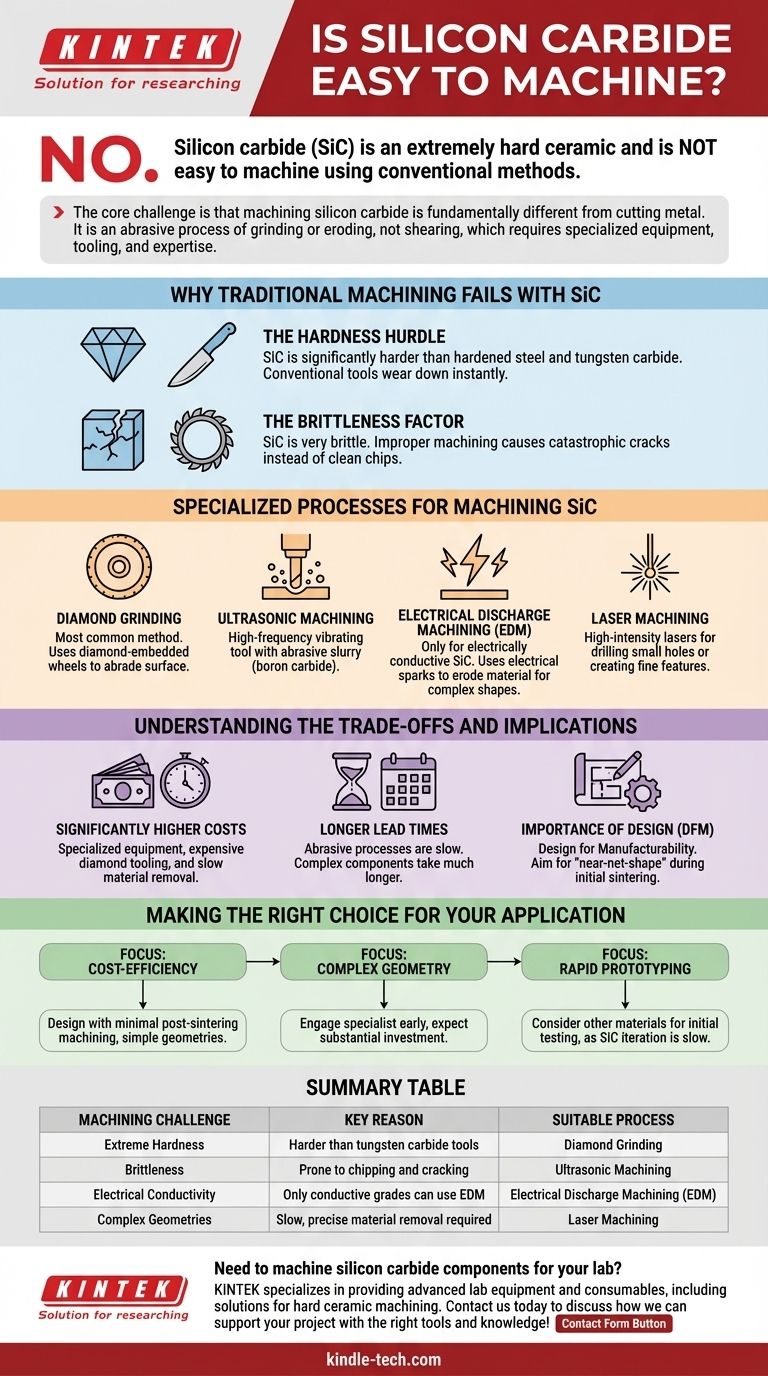
In short, no. Silicon carbide (SiC) is not easy to machine using conventional methods. Its exceptional hardness, which surpasses that of many standard cutting tool materials, makes it one of the most challenging materials to shape.
The core challenge is that machining silicon carbide is fundamentally different from cutting metal. It is an abrasive process of grinding or eroding, not shearing, which requires specialized equipment, tooling, and expertise.

Why Traditional Machining Fails with SiC
Silicon carbide's unique properties make standard machining techniques like milling or turning with steel tools ineffective and destructive. The difficulty stems from two primary material characteristics.
The Hardness Hurdle
Silicon carbide is an extremely hard ceramic. It is significantly harder than hardened steel and even tungsten carbide, a material commonly used for high-performance cutting tools.
Attempting to cut SiC with a conventional tool is like trying to cut a diamond with a steel knife. The tool will wear down almost instantly, generating immense heat and failing to remove material effectively.
The Brittleness Factor
Like many hard ceramics, SiC is also very brittle. This means it is prone to fracturing, chipping, and cracking under the stress of conventional cutting forces.
Instead of producing a clean chip as you would with metal, an improper machining attempt will likely cause catastrophic cracks in the workpiece, rendering the part useless.
The Specialized Processes for Machining SiC
Because of its hardness and brittleness, shaping silicon carbide relies on advanced, non-traditional machining methods. These processes focus on controlled material removal through abrasion or erosion.
Diamond Grinding
This is the most common method for machining SiC. It uses grinding wheels embedded with industrial diamonds—the only material significantly harder than silicon carbide—to slowly and precisely abrade the workpiece surface.
Ultrasonic Machining
This process uses a high-frequency vibrating tool to propel an abrasive slurry (containing particles like boron carbide) against the SiC surface. The repeated impact of these hard particles chips away at the material on a microscopic scale.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
EDM can be used, but only on electrically conductive grades of SiC. It uses a series of precisely controlled electrical sparks to erode the material, which is ideal for creating complex shapes that are difficult to achieve with grinding.
Laser Machining
High-intensity lasers can be used to ablate or vaporize material from the surface of the silicon carbide. This technique is often employed for drilling small holes or creating fine surface features.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Implications
Choosing silicon carbide for a component has significant downstream consequences for manufacturing. Understanding these is critical for project planning and budgeting.
Significantly Higher Costs
The specialized equipment, expensive diamond tooling, and slow material removal rates all contribute to much higher machining costs compared to metals or even other ceramics.
Longer Lead Times
Abrasive processes like diamond grinding are inherently slow. Machining a complex SiC component can take orders of magnitude longer than machining a similar part from aluminum or steel, leading to extended production timelines.
The Importance of Design
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) is paramount. To control costs and ensure success, parts should be designed to be as close to their final shape ("near-net-shape") as possible during the initial ceramic sintering process, minimizing the amount of material that needs to be removed later.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your approach to using silicon carbide should be guided by your project's specific priorities.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency: Design the component to require minimal post-sintering machining, focusing on simple geometries that can be achieved in the initial molding stage.
- If your primary focus is achieving complex geometry: Engage with a specialist in hard ceramic machining early in the design phase and be prepared for substantial investment in both cost and time.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping: Consider if another material can meet your initial testing needs, as iterating on SiC designs is a slow and expensive process.
Understanding these machining realities is the first step toward successfully engineering with this remarkable material.
Summary Table:
| Machining Challenge | Key Reason | Suitable Process |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Hardness | Harder than tungsten carbide tools | Diamond Grinding |
| Brittleness | Prone to chipping and cracking | Ultrasonic Machining |
| Electrical Conductivity | Only conductive grades can use EDM | Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) |
| Complex Geometries | Slow, precise material removal required | Laser Machining |
Need to machine silicon carbide components for your lab? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for hard ceramic machining. Our expertise ensures precise, efficient shaping of silicon carbide for your specific laboratory needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your project with the right tools and knowledge!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Hybrid High Energy Vibratory Ball Mill for Lab Use
- Open Type Two Roll Mixing Mill Machine for Rubber Crusher
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
People Also Ask
- What is a silicon carbide heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat for Industrial Processes
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- What is SiC melting point? Discover the Extreme Thermal Stability of Silicon Carbide
- What kind of metal is used in heating elements? A Guide to Materials for Every Temperature & Atmosphere
- What is SiC elements? The Ultimate High-Temperature Heating Solution



















