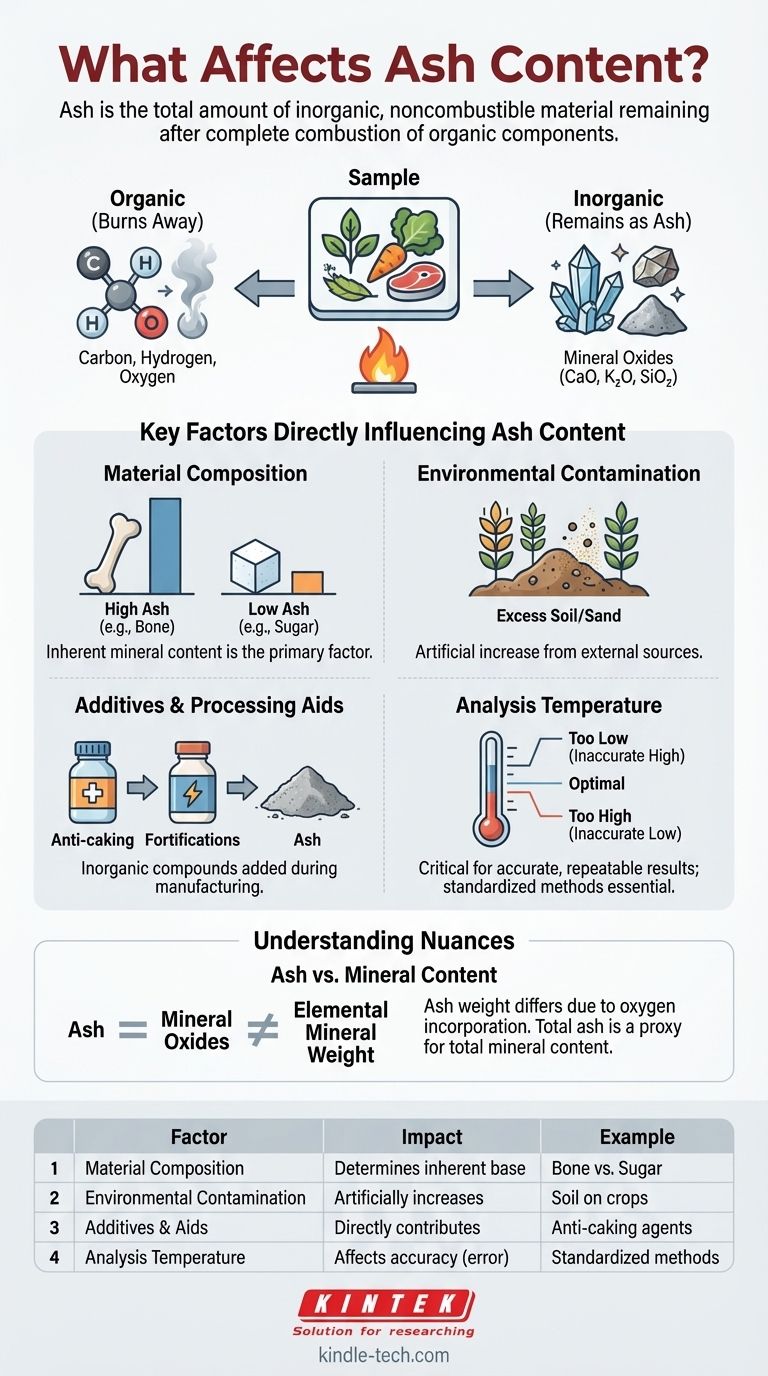
At its core, ash content is determined by the total amount of inorganic, noncombustible material present in a sample. When a substance is completely burned, all the organic components (like carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen) are driven off, leaving behind a residue of inorganic minerals and salts.
Ash is not simply what's left after burning; it is the direct quantitative measure of a material's mineral and inorganic composition. Understanding what affects it requires looking at the fundamental makeup of the original substance, not just the combustion process.

What is Ash? A Foundational Understanding
To control or interpret ash content, you must first understand what it represents chemically. It's a window into the non-organic portion of any material.
From Organic to Inorganic
Most materials, from food to fuel, are primarily organic, meaning they are built around carbon-based molecules. The process of ashing uses high heat to completely oxidize and remove these organic structures.
What remains is the inorganic fraction. This material does not burn away and is left behind as the final ash.
The Chemical Nature of Ash
The reference states that ash typically consists of oxides of inorganic elements. During combustion, elements like calcium, potassium, magnesium, and silicon react with oxygen.
Therefore, the ash you measure is not pure elemental mineral but rather a mixture of mineral oxides, such as calcium oxide (CaO), potassium oxide (K₂O), and silicon dioxide (SiO₂).
Key Factors That Directly Influence Ash Content
Several factors contribute to the final ash percentage of a sample. These can be intrinsic to the material or introduced from external sources.
The Original Material's Composition
This is the most significant factor. A material's inherent mineral content dictates its potential ash content. For example, bone has a very high mineral content (primarily calcium phosphate) and will thus produce a high ash percentage.
In contrast, a highly purified organic substance like sugar contains virtually no inorganic elements and will have an ash content near zero. Plant materials like wood or grains fall in between, with ash content reflecting the minerals they absorbed from the soil.
Environmental Contamination
External, inorganic materials can be unintentionally added to a sample, artificially inflating its ash content. This is a critical factor in agriculture and food production.
For instance, crops harvested with excess soil or sand will show a higher ash content. This "extraneous ash" is often an indicator of poor handling or contamination, not nutritional mineral content.
Additives and Processing Aids
In manufactured products, inorganic compounds are often added for specific functions. These will directly contribute to the final measured ash.
Common examples include anti-caking agents in powders (like silicon dioxide), mineral fortifications in food (like calcium carbonate), or catalysts used in chemical production.
Understanding the Nuances and Limitations
Measuring ash seems straightforward, but interpreting the results requires understanding the trade-offs and potential for error in the analysis itself.
The Impact of Analysis Temperature
The temperature used for ashing is critical for accurate and repeatable results. Standard methods define precise temperatures for this reason.
If the temperature is too low, some inorganic compounds (like carbonates) may not fully decompose, leading to an inaccurately high ash value. If it's too high, some minerals can volatilize and be lost, leading to an inaccurately low value.
"Ash" vs. "Mineral Content"
It is a common mistake to use these terms interchangeably. Ash is the total inorganic residue after incineration. Mineral content refers to the amount of specific elemental minerals.
Because ash consists of mineral oxides, its weight is different from the original elemental mineral weight. However, total ash is often used as a practical and fast proxy for total mineral content.
The Limitation of "Total Ash"
A total ash measurement gives you a single number—it does not tell you about the composition of that ash. For many applications, this distinction is vital.
High ash in a food product could mean it's rich in beneficial minerals like calcium and magnesium, or it could mean it's contaminated with sand. Further analysis is required to determine the specific mineral profile.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your reason for measuring ash will determine which factors are most important to you.
- If your primary focus is food or feed quality: Consider ash a primary indicator of both nutritional mineral content and potential contamination from soil or sand.
- If your primary focus is biofuel evaluation: View low ash content as a critical quality parameter, as high ash can lead to slagging, fouling, and damage in combustion systems.
- If your primary focus is general laboratory analysis: Recognize that strict adherence to standardized methods, particularly temperature and duration, is non-negotiable for producing comparable and accurate data.
Understanding ash content is about understanding the fundamental inorganic fingerprint of your material.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Ash Content | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Determines the inherent mineral base | Bone (high ash) vs. Sugar (near-zero ash) |
| Environmental Contamination | Artificially increases ash value | Soil or sand on harvested crops |
| Additives & Processing Aids | Directly contributes to inorganic residue | Anti-caking agents (e.g., silicon dioxide) |
| Analysis Temperature | Affects accuracy; too low/high causes errors | Standardized methods ensure reliable results |
Need precise ash content analysis for your materials? Understanding the factors that influence ash is critical for quality control in food, fuel, and laboratory settings. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables for accurate ashing and material testing. Let our expertise enhance your analytical results—contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and find the right solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the critical function of a high-temperature furnace in MEC carbon brush preparation? Optimize Bio-Anode Surface
- How does a high-temperature box resistance furnace assist in PBF annealing? Optimize Stress Relief and Microstructure
- What is the purpose of using heating equipment for annealing Li2OHBr-coated LAGP? Enhance Solid Electrolyte Performance
- What is a furnace used in a chemistry lab? A Guide to High-Temperature Material Transformation
- What is the significance of the precision roasting in niobate studies? Achieve Pure Crystal Structure Transitions
- What is the purpose of ash content determination? A Key to Quality, Purity, and Nutrition
- What is the temperature range of a laboratory muffle furnace? Find the Right Model for Your Application
- What is the use of muffle furnace in food laboratory? Essential for Accurate Nutritional Analysis & Quality Control



















