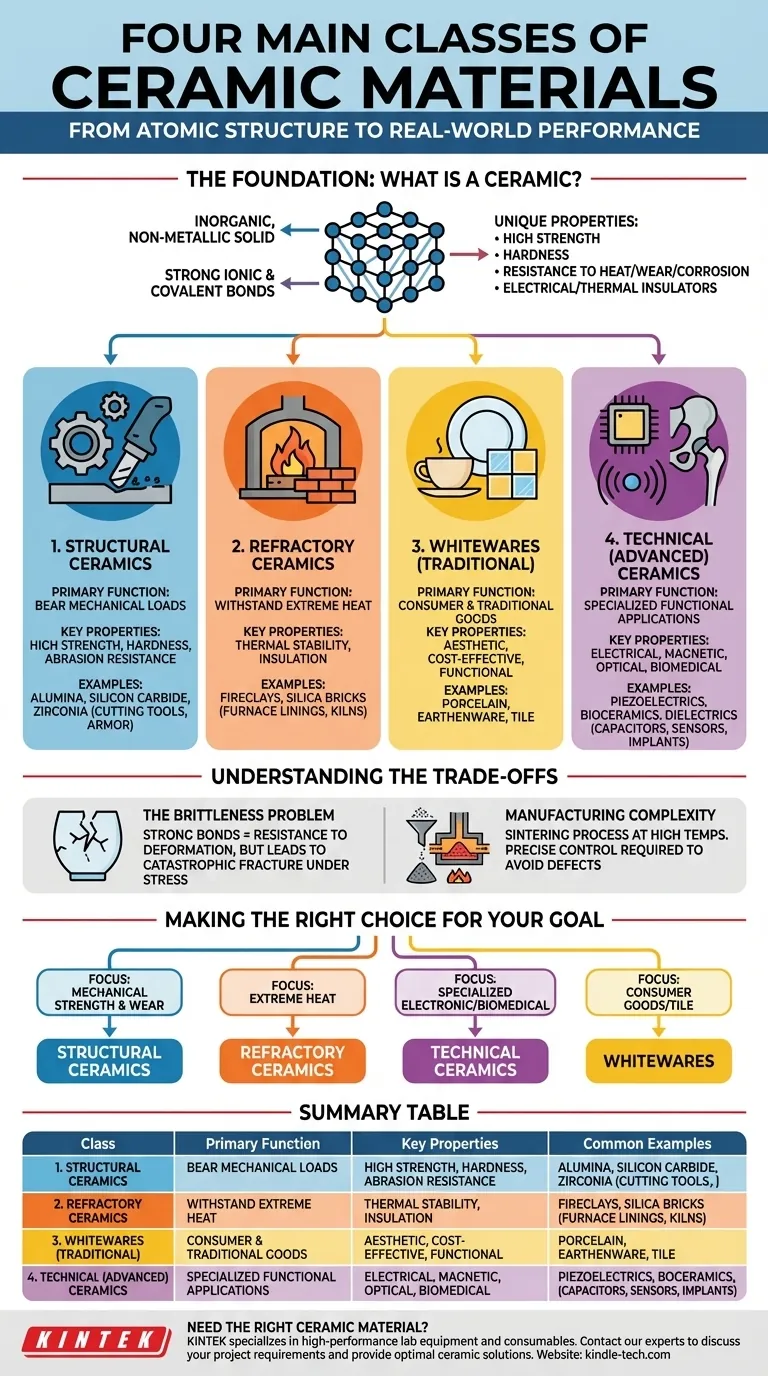
At their core, ceramic materials are generally categorized into four main classes: structural ceramics, refractory ceramics, whitewares, and technical (or advanced) ceramics. These classifications are based on their composition and, more importantly, their intended function and dominant properties.
The classification of ceramics is not merely academic; it provides a direct map from a material's fundamental composition and atomic structure to its real-world performance in applications ranging from engine components to high-temperature furnace linings.

The Foundation: What Is a Ceramic?
An Inorganic, Non-Metallic Solid
A ceramic is an inorganic, non-metallic material. This distinguishes it from the other two major material classes: metals and polymers.
The atoms within a ceramic are held together by extremely strong chemical bonds, primarily ionic and covalent bonds. This is the key to their unique set of properties.
The Source of Ceramic Properties
These powerful atomic bonds give ceramics their characteristic traits mentioned in advanced applications: high strength, exceptional hardness, and resistance to heat, wear, and corrosion. Unlike metals, they do not have free-floating electrons, which makes them excellent electrical and thermal insulators.
The Four Primary Classes of Ceramics
While there are many sub-categories, most ceramics fall into one of four functional groups.
1. Structural Ceramics
Structural ceramics are engineered for applications where high strength, hardness, and abrasion resistance are the primary requirements. They are designed to bear significant mechanical loads.
Common examples include alumina (aluminum oxide), silicon carbide, and zirconia, which are used for cutting tools, industrial wear parts, and even armor.
2. Refractory Ceramics
Refractories are defined by their ability to withstand extreme temperatures without degrading. Their main purpose is thermal containment and insulation.
These materials, such as fireclays and silica bricks, are the essential lining for high-temperature furnaces, kilns, and reactors used in manufacturing steel, glass, and cement.
3. Whitewares (Traditional Ceramics)
Whitewares are the most traditional class of ceramics, including materials like earthenware, porcelain, and stoneware. They are primarily composed of clay, feldspar, and quartz.
Their applications are widespread in consumer goods, from pottery and dinnerware to wall tiles and sanitaryware. Aesthetics and cost are often as important as their functional properties.
4. Technical (Advanced) Ceramics
This is a broad category of ceramics developed for specific functional applications, often electrical, magnetic, optical, or biomedical.
This class includes everything from the dielectric materials in capacitors to the piezoelectric sensors in sonar systems and the biocompatible ceramics used in medical implants. Their composition is highly controlled to achieve a specific performance target.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Brittleness Problem
The primary trade-off for a ceramic's incredible hardness and strength is its brittleness. The same strong atomic bonds that resist deformation also prevent the material from yielding under stress.
Instead of bending like a metal, a ceramic will fracture catastrophically once its elastic limit is exceeded. This is the single most important design consideration when working with ceramics.
Manufacturing Complexity
Ceramics are typically processed from powders at very high temperatures in a process called sintering. This can make manufacturing complex shapes difficult and expensive compared to casting metals or molding plastics.
Achieving consistent, defect-free parts requires precise control over the entire manufacturing process, as even microscopic flaws can lead to premature failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting a ceramic, your primary application will guide you to the correct class.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and wear resistance: Your starting point is the class of structural ceramics like alumina or silicon carbide.
- If your primary focus is withstanding extreme heat: You need to investigate refractory ceramics designed specifically for thermal stability.
- If your primary focus is a specialized electronic or biomedical function: You should explore the vast world of technical ceramics to find a material with the precise properties required.
- If your primary focus is on consumer goods, tile, or sanitaryware: The materials and processes of the whitewares class are most relevant.
Understanding these fundamental classes empowers you to navigate the world of ceramics and select materials based on their core purpose and capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Class | Primary Function | Key Properties | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structural Ceramics | Bear mechanical loads | High strength, hardness, wear resistance | Alumina, Silicon Carbide, Zirconia |
| Refractory Ceramics | Withstand extreme heat | Excellent thermal stability, insulation | Fireclays, Silica Bricks |
| Whitewares | Consumer & traditional goods | Aesthetic, cost-effective, functional | Porcelain, Earthenware, Tile |
| Technical Ceramics | Specialized functional applications | Electrical, magnetic, optical, biomedical | Piezoelectrics, Bioceramics, Dielectrics |
Need the right ceramic material for your specific application?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, serving diverse laboratory needs. Whether you require durable structural components, high-temperature furnace linings (refractories), or specialized technical ceramics for advanced research, our expertise can help you select the optimal material for superior performance and reliability.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK can provide the ceramic solutions you need.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can ceramic withstand high heat? Understanding the Limits of Thermal Stability
- What is the overview of ceramics? Unlocking the Potential of Advanced Materials
- What are alloys in simple words? Unlock the Power of Engineered Materials
- What is the strongest zirconia phase? Tetragonal Zirconia Offers Unmatched Toughness
- Which ceramic materials are most widely used? A Guide to Alumina, Zirconia, SiC, and Si3N4



















