At its core, Chemical Vapour Deposition (CVD) is a highly versatile process capable of producing exceptionally pure, durable, and uniform coatings on even the most complex surfaces. Its main advantages stem from its chemical nature, which allows for precise control over material properties, while its disadvantages are rooted in the practical constraints of its high-temperature requirements and complex precursor chemistry.
The central trade-off of CVD is choosing between superior coating quality and versatility versus significant process limitations. It excels at creating high-performance films on complex, heat-tolerant objects but is often impractical for temperature-sensitive materials or large-scale, on-site applications.

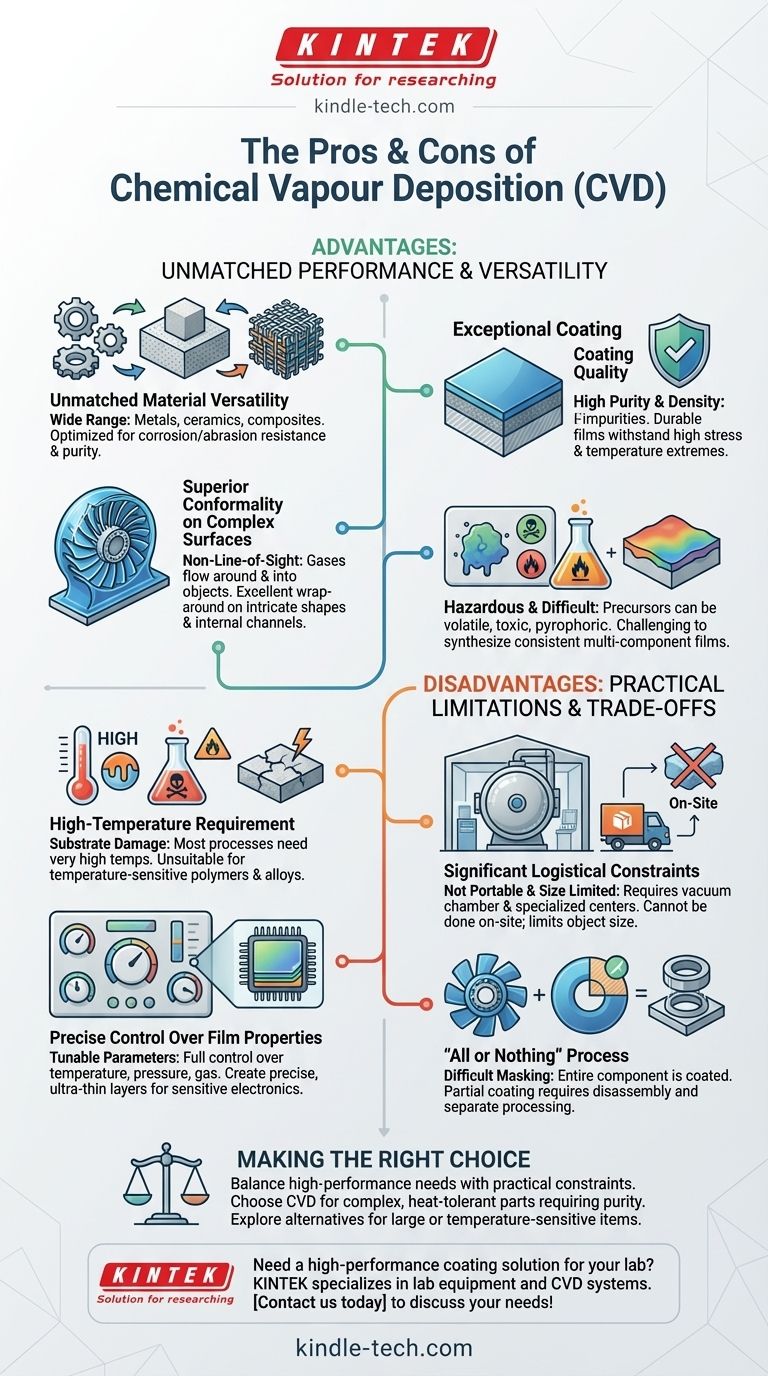
The Core Strengths of Chemical Vapour Deposition
The power of CVD comes from its fundamental approach: building a solid material layer-by-layer from chemical precursors in a gas phase. This "bottom-up" construction gives it several distinct advantages over other coating methods.
Unmatched Versatility of Materials
Because the process is driven by chemical reactions, CVD can be used to deposit an incredibly wide range of materials. This includes metals, ceramics, and various composites.
This allows engineers to select gases optimized for specific performance characteristics, such as exceptional corrosion resistance, high abrasion resistance, or extreme purity.
Exceptional Coating Quality
CVD produces films that are highly pure and dense. The controlled reaction environment minimizes impurities, resulting in coatings with superior performance.
These coatings are known for being extremely durable and can withstand high-stress environments and extreme temperature variations without degrading.
Superior Conformality on Complex Surfaces
CVD is a non-line-of-sight process. The precursor gases flow around and into an object, reacting on all exposed surfaces.
This gives it an excellent "wrap-around" capability, ensuring a perfectly uniform and even coating on components with intricate shapes, internal channels, or complex geometries where spray-on methods would fail.
Precise Control Over Film Properties
Technicians have full control over the process parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and gas composition.
This allows for the precise creation of ultra-thin layers, a critical capability for manufacturing sensitive products like electrical circuits and semiconductors.
Understanding the Practical Limitations and Trade-offs
While powerful, the CVD process introduces significant logistical and chemical challenges that make it unsuitable for certain applications. These limitations must be carefully considered.
The High-Temperature Requirement
Most CVD processes are performed at very high temperatures. This can be a major problem when working with substrates that have low melting points or can be damaged by thermal stress.
This single factor often disqualifies CVD as an option for coating certain polymers, alloys, or other temperature-sensitive materials.
Complexity of Precursor Chemistry
Finding suitable chemical precursors can be challenging. Many are volatile, toxic, or pyrophoric (ignite spontaneously in air), which requires specialized handling and safety protocols.
Furthermore, synthesizing films with multiple components is difficult. Different precursors have different vapor pressures and reaction rates, which can lead to a heterogeneous and inconsistent final composition.
Significant Logistical Constraints
CVD is not a portable technology; it cannot be performed on-site. Parts must be shipped to a specialized coating center.
The process also requires a vacuum chamber, and the size of this chamber limits the maximum size of the object that can be coated. For very large surfaces, this is a prohibitive constraint.
The "All or Nothing" Process
It is very difficult to mask off areas and create a partial coating with CVD. The process is typically all-encompassing, meaning the entire component inside the chamber gets coated.
To coat individual components of an assembly, the entire product must be broken down, coated separately, and then reassembled.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the decision to use CVD depends entirely on balancing the need for a high-performance coating against the practical constraints of the process.
- If your primary focus is performance on complex parts: CVD is an excellent choice for creating highly pure, uniform, and durable coatings on heat-tolerant components with intricate shapes.
- If your primary focus is coating large or temperature-sensitive items: You should explore alternative methods, as CVD's high temperatures and chamber size limitations are likely prohibitive.
- If your primary focus is cost and logistical simplicity: The need to ship parts to an off-site facility and handle complex chemicals may make other coating processes more attractive.
Choosing the right deposition technique requires a clear understanding of your material's limits and your project's ultimate goal.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Quality | High purity, dense, durable films | Requires very high temperatures |
| Versatility | Wide range of materials (metals, ceramics) | Complex, often toxic precursor chemistry |
| Uniformity | Excellent conformality on complex shapes | Limited to chamber size; not portable |
| Control | Precise layer thickness and properties | Difficult to mask; entire part gets coated |
Need a high-performance coating solution for your lab? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including CVD systems designed for superior material deposition. Whether you're working with complex components or require precise film properties, our expertise ensures you get durable, uniform coatings tailored to your research or production needs. Contact us today to discuss how our CVD solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is plasma in CVD process? Lowering Deposition Temperatures for Heat-Sensitive Materials
- What is the difference between CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is meant by vapor deposition? A Guide to Atomic-Level Coating Technology
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films



















