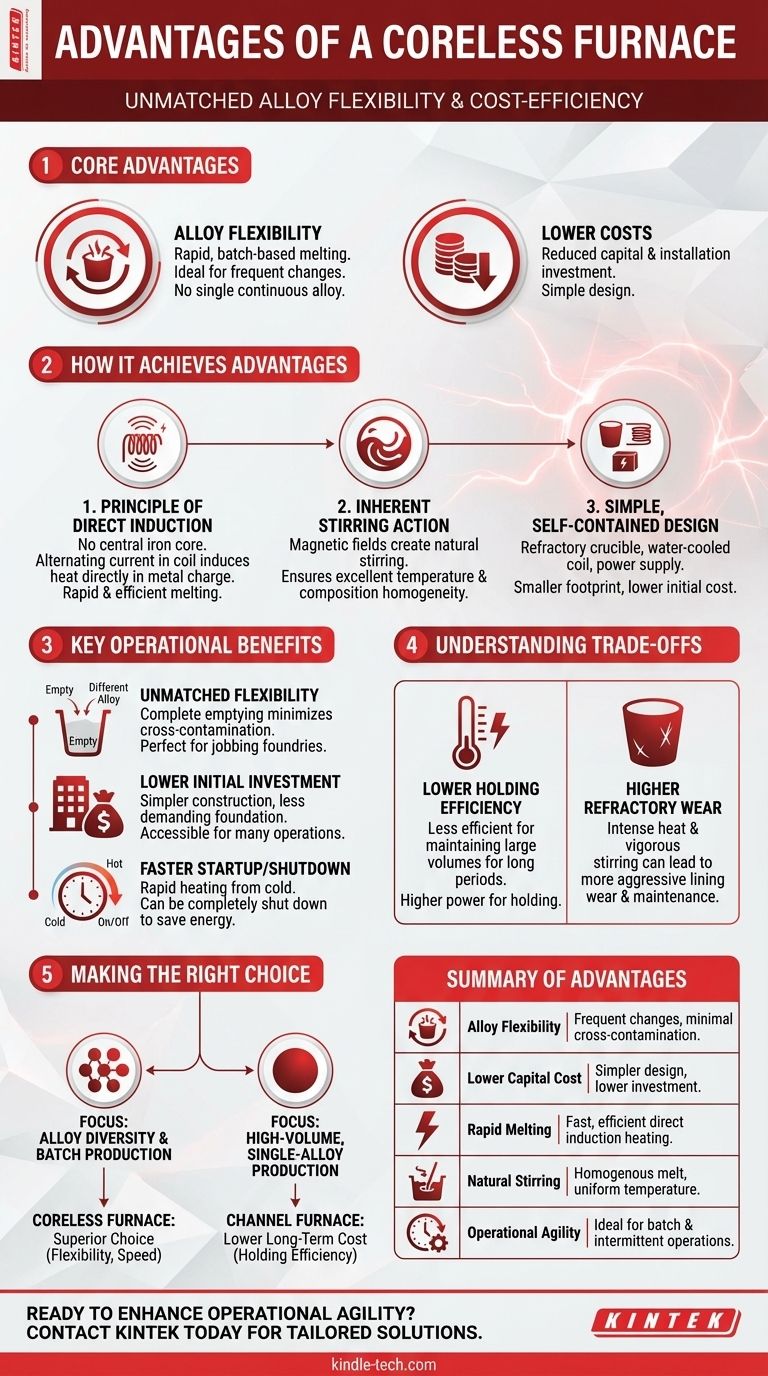
At its core, the primary advantages of a coreless furnace are its exceptional alloy flexibility and significantly lower capital and installation costs. This design allows for rapid melting and frequent changes in the type of metal being processed, making it ideal for operations that do not produce a single, continuous alloy.
A coreless furnace excels in environments requiring operational agility and frequent alloy changes. Its fundamental design prioritizes rapid, batch-based melting over the long-term, high-volume holding capacity of alternative designs like the channel furnace.

How a Coreless Furnace Achieves Its Advantages
A coreless induction furnace's benefits stem directly from its straightforward and efficient design. It operates by generating a powerful magnetic field within a primary coil, which in turn induces a strong electrical current directly into the metal charge placed inside a crucible.
The Principle of Direct Induction
The furnace is "coreless" because it lacks a central iron core to link the coil and the metal. Instead, the alternating current in the copper coil induces heat directly within the metallic charge itself.
This direct heating method is extremely rapid and efficient for melting solid metal.
Inherent Stirring Action
The powerful magnetic fields create a natural and vigorous stirring motion within the molten metal bath. This ensures excellent temperature uniformity and helps create a highly homogenous alloy composition without mechanical mixers.
A Simple, Self-Contained Design
The furnace consists of a few primary components: a refractory-lined crucible, a water-cooled copper coil, and a power supply. This relative simplicity contributes directly to its lower initial cost and often smaller physical footprint compared to more complex systems.
Key Operational Benefits Explained
The design of a coreless furnace translates into distinct operational advantages, particularly for foundries with diverse or intermittent production schedules.
Unmatched Alloy Flexibility
Because the crucible can be completely emptied after each melt, there is minimal risk of cross-contamination between different alloys. An operator can melt a batch of steel, empty the furnace, and then melt a batch of a different alloy shortly after.
This makes it the furnace of choice for jobbing foundries and research facilities.
Lower Initial Investment
Coreless furnaces typically have significantly lower capital and installation costs than channel furnaces. Their simpler construction and less demanding foundation requirements make them more accessible for a wide range of operations.
Faster Startup and Shutdown
A coreless furnace can be started from a cold state and brought to operating temperature quickly. It can also be completely shut down when not in use, saving considerable energy. This is a major benefit for operations that do not run 24/7.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single technology is superior for all applications. The advantages of a coreless furnace come with specific limitations that must be understood.
Lower Efficiency for Holding
While excellent for melting, a coreless furnace is less energy-efficient for holding large volumes of molten metal at a specific temperature for extended periods. The power required to maintain temperature is higher than that of a channel furnace designed for this purpose.
Higher Refractory Wear
The intense, direct heating and vigorous stirring action can lead to more aggressive wear on the refractory lining of the crucible. This can result in more frequent maintenance cycles and relining costs compared to the gentler heating in other furnace types.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Choosing the right furnace technology depends entirely on your specific production demands and business model.
- If your primary focus is alloy diversity and batch production: The coreless furnace is the superior choice due to its flexibility, fast startup, and ability to be completely emptied between melts.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, single-alloy production: A channel furnace's efficiency in holding large quantities of molten metal for extended periods will likely offer a lower long-term operational cost.
Ultimately, understanding your specific melting, holding, and alloy requirements is the key to leveraging the right technology for maximum efficiency and return on investment.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Alloy Flexibility | Can be completely emptied between melts, allowing for frequent alloy changes with minimal cross-contamination. |
| Lower Capital Cost | Simpler design and less demanding installation requirements lead to a significantly lower initial investment. |
| Rapid Melting | Direct induction heating provides fast and efficient melting from a cold start. |
| Natural Stirring | Magnetic fields create a homogenous melt, ensuring excellent temperature and composition uniformity. |
| Operational Agility | Ideal for batch production and operations that do not require 24/7, continuous melting. |
Ready to enhance your foundry's operational agility?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right lab and industrial equipment to meet your specific melting needs. Whether you're a jobbing foundry requiring alloy flexibility or a research facility needing rapid batch processing, our coreless furnace solutions are designed for superior performance and cost-efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK coreless furnace can optimize your melting process and deliver a faster return on investment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting



















