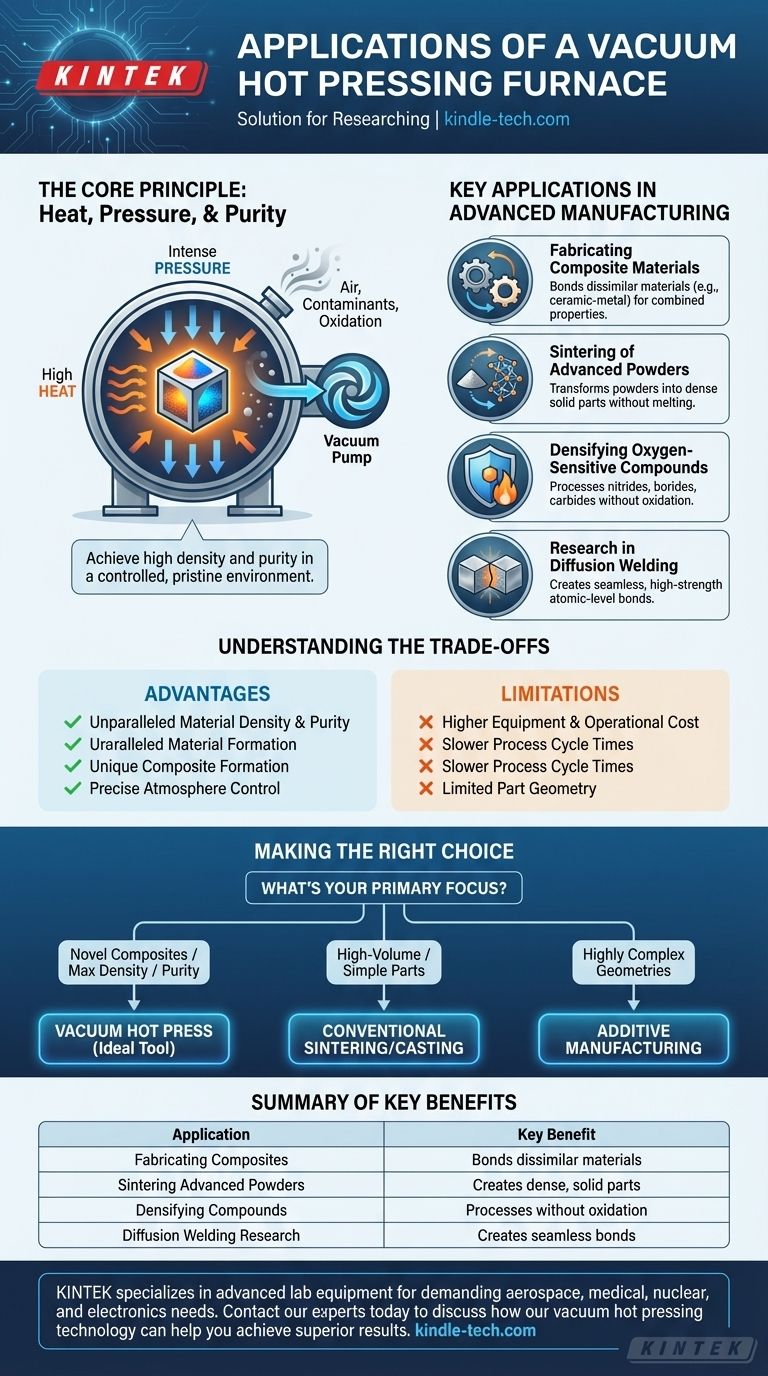
At its core, a vacuum hot pressing furnace is a specialized tool used for the densification and sintering of advanced materials. Its primary applications include creating high-performance metal and ceramic powders, fabricating ceramic-metal composites and intermetallic compounds, developing diffusion welding processes, and densifying oxygen-sensitive compounds like nitrides, borides, and carbides.
The essential value of a vacuum hot pressing furnace is its unique ability to apply high heat and intense pressure simultaneously within a pristine, controlled atmosphere. This combination is critical for producing highly dense, pure, and advanced materials that cannot be fabricated using conventional methods where air and other contaminants would ruin the final product.
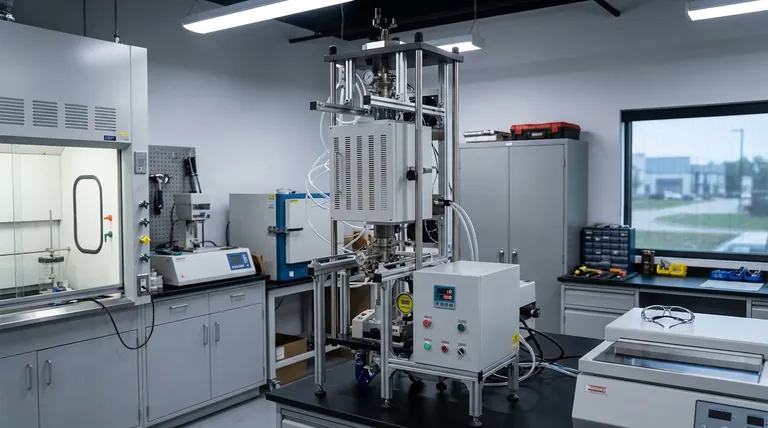

The Core Principle: Heat, Pressure, and Purity
A vacuum hot press furnace isn't just a high-temperature oven; it's a complete system that manipulates a material's environment to achieve specific properties. Understanding its three core functions explains why it is used for such demanding applications.
How It Works
The process involves placing a material, often in powder form, into a die within the furnace. The chamber is sealed, and a powerful vacuum system removes all the air and other atmospheric gases. Once the vacuum is established, the material is heated to very high temperatures while a hydraulic system applies immense pressure.
Eliminating Contamination and Oxidation
The vacuum environment is the most critical feature. By removing oxygen, the furnace completely prevents oxidation, which would otherwise occur when heating metals and other reactive materials to high temperatures. This process also pulls out other gaseous byproducts from the material, resulting in a higher-purity end product.
Achieving Full Densification
While heat helps bond material particles together (sintering), the addition of pressure mechanically forces them closer. This action collapses the microscopic voids between particles, leading to a final product that is extremely dense, strong, and non-porous.
Key Applications in Advanced Manufacturing
The furnace's unique capabilities make it indispensable in industries like aerospace, medical, nuclear, and advanced electronics, where material performance is paramount.
Fabricating Composite Materials
The furnace excels at creating ceramic-metal composites. The controlled environment allows for the bonding of dissimilar materials that would otherwise be difficult to join, creating new materials with combined properties like high strength and heat resistance.
Sintering of Advanced Powders
It is used to transform metal and ceramic powders into solid, dense parts without melting them. This is crucial for materials with extremely high melting points or for creating specific microstructures that melting would destroy.
Densifying Oxygen-Sensitive Compounds
Materials like nitrides, borides, and carbides are essential for cutting tools and high-wear components. These compounds react aggressively with oxygen at high temperatures, making the vacuum environment of a hot press the only viable method for their densification.
Research in Diffusion Welding
The pristine, high-pressure environment is ideal for diffusion welding, a solid-state joining process. It allows researchers to bond materials at an atomic level, creating seamless joints with strength equal to the parent material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a vacuum hot press furnace is not the right tool for every job. Its specialized nature comes with specific limitations.
Higher Equipment and Operational Cost
These furnaces are complex systems involving integrated vacuum, hydraulic, and cooling units. This complexity results in a significantly higher initial investment and operational cost compared to standard atmospheric furnaces.
Slower Process Cycle Times
Achieving a deep vacuum, heating, pressing, and cooling takes more time than conventional processes. This makes it less suitable for high-volume, low-cost manufacturing.
Limitations on Part Geometry
The material must be contained within a die set to be pressed. This inherently limits the size and geometric complexity of the parts that can be produced, unlike more flexible methods such as additive manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting this technology depends entirely on whether your material's final properties justify the process complexity and cost.
- If your primary focus is creating novel composites or bonding dissimilar materials: A vacuum hot press is the ideal tool, as its pressure and clean environment facilitate superior bonding.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density in oxygen-sensitive ceramics or metals: The combination of pressure and vacuum is essential for eliminating porosity without causing chemical reactions.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of simple metal parts: Conventional sintering, casting, or metal injection molding are likely far more cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is fabricating parts with highly complex geometries: Additive manufacturing is a better choice, though a vacuum furnace may be used afterward for densification.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum hot press is a strategic decision for applications where material purity, density, and performance are non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Fabricating Composites | Bonds dissimilar materials like ceramics & metals |
| Sintering Advanced Powders | Creates dense, solid parts without melting |
| Densifying Oxygen-Sensitive Compounds | Processes nitrides, borides & carbides without oxidation |
| Diffusion Welding Research | Creates seamless, high-strength atomic-level bonds |
Need to develop high-purity, high-density materials for your research or production?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment, including vacuum hot pressing furnaces, to meet the demanding needs of laboratories in aerospace, medical, nuclear, and electronics. Our solutions are designed for applications where material performance is critical.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our vacuum hot pressing technology can help you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- Is sintering the same as hot press? Unlock the Key Differences for Better Material Performance
- Why is precise pressure regulation in a vacuum hot pressing furnace necessary? Optimize Ti/Ti-Al Composite Synthesis
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot-press furnace? Superior Bonding for Diamond/Aluminum Composites
- Why does the high-temperature sealing process for inorganic-carbonate dual-phase membranes require a heating furnace with precise temperature control? Ensure Leak-Free Bonds.
- What is pressure-assisted sintering process? Achieve Higher Density and Strength in Less Time



















