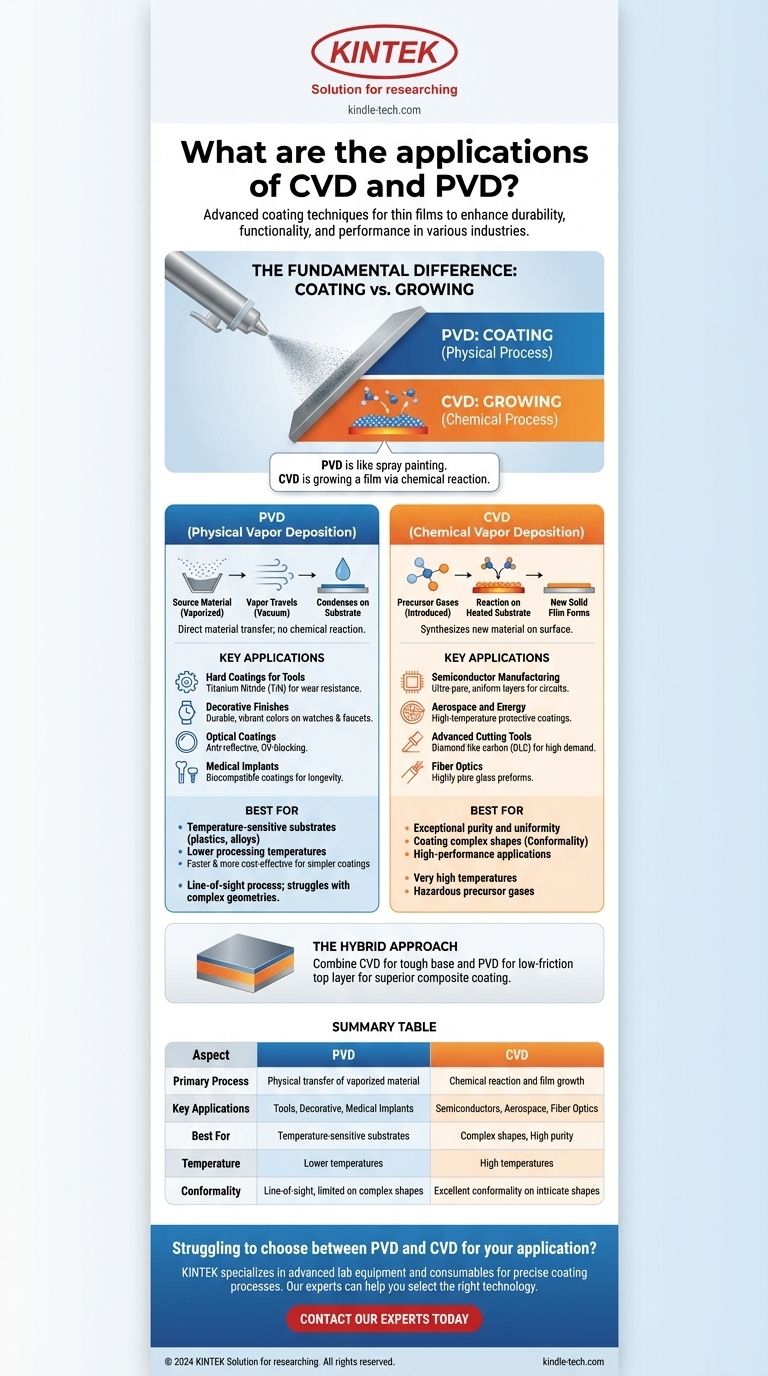
At their core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) are advanced coating techniques used to apply extremely thin films of material onto a surface. They are critical in industries ranging from semiconductors and aerospace to medical devices, where they are used to enhance a product's durability, functionality, and performance.
The essential difference guiding their applications is how the film is created. PVD is a physical process that "coats" a surface, much like spray painting, while CVD is a chemical process that "grows" a film directly on the surface through a reaction.

The Fundamental Difference: Coating vs. Growing
To understand the specific applications of PVD and CVD, you must first grasp the fundamental distinction between them. This difference in process dictates the properties of the final coating and, therefore, its ideal use.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): A Physical Process
In PVD, a solid source material is vaporized in a vacuum chamber through methods like sputtering or thermal evaporation. This vapor then travels in a straight line and condenses onto the target substrate, forming a thin, solid film.
Because no chemical reaction occurs, PVD is a direct transfer of material from a source to a surface.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): A Chemical Process
CVD involves introducing one or more volatile precursor gases into a reaction chamber. These gases decompose and react on the heated substrate's surface, creating a new solid material that forms the desired film.
This process doesn't transfer an existing material; it synthesizes a new one directly on the component.
Key Applications by Technique
The distinct natures of PVD and CVD make them suitable for very different, though sometimes overlapping, applications. The choice depends entirely on the desired properties of the final film.
Common Applications of PVD
PVD is often favored for its lower processing temperatures and its ability to deposit a wide variety of metals, alloys, and ceramics.
- Hard Coatings for Tools: Applying materials like Titanium Nitride (TiN) to cutting tools, drills, and molds dramatically increases wear resistance and reduces friction.
- Decorative Finishes: PVD creates the durable, vibrant metallic finishes found on watches, faucets, and door hardware, offering a finish that is far more resilient than traditional plating.
- Optical Coatings: Thin layers are applied to lenses, glasses, and solar cells to create anti-reflective, UV-blocking, or mirrored surfaces.
- Medical Implants: Biocompatible coatings are applied to implants like artificial joints or pacemakers to improve their longevity and integration with the body.
Common Applications of CVD
CVD excels where exceptional purity, uniformity, and the ability to coat complex shapes are paramount.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: This is a primary application. CVD is used to deposit the ultra-pure, perfectly uniform layers of silicon, silicon dioxide, and other materials required to build integrated circuits.
- Aerospace and Energy: High-temperature protective coatings are grown on turbine blades and engine components to protect them from extreme heat and corrosion.
- Advanced Cutting Tools: CVD can create exceptionally hard and thick coatings, such as diamond-like carbon (DLC), providing unparalleled performance for high-demand machining.
- Fiber Optics: The process is used to create the highly pure glass preforms from which optical fibers are drawn.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technique is universally superior. The selection process involves a careful analysis of the project's specific requirements.
When to Choose PVD
PVD is generally the better option when working with temperature-sensitive substrates, such as plastics or certain metal alloys, due to its significantly lower operating temperatures. It is also often faster and more cost-effective for simpler coating requirements.
However, PVD is a "line-of-sight" process, meaning it can struggle to coat complex internal geometries or heavily textured surfaces evenly.
When to Choose CVD
CVD's major advantage is its conformality. Because the film is grown from a gas, it can evenly coat intricate and complex shapes, inside and out. The process also produces films of extremely high purity and structural uniformity, which is non-negotiable for electronics.
The main drawbacks are the very high temperatures required, which can damage many substrates, and the often hazardous and expensive nature of the precursor gases.
The Hybrid Approach
In high-performance applications, the two techniques can be combined. A component might receive a tough, adhesive base layer via CVD, followed by a low-friction top layer via PVD, leveraging the strengths of both methods to create a superior composite coating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be driven by the most critical property your application demands.
- If your primary focus is high purity and uniformity for electronics: CVD is the industry standard for its ability to grow flawless crystalline films.
- If your primary focus is a hard, wear-resistant coating on a heat-sensitive part: PVD is the logical choice due to its lower processing temperatures.
- If your primary focus is evenly coating a complex shape: CVD's gas-phase deposition provides superior conformal coverage that PVD cannot match.
- If your primary focus is a decorative metallic finish: PVD offers a wide palette of colors and is highly effective for these applications.
Understanding the core distinction between these physical and chemical processes empowers you to select the precise method for enhancing your material's performance.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Process | Physical transfer of vaporized material | Chemical reaction and film growth on the surface |
| Key Applications | Hard tool coatings, decorative finishes, medical implants | Semiconductor manufacturing, aerospace coatings, fiber optics |
| Best For | Temperature-sensitive substrates, line-of-sight surfaces | Complex shapes, high purity, and uniform coatings |
| Temperature Range | Lower temperatures | High temperatures |
| Coating Conformality | Line-of-sight, may struggle with complex geometries | Excellent conformality, even on intricate shapes |
Struggling to choose between PVD and CVD for your application? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise coating processes. Whether you're developing cutting tools, medical implants, or semiconductor components, our expertise can help you select the right technology to enhance durability, functionality, and performance. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can drive your project's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is diamond coating made? A Guide to CVD and PVD Methods
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















