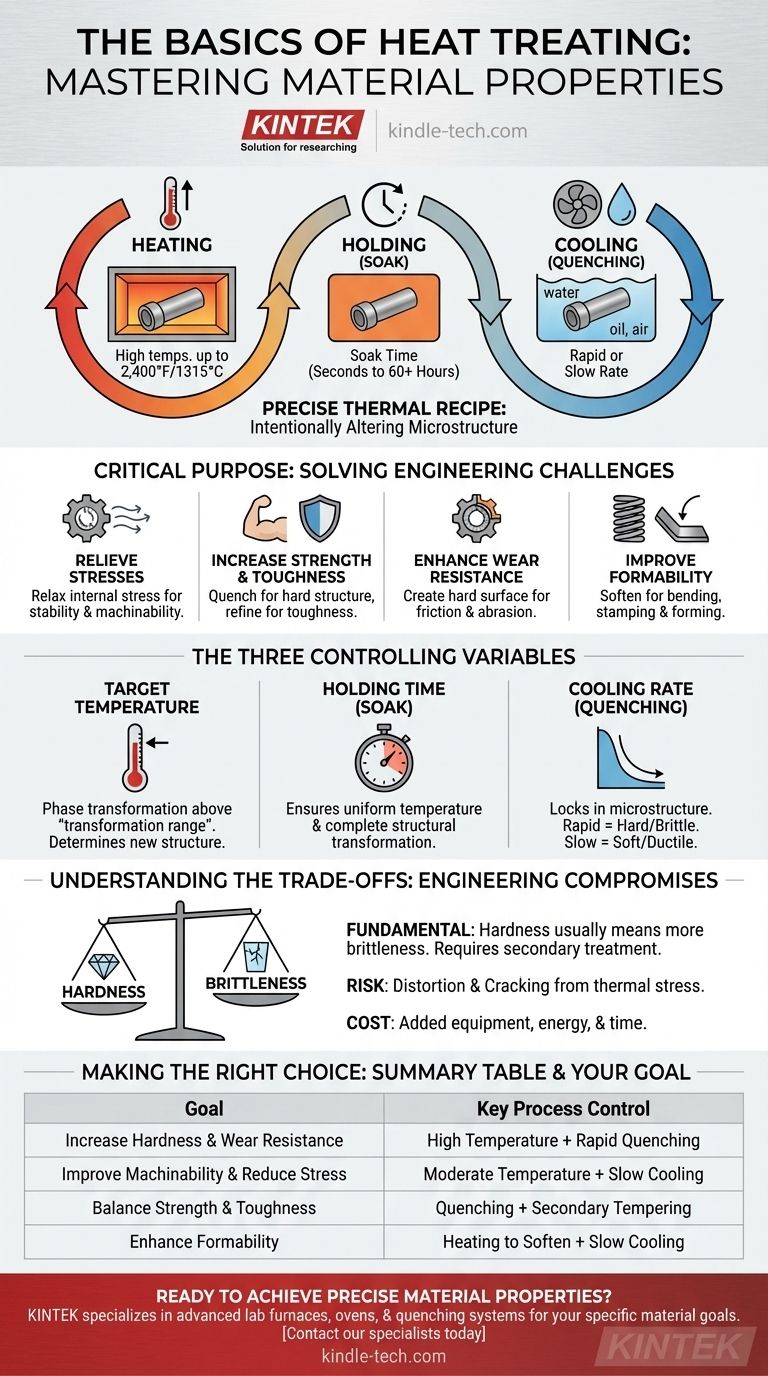
At its core, heat treating is a highly controlled manufacturing process used to intentionally alter the physical and mechanical properties of a metal. It is not a single action but a precise thermal recipe involving three fundamental stages: heating the material to a specific temperature, holding it there for a set duration, and cooling it at a predetermined rate. The goal is to change the metal's internal microstructure to achieve desired outcomes like increased hardness, softness, strength, or wear resistance.
Think of heat treating not as one process, but as a set of controls for a material's final performance. The entire outcome hinges on three variables: temperature, time, and cooling rate. By mastering this recipe, you can predictably transform a standard metal into a component perfectly suited for its specific engineering application.

The Purpose of Heat Treatment: Why It's Critical
Heat treatment is performed to solve specific engineering challenges by modifying a material's inherent properties. It's a critical step that unlocks the full potential of many metals, especially steel.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Manufacturing processes like welding, casting, or heavy machining introduce significant stress into a material. Heat treatment, particularly slower cooling cycles, can relax this internal stress, making the part more dimensionally stable and far easier to machine accurately.
Increasing Strength and Toughness
The most common reason for heat treatment is to increase a material's strength. By heating and then rapidly cooling (quenching) steel, you can create an internal structure that is exceptionally hard and strong. Subsequent treatments can then refine this structure to improve toughness and reduce brittleness.
Enhancing Wear Resistance
For components that experience friction or abrasion, like gears or bearings, creating a very hard surface is essential for a long service life. Heat treatment processes, including induction heating, can be used to harden just the surface layer of a part while leaving the core tougher and more ductile.
Improving Formability
Conversely, some heat treatment processes are designed to make a metal softer and more ductile. This is done to make the material easier to bend, stamp, or form into a complex shape without cracking.
The Three Controlling Variables Explained
The final properties of a heat-treated part are a direct result of how you manipulate the three core variables of the process.
The Target Temperature
Metals, particularly steel, undergo phase transformations at specific temperatures. Heating a part above its "transformation range" causes its internal crystal structure to change. The temperature you choose determines which new structure you can form upon cooling. Temperatures can range up to 2,400°F (1315°C).
The Holding Time (Soak Time)
Once at temperature, the material must be held there for a specific amount of time, known as soaking. This ensures two things: that the entire part, including its core, reaches a uniform temperature, and that the desired structural transformation has enough time to complete throughout the material. This can range from a few seconds to over 60 hours.
The Cooling Rate (Quenching)
This is often the most critical step. The speed at which you cool the metal "locks in" a specific microstructure.
- Rapid cooling (quenching) in water or oil traps a hard, brittle structure.
- Slow cooling in open air or a furnace allows a softer, more ductile structure to form.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is an exercise in engineering compromises. Improving one property often comes at the expense of another.
The Hardness vs. Brittleness Compromise
The most fundamental trade-off is between hardness and brittleness. A process that creates extreme hardness will almost always result in a more brittle material that is susceptible to fracturing under impact. A secondary, lower-temperature heat treatment is often required to restore some toughness.
Risk of Distortion and Cracking
The rapid heating and cooling central to many heat treatments creates immense thermal stress within a component. If not managed properly, this stress can cause the part to warp, distort, or even crack during the quenching process.
Added Cost and Process Time
Heat treatment is an additional step in the manufacturing workflow. It requires specialized equipment, energy, and time, all of which add to the final cost of the component. This cost must be justified by the required performance improvement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of heat treatment parameters should be driven directly by the component's intended function.
- If your primary focus is improving machinability: Use a process with a slow cooling rate to relieve internal stresses and soften the material.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: Use a process with a very rapid cooling rate (quenching) to create the hardest possible structure.
- If your primary focus is a balance of strength and toughness: Use a rapid quench followed by a secondary tempering cycle, or use a more moderate cooling rate to avoid extreme brittleness.
Ultimately, understanding these principles allows you to specify and control the final performance of your metal components.
Summary Table:
| Goal | Key Process Control |
|---|---|
| Increase Hardness & Wear Resistance | High Temperature + Rapid Quenching |
| Improve Machinability & Reduce Stress | Moderate Temperature + Slow Cooling |
| Balance Strength & Toughness | Quenching + Secondary Tempering |
| Enhance Formability | Heating to Soften + Slow Cooling |
Ready to Achieve Precise Material Properties?
Your metal components' performance hinges on the precise control of heat treatment. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab furnaces, ovens, and quenching systems needed to master temperature, time, and cooling rates for your specific material goals—whether you need maximum hardness, improved toughness, or stress relief.
Let our expertise in lab equipment help you unlock the full potential of your materials. Contact our specialists today to discuss your application and find the perfect heat treatment solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Is a muffle furnace an oven? A Guide to High-Temperature vs. Low-Temperature Heating
- What is the use of muffle furnace in food lab? Essential for Accurate Ash Content Analysis
- What is the difference between a furnace and oven? Understanding Their Unique Heating Purposes
- What is the operating range of a muffle furnace? Unlock the Key to Your High-Temperature Tasks
- What is the temperature of heat treatment? It Depends on Your Metal and Desired Properties



















