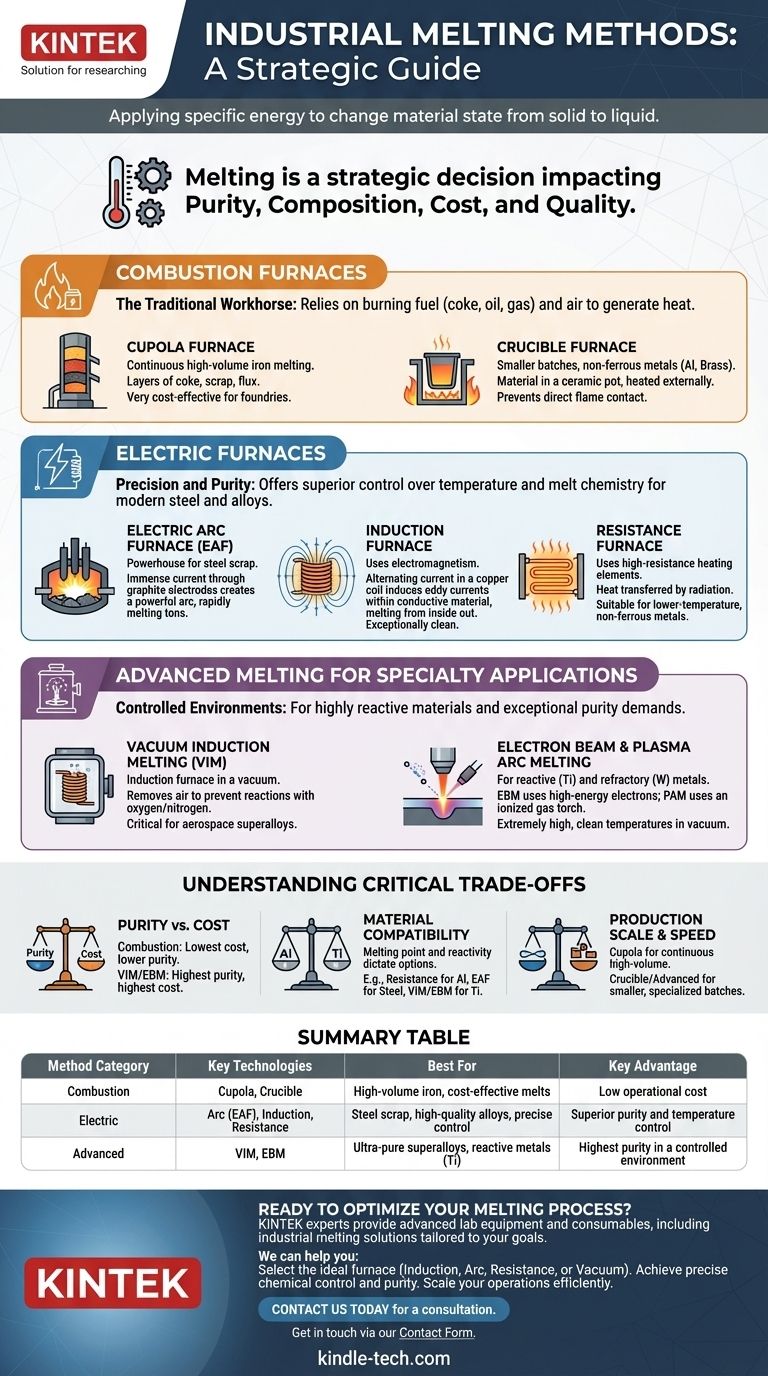
At its core, industrial melting is the process of applying a specific type of energy to a material to change its state from solid to liquid. The methods to achieve this are broadly categorized by their primary heat source: the chemical energy from combustion, the power of electrical energy, or highly focused specialty energy sources for advanced applications. Each category contains distinct technologies designed for specific materials, purity levels, and production scales.
The choice of a melting method is not just about reaching a target temperature. It is a strategic decision that directly impacts the final material's purity, chemical composition, production cost, and overall quality.

Combustion Furnaces: The Traditional Workhorse
Combustion furnaces are the oldest form of melting technology, relying on the burning of fuel—such as coke, oil, or natural gas—to generate heat.
The Principle of Fuel and Air
These furnaces operate by mixing a fuel source with an oxidant (typically air) and igniting it. The resulting chemical reaction releases immense thermal energy, which is then transferred to the material charge, causing it to melt.
The Cupola Furnace
The cupola is a tall, cylindrical furnace used almost exclusively for melting iron in foundries. It operates continuously by layering coke, metal scrap, and flux (like limestone) from the top, providing a very high-volume and cost-effective source of molten iron.
The Crucible Furnace
For smaller batches and non-ferrous metals like aluminum or brass, the crucible furnace is common. The material is placed inside a high-temperature ceramic pot (the crucible), which is then heated externally by the combustion flame, preventing direct contact between the flame and the metal.
Electric Furnaces: Precision and Purity
Electric furnaces offer significantly more control over temperature and melt chemistry than combustion methods, making them essential for modern steelmaking and specialty alloys.
The Electric Arc Furnace (EAF)
The EAF is a powerhouse designed for melting steel scrap. It works by passing an immense electrical current through large graphite electrodes. This creates a powerful arc that strikes the metal charge, generating intense temperatures that can rapidly melt tons of steel.
The Induction Furnace
An induction furnace uses the principle of electromagnetism. An alternating current flows through a copper coil, creating a strong magnetic field. When conductive material is placed inside this field, it induces internal electrical currents (eddy currents) that generate heat, melting the metal from the inside out without any external contact.
This method is exceptionally clean and provides excellent temperature control and stirring action, making it ideal for high-quality steels and specialty alloys.
The Resistance Furnace
A resistance furnace operates much like a home toaster or oven. It uses high-resistance heating elements that glow red hot when electricity passes through them. The heat is transferred to the material primarily through radiation, making it suitable for lower-temperature, non-ferrous metals like aluminum.
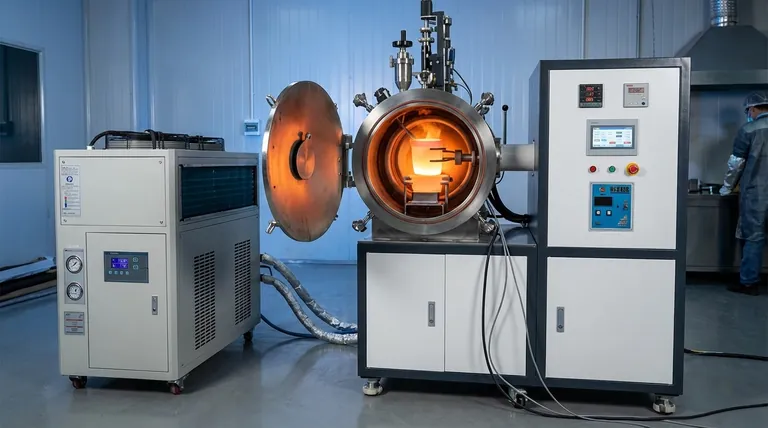
Advanced Melting for Specialty Applications
When materials are highly reactive or demand exceptional purity, standard methods are insufficient. Advanced processes are conducted in controlled environments, often a vacuum.
Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM)
VIM is simply an induction furnace housed inside a vacuum chamber. By removing the air, this process prevents oxygen, nitrogen, and other atmospheric gases from reacting with the molten metal. This is critical for producing the high-purity superalloys used in aerospace and medical implants.
Electron Beam and Plasma Arc Melting
For the most demanding applications, such as melting reactive metals like titanium or refractory metals like tungsten, even more advanced methods are used. Electron Beam Melting (EBM) uses a focused beam of high-energy electrons, and Plasma Arc Melting (PAM) uses an ionized gas torch to achieve extremely high and clean temperatures within a vacuum.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Choosing a melting process involves balancing competing priorities. No single method is universally superior.
Purity vs. Cost
The fundamental trade-off is between the final purity of the metal and the cost of the operation. Combustion furnaces are generally the cheapest to operate but introduce impurities from the fuel. VIM and EBM produce the highest purity metals but at a significantly higher capital and operational cost.
Material Compatibility
The melting point and chemical reactivity of the material dictate the viable options. A low-temperature resistance furnace is perfect for aluminum but useless for steel. A reactive metal like titanium cannot be melted in open air and requires a vacuum process.
Production Scale and Speed
The required output is a major factor. A cupola furnace is designed for continuous, high-volume production of cast iron. In contrast, crucible and many advanced furnaces are batch-based processes, better suited for smaller, specialized runs where quality is more important than quantity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision must be aligned with the specific requirements of your material and end product.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, cost-effective iron casting: The cupola furnace remains the industry standard for its efficiency and throughput.
- If your primary focus is recycling steel scrap at a massive scale: The Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) offers the raw power and capacity required for modern steelmaking.
- If your primary focus is creating high-quality alloys with precise chemical control: The cleanliness and control of an induction furnace are essential.
- If your primary focus is producing ultra-pure superalloys or reactive metals: A vacuum-based system like Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) or Electron Beam Melting (EBM) is non-negotiable.
Understanding these core methods transforms the challenge of melting from a brute-force heating task into a precise and calculated engineering decision.
Summary Table:
| Method Category | Key Technologies | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Combustion | Cupola, Crucible | High-volume iron, cost-effective melts | Low operational cost |
| Electric | Arc (EAF), Induction, Resistance | Steel scrap, high-quality alloys, precise control | Superior purity and temperature control |
| Advanced | Vacuum Induction (VIM), Electron Beam (EBM) | Ultra-pure superalloys, reactive metals (e.g., titanium) | Highest purity in a controlled environment |
Ready to Optimize Your Melting Process?
Choosing the right furnace is critical to your product's quality, purity, and cost-efficiency. The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables, including industrial melting solutions tailored to your specific material and production goals.
We can help you:
- Select the ideal furnace (Induction, Arc, Resistance, or Vacuum) for your metal or alloy.
- Achieve precise chemical control and superior material purity.
- Scale your operations efficiently, from R&D to full production.
Contact us today for a consultation, and let's discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory or production line.
Get in touch via our Contact Form to speak with an expert.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision



















