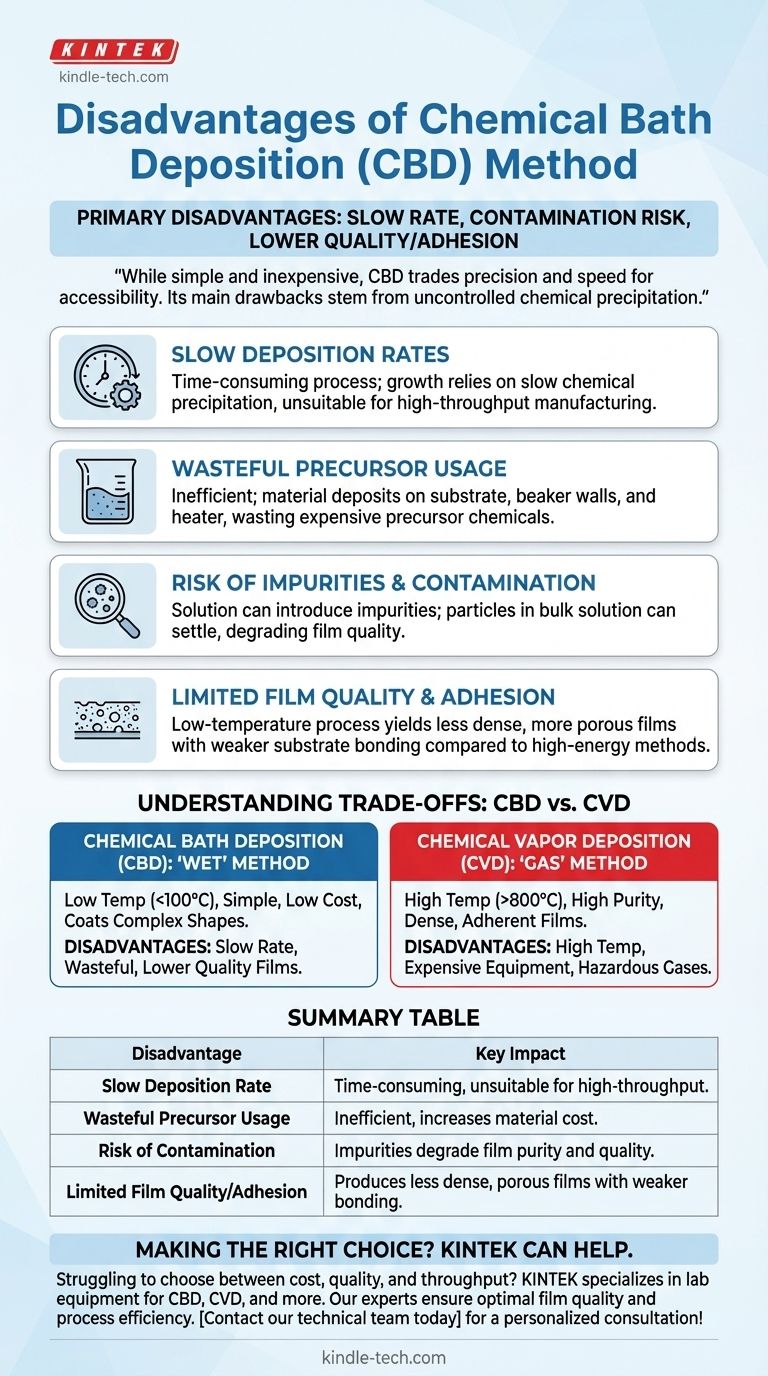
The primary disadvantages of Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD) are its slow deposition rate, potential for contamination from the solution, and the often lower film quality and adhesion compared to higher-energy methods. It is also important to distinguish CBD, a low-temperature "wet" chemical method, from Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), a high-temperature gas-phase method, as they are frequently confused.
While simple and inexpensive, Chemical Bath Deposition trades precision and speed for accessibility. Its main drawbacks stem from the uncontrolled nature of chemical precipitation in a solution, leading to slower growth, potential impurities, and films that can be less dense and adherent than those from vapor-based techniques.

Unpacking Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD)
To understand its limitations, we must first understand the process. CBD is a "bottom-up" technique used to create thin films on a substrate.
The Basic Mechanism
In CBD, a substrate is simply immersed in a dilute aqueous solution containing the chemical precursors. The solution is heated gently, typically well below 100°C, which triggers a controlled chemical reaction.
This reaction causes the desired material to slowly precipitate out of the solution and deposit as a thin film onto all submerged surfaces, including the substrate and the container walls.
The Core Disadvantages of CBD
The simplicity of the CBD process is also the source of its main drawbacks.
Slow Deposition Rates
The growth of the film relies on a slow, controlled chemical precipitation. This makes the process inherently time-consuming, often taking several hours to produce a film of the desired thickness. This is a significant drawback for any high-throughput manufacturing.
Wasteful Precursor Usage
Deposition occurs on every surface immersed in the bath—the substrate, the beaker walls, and even the heater. This is highly inefficient, as a significant portion of the expensive precursor chemicals is wasted instead of forming the intended film.
Risk of Impurities and Contamination
The chemical bath itself can be a source of contamination. Any impurities in the water or precursor chemicals can become incorporated into the growing film. Furthermore, unwanted particles can precipitate in the bulk solution and settle onto the substrate, degrading the film's quality.
Limited Film Quality and Adhesion
Because CBD is a low-temperature, low-energy process, the resulting films are often less dense and more porous than those from methods like sputtering or CVD. The adhesion of the film to the substrate can also be weaker, as there is no high-energy particle bombardment to promote strong bonding.
Understanding the Trade-offs: CBD vs. Other Methods
No deposition method is universally superior; the choice depends entirely on the application's specific requirements. The references provided discuss disadvantages that apply to Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), a fundamentally different process.
Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD): The "Wet" Method
This process uses a liquid solution at low temperatures (typically <100°C). It is valued for its simplicity, low cost, and ability to coat large, complex shapes on temperature-sensitive substrates like plastics.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): The "Gas" Method
This process uses volatile gas precursors in a vacuum chamber at very high temperatures (often >800°C). The gases react and decompose on the hot substrate to form a very high-purity, dense, and adherent film. Its primary disadvantages, noted in the references, are the high temperatures required, the need for expensive vacuum equipment, and the use of potentially toxic and hazardous precursor gases.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition technique requires balancing cost, quality, material constraints, and desired throughput.
- If your primary focus is low cost and coating large areas at low temperatures: CBD is an excellent candidate, especially for materials like CdS or ZnO, as long as you can accept slower deposition rates.
- If your primary focus is maximum film purity, density, and adhesion: A high-energy process like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) or Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is necessary, despite the higher equipment cost and operational complexity.
- If you are working with temperature-sensitive substrates like polymers: CBD's low operating temperature gives it a significant advantage over conventional, high-temperature CVD.
Ultimately, choosing the right method means aligning the technique's inherent capabilities with your project's specific priorities and constraints.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Slow Deposition Rate | Time-consuming process, unsuitable for high-throughput manufacturing. |
| Wasteful Precursor Usage | Inefficient; material deposits on container walls, increasing cost. |
| Risk of Contamination | Impurities from the solution can degrade film purity and quality. |
| Limited Film Quality/Adhesion | Produces less dense, more porous films with weaker substrate bonding. |
Struggling to choose the right deposition method for your specific materials and substrates? The trade-offs between cost, quality, and throughput are complex. At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables for all your deposition needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect solution—whether it's a simple CBD setup or a high-performance CVD system—to ensure optimal film quality and process efficiency for your laboratory. Contact our technical team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- How does a Hot Filament Chemical Vapor Deposition (HFCVD) reactor function? Expert Guide to Diamond Film Fabrication
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth

















