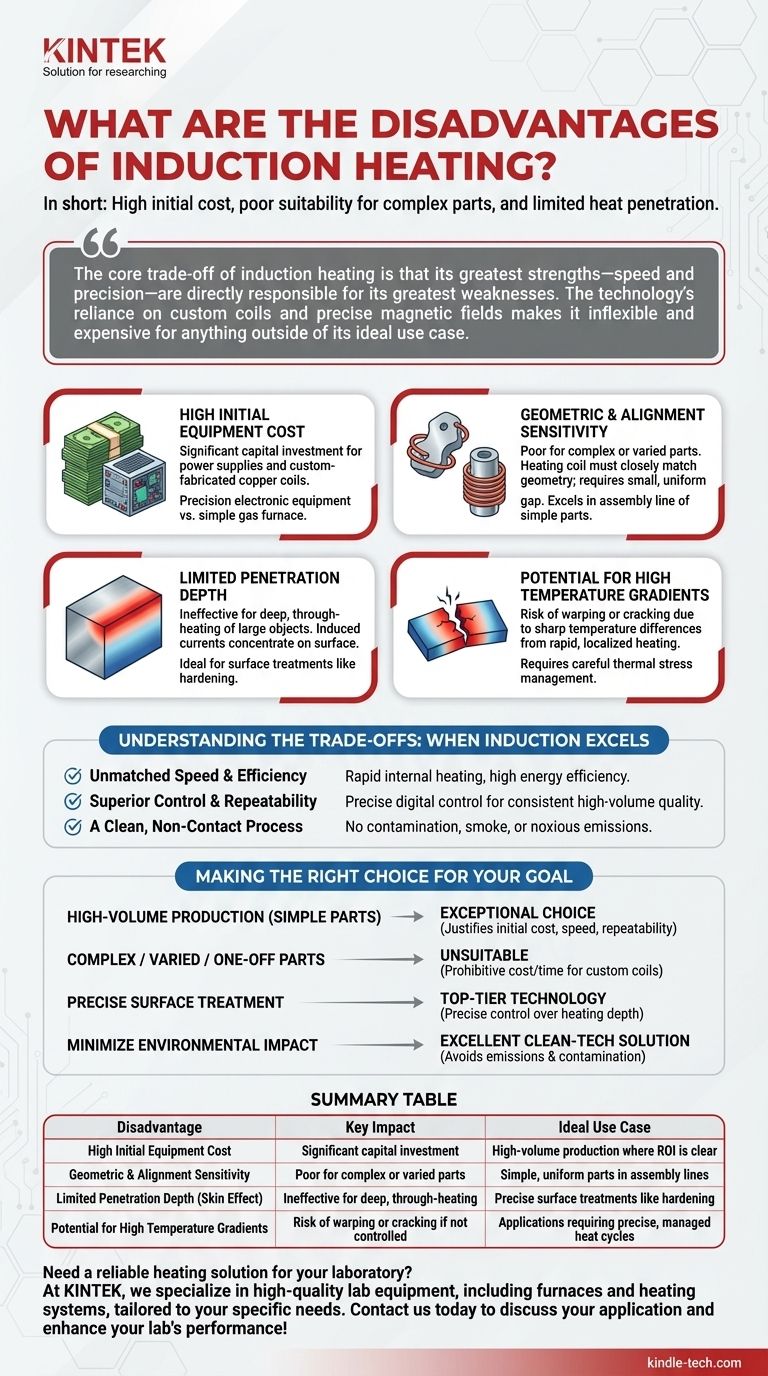
In short, the primary disadvantages of induction heating are its high initial equipment cost, its poor suitability for complex or irregularly shaped parts, and its limited heat penetration depth. These factors make it a highly specialized tool rather than a universal heating solution.
The core trade-off of induction heating is that its greatest strengths—speed and precision—are directly responsible for its greatest weaknesses. The technology's reliance on custom coils and precise magnetic fields makes it inflexible and expensive for anything outside of its ideal use case.
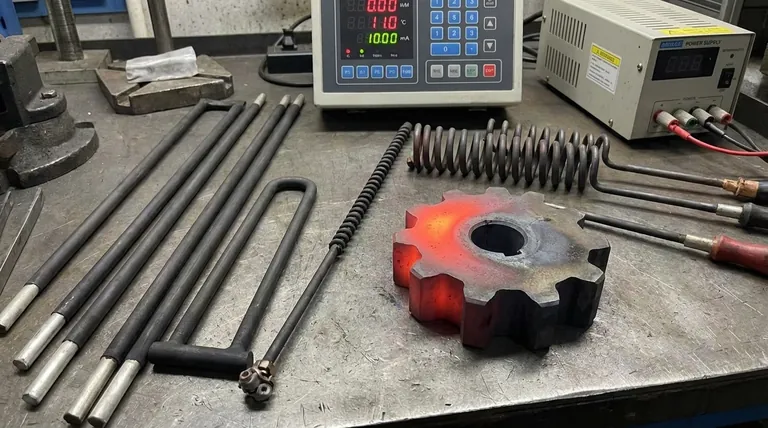

The Core Challenge: Precision Has a Price
Induction heating works by generating an electromagnetic field that induces electrical currents directly within a conductive workpiece. While this method is incredibly efficient, its physical principles create several practical limitations.
High Initial Equipment Cost
The power supplies and custom-fabricated copper coils required for an induction system represent a significant capital investment. Unlike a simple gas furnace, an induction heater is a piece of precision electronic equipment, and its cost reflects that.
Geometric and Alignment Sensitivity
This is arguably the most significant operational drawback. The heating coil must be designed to closely match the geometry of the part being heated, and the gap between the coil and the part must be small and uniform.
This makes induction heating poorly suited for complicated mechanical workpieces. It excels in assembly line production of simple, uniform parts but lacks the adaptability for low-volume or varied jobs.
Limited Penetration Depth
The induced eddy currents naturally concentrate on the surface of the conductor, a phenomenon known as the "skin effect." This makes induction heating exceptional for surface hardening, brazing, or other treatments where only the outer layer needs heat.
However, it is not an effective method for deep, through-heating of very large or thick metal objects, as the core of the material will remain significantly cooler than the surface.
Potential for High Temperature Gradients
Because heating can be both rapid and highly localized, it can create sharp temperature differences within the workpiece. This thermal stress can lead to warping or even cracking if not carefully managed through proper coil design and power control.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When Induction Excels
To make an informed decision, you must weigh the disadvantages against the technology's profound benefits in the right context.
Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
The heat is generated inside the workpiece itself, not from an external source. This results in extremely rapid heating cycles and higher energy efficiency, as you are not wasting energy heating the surrounding atmosphere or furnace components.
Superior Control and Repeatability
Modern solid-state induction systems offer precise, digital control over the heating cycle. Once a process is dialed in, it can be repeated thousands oftimes with virtually no deviation, ensuring consistent product quality in high-volume manufacturing.
A Clean, Non-Contact Process
The workpiece never touches a flame or heating element, which eliminates product contamination. As a process, it produces no smoke, waste heat, or noxious emissions, making it a "green" technology that contributes to a safer and cleaner work environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the choice to use induction heating depends entirely on your specific application and production goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of simple, uniform parts: Induction heating is an exceptional choice where the initial cost is justified by long-term speed and repeatability.
- If your primary focus is heating complex, varied, or one-off parts: This technology is likely unsuitable, as the cost and time required for custom coils would be prohibitive.
- If your primary focus is precise surface treatment (like hardening or brazing): Induction heating is a top-tier, often superior, technology due to its precise control over heating depth.
- If your primary focus is minimizing environmental impact and contamination: Induction is an excellent clean-tech solution that avoids the emissions and contact-based contamination of alternatives.
Induction heating is a specialist's tool that offers unparalleled performance when applied to the right problem.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| High Initial Equipment Cost | Significant capital investment | High-volume production where ROI is clear |
| Geometric & Alignment Sensitivity | Poor for complex or varied parts | Simple, uniform parts in assembly lines |
| Limited Penetration Depth (Skin Effect) | Ineffective for deep, through-heating | Precise surface treatments like hardening |
| Potential for High Temperature Gradients | Risk of warping or cracking if not controlled | Applications requiring precise, managed heat cycles |
Need a reliable heating solution for your laboratory? Choosing the right equipment is critical for efficiency and product quality. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including furnaces and heating systems, tailored to your specific needs. Whether you're focused on high-volume production or complex, one-off projects, our experts can help you find the perfect solution to enhance your lab's performance and ensure consistent results. Contact us today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Aluminum Oxide Al2O3 Heat Sink for Insulation
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is silicon carbide rod heated to high temperature used as? A Premier Heating Element for Extreme Environments
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- What are the uses of silicon carbide rod? The Ultimate Heating Solution for Extreme Temperatures
- What kind of metal is used in heating elements? A Guide to Materials for Every Temperature & Atmosphere
- What are silicon carbide heating elements used for? Reliable High-Temp Heating for Industrial Processes



















