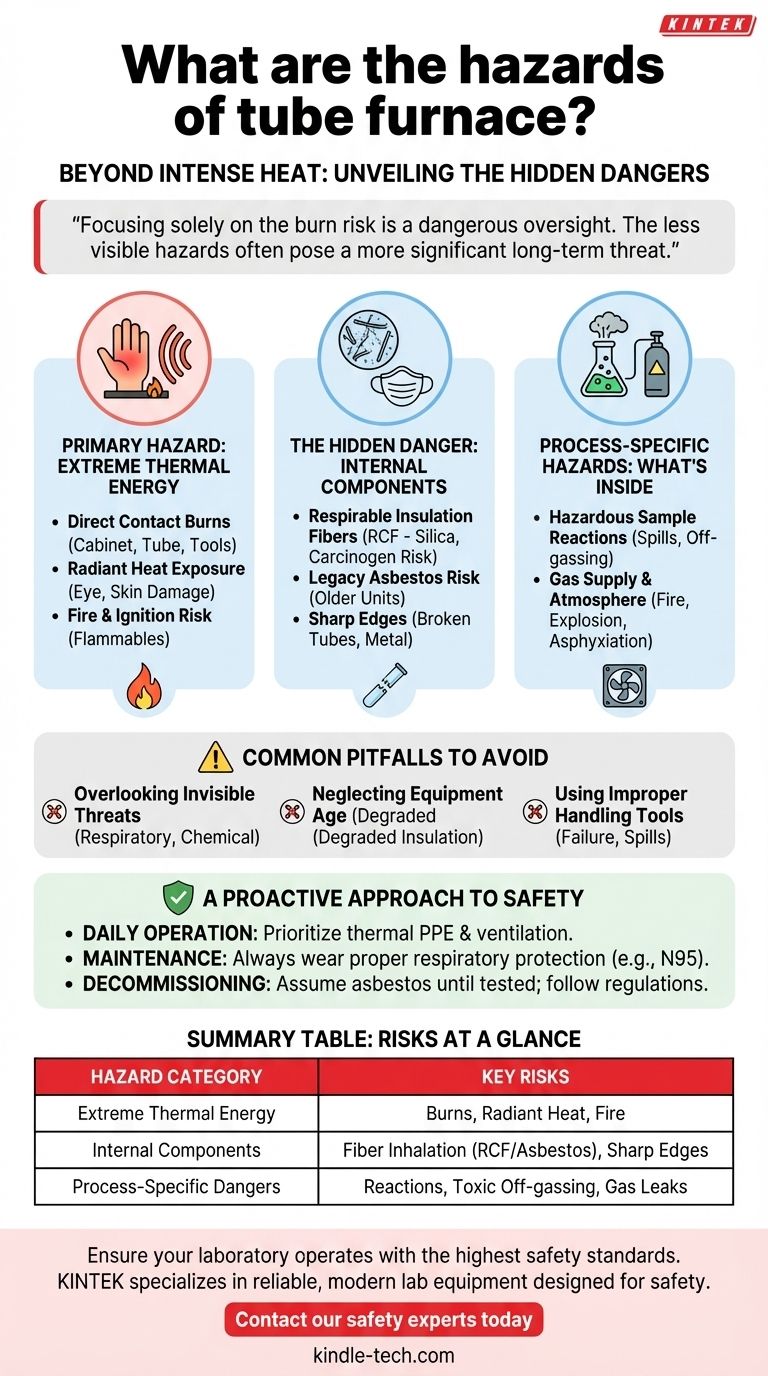
Beyond the obvious danger of intense heat, the primary hazards of a tube furnace fall into three categories. These include severe thermal risks from direct contact and radiation, invisible respiratory dangers from the furnace's insulation materials, and process-specific hazards related to the chemical samples being heated.
The most critical takeaway is that focusing solely on the burn risk is a common and dangerous oversight. The less visible hazards, such as inhaling carcinogenic ceramic fibers from insulation or managing unexpected reactions from samples, often pose a more significant long-term threat.
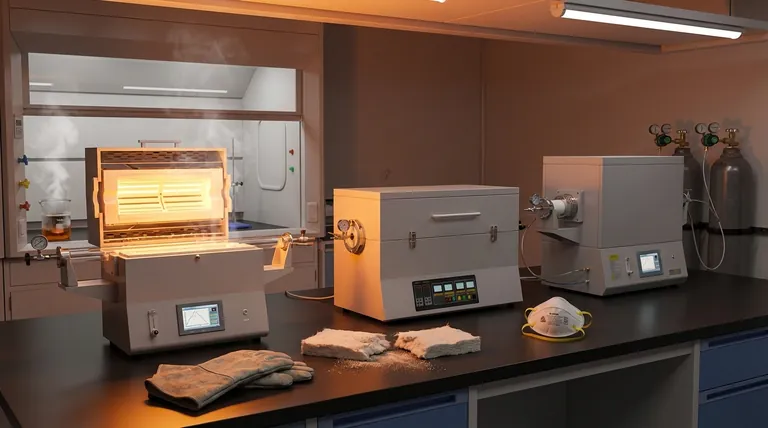

Primary Hazard: Extreme Thermal Energy
The most immediate and apparent danger of any furnace is the extreme temperature it generates. This energy presents a risk in several distinct ways.
Direct Contact Burns
The furnace cabinet, the process tube (whether quartz or alumina), handling tools, and the samples themselves can all be at temperatures capable of causing instant, severe burns. Surfaces will remain dangerously hot long after the power is turned off.
Radiant Heat Exposure
Even without touching the furnace, radiant heat can be a significant hazard. The intense glare from very hot objects can damage the eyes, and prolonged exposure to infrared radiation can cause serious skin burns.
Fire and Ignition Risk
The high temperatures create a constant ignition source. Any flammable materials, including incompatible samples, solvents, or even improperly rated wiring placed too close to the furnace, can easily catch fire.
The Hidden Danger: Internal Components and Materials
Some of the most serious hazards are not related to heat but to the physical materials used to construct the furnace. These risks are most prominent during maintenance, repair, or decommissioning.
Respirable Insulation Fibers
Many laboratory furnaces use refractory ceramic fiber (RCF) for insulation. Over time, this material can degrade and release microscopic fibers and dust containing crystalline silica, which can cause chronic lung injury (silicosis) if inhaled. RCF is classified as a possible human carcinogen.
Legacy Asbestos Risk
Older furnace models may contain asbestos as an insulating material. Disturbing this material can release fibers that lead to severe respiratory diseases. Proper identification and professional disposal are crucial when handling older equipment.
Sharp Edges and Physical Cuts
Furnace tubes, especially those made of quartz or alumina, can break and create extremely sharp edges. Gas supply lines and other metal components can also present a physical cutting hazard during setup or maintenance.
Process-Specific Hazards: What's Inside the Tube
The furnace itself is only one part of the equation. The materials you place inside it introduce a new layer of potential hazards that are unique to your specific application.
Hazardous Sample Reactions
The samples being heated can pose a significant risk. This includes potential spills of hazardous materials inside the hot tube, unexpected chemical reactions at high temperatures, or the production of toxic off-gassing that requires proper ventilation and exhaust.
Gas Supply and Atmosphere Control
Many processes require specific atmospheres, involving flammable, inert, or reactive gases. Leaks in the gas supply lines can lead to fire, explosion, or asphyxiation risks depending on the gas being used.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Trust and safety are built on recognizing and mitigating not just the obvious risks but the commonly overlooked ones as well.
Overlooking Invisible Threats
The most common mistake is focusing exclusively on the thermal hazard. Operators often neglect to wear proper respiratory protection during maintenance or fail to consider the chemical risks of their samples, which can have severe long-term consequences.
Neglecting Equipment Age
Assuming a furnace is safe simply because it functions is a critical error. The insulation in older units degrades, increasing the risk of respiratory exposure. Always consider the age and condition of the equipment.
Using Improper Handling Tools
Using tools, sample boats, or carriers not rated for the furnace's operating temperature can lead to failure. A dropped sample or a broken tool inside a hot furnace can create a spill and a sudden release of hazardous vapors.
A Proactive Approach to Tube Furnace Safety
To ensure a safe operating environment, your safety protocols must be tailored to your specific tasks and equipment.
- If your primary focus is daily operation: Prioritize PPE for thermal hazards (heat-resistant gloves, face shield) and ensure proper ventilation for potential sample off-gassing.
- If your primary focus is equipment maintenance: Always wear appropriate respiratory protection (e.g., an N95 respirator or better) when handling or replacing insulation to prevent inhaling harmful ceramic fibers.
- If your primary focus is decommissioning old equipment: Assume the presence of asbestos until proven otherwise by professional testing and follow all mandated disposal regulations.
A truly effective safety plan addresses not only the visible heat of the furnace but also the invisible risks within its components and your samples.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Category | Key Risks |
|---|---|
| Extreme Thermal Energy | Direct contact burns, radiant heat exposure, fire risk from flammable materials. |
| Internal Components | Inhalation of carcinogenic ceramic fibers (RCF), potential asbestos in old units, sharp edges from broken tubes. |
| Process-Specific Dangers | Hazardous sample reactions, toxic off-gassing, leaks from flammable or inert gas supplies. |
Ensure your laboratory operates with the highest safety standards. The hazards of tube furnaces are complex, but managing them effectively is crucial for protecting your team and your research. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable, modern lab equipment and consumables designed with safety in mind. From furnaces with updated insulation to appropriate handling tools, we help you mitigate risks.
Contact our safety experts today to discuss your specific needs. Let KINTEK be your partner in creating a safer, more productive lab environment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does an alumina tube furnace with a controlled atmosphere simulate conditions in CSP environments? Master Accuracy.
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- What temperature is alumina activated? Unlock Optimal Porosity for Adsorption



















