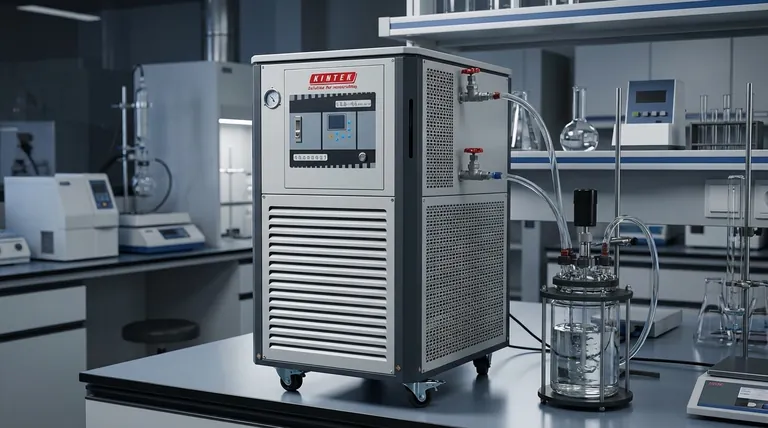
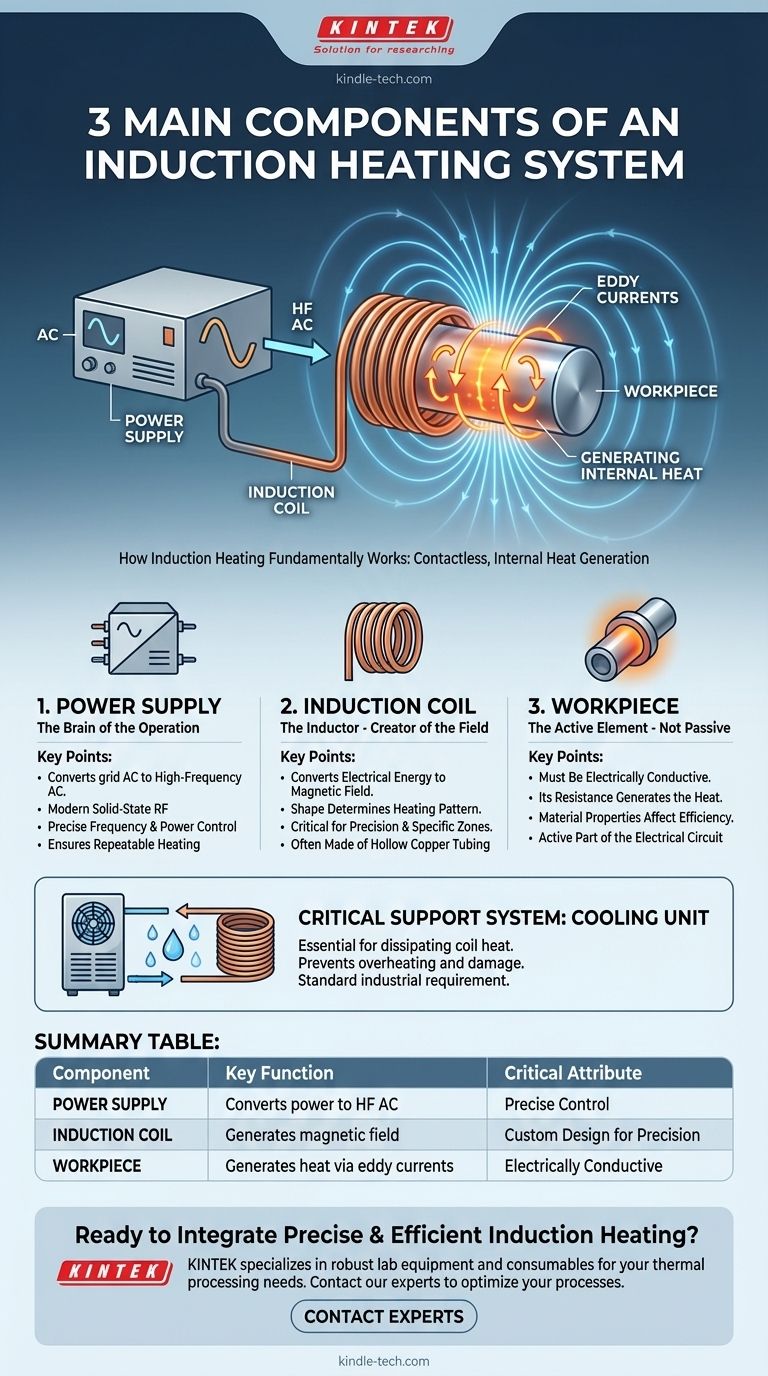
At its core, an induction heating system operates using three primary components: the power supply, the induction coil, and the workpiece being heated. These elements work together to generate heat directly within a conductive material, leveraging fundamental principles of electromagnetism to achieve rapid and precise results without physical contact.
The central principle is electromagnetic induction. A high-frequency alternating current in the coil creates a powerful, changing magnetic field, which in turn induces electrical currents (known as eddy currents) within the workpiece, generating heat from the inside out.

How Induction Heating Fundamentally Works
To understand the components, it's essential to first grasp the physics at play. The process is clean, contactless, and remarkably efficient because the heat isn't transferred from an external source—it's generated within the part itself.
Creating the Magnetic Field
The process begins when an alternating current (AC) from the power supply flows through the induction coil. This flow of electricity generates a concentrated and rapidly alternating magnetic field around the coil, as described by Maxwell's equations.
Inducing Eddy Currents
When an electrically conductive workpiece is placed within this magnetic field, the field induces circulating electrical currents within the material. These are known as eddy currents.
Generating Internal Heat
The workpiece's natural electrical resistance opposes the flow of these eddy currents. This opposition creates friction on a molecular level, which manifests as intense and localized heat. It is this internal friction, not an external flame or heating element, that heats the part.
A Breakdown of the Core Components
Each of the three core components plays a distinct and indispensable role in making the induction process successful. The system is only as effective as its weakest link.
The Power Supply
The power supply is the brain of the operation. It takes standard AC power from the grid and converts it into a high-frequency alternating current suitable for induction heating.
Modern systems use solid-state RF (Radio Frequency) power supplies because their output frequency and power can be precisely controlled, allowing for repeatable and optimized heating cycles.
The Induction Coil (The Inductor)
The induction coil, typically made of copper tubing, is where the electrical energy is converted into the magnetic field. It is arguably the most critical component for application-specific results.
The shape and design of the coil determine the shape of the magnetic field and, therefore, where the heat is generated in the workpiece. This allows for incredibly precise heating of specific areas.
The Workpiece
The workpiece is not a passive element; it is an active part of the electrical circuit. For induction to work, the material must be electrically conductive.
The specific properties of the workpiece material—its conductivity and magnetic characteristics—will determine how efficiently it heats up in response to the induced currents.
Essential Support Systems to Consider
While the three components above are the core of the process, industrial applications almost always require a critical support system to function reliably.
The Absolute Need for Cooling
The massive currents flowing through the induction coil generate significant heat in the coil itself due to electrical resistance. Without active cooling, the coil would quickly overheat and melt.
For this reason, a water cooling unit or chiller is a standard and necessary part of any industrial induction heating installation. Water is typically circulated through the hollow copper tubing of the coil to dissipate this waste heat and protect the equipment.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Understanding the role of each component allows you to focus on the variables that matter most for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is speed and efficiency: Concentrate on the coupling, which is the physical proximity of the induction coil to the workpiece. A closer, more conformed coil transfers energy much faster.
- If your primary focus is precision and control: The design of the induction coil is your most important variable. Custom-shaped coils are essential for heating specific zones or complex geometries.
- If your primary focus is system longevity: A properly sized and maintained water cooling system is non-negotiable. It is the single most important factor in protecting the power supply and coil from damage.
By understanding how these components interact, you are empowered to specify, operate, and troubleshoot any induction heating system effectively.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Critical Attribute |
|---|---|---|
| Power Supply | Converts grid power to high-frequency AC | Precise control of frequency and power |
| Induction Coil | Generates the alternating magnetic field | Custom design for precise heating patterns |
| Workpiece | Generates internal heat via induced eddy currents | Must be electrically conductive |
Ready to integrate precise and efficient induction heating into your lab or production line?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific thermal processing needs. Whether your goal is rapid heating, precise temperature control for complex geometries, or ensuring maximum system longevity, our expertise in induction heating technology can help you achieve it.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your heating processes and deliver the reliable performance your laboratory requires.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 30L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 20L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- Infrared Heating Quantitative Flat Plate Press Mold
- 50L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
People Also Ask
- How does a high-precision constant temperature circulator contribute to mineral dissolution kinetic studies?
- What is the function of a constant temperature water bath in CO2 absorption kinetics? Achieve High-Precision Research
- For which types of substances are water baths and chillers considered ideal? Essential Care for Sensitive Samples
- How does a thermostatic water bath function in ODS steel corrosion tests? Ensure Precise Bio-Simulation Accuracy
- What are water baths used for? Achieve Precise & Gentle Temperature Control for Your Lab Samples















