In short, an induction heater can melt any material that is electrically conductive. This includes virtually all metals, such as steel, iron, gold, silver, copper, aluminum, and brass. The process is remarkably efficient because it heats the material directly from within, without any physical contact or open flame.
The critical factor for induction melting is not the material's melting point, but its ability to conduct electricity. If a material can have an electrical current induced within it, a sufficiently powerful induction system can be configured to melt it.
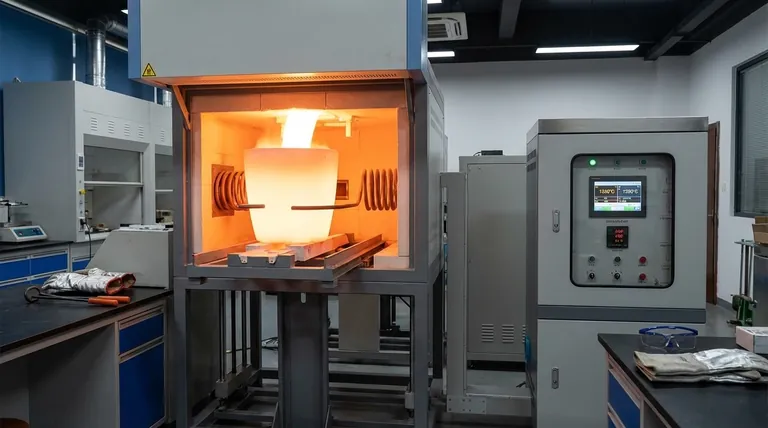

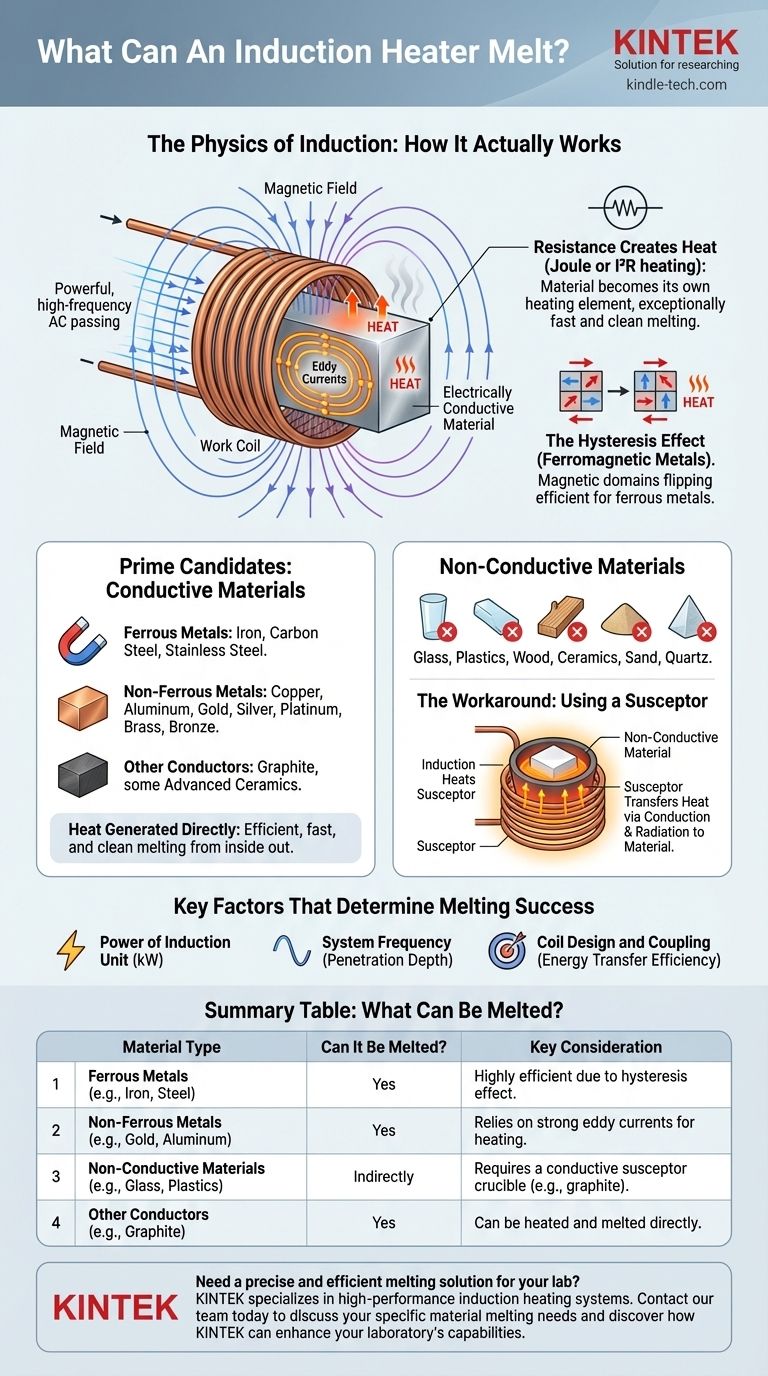
The Physics of Induction: How It Actually Works
To understand what induction can melt, you must first understand how it generates heat. The process is a clever application of electromagnetism.
The Role of the Work Coil
An induction heater uses a copper coil, known as the work coil. A powerful, high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through this coil.
This creates a rapidly changing and intense magnetic field in the space within and around the coil.
Inducing Eddy Currents
When an electrically conductive material is placed within this magnetic field, the field induces circular electrical currents inside the material itself. These are called eddy currents.
Resistance Creates Heat
The material being heated has a natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents. This resistance causes immense friction on an atomic level, which generates precise and rapid heat. This is known as Joule or I²R heating.
The material effectively becomes its own heating element, allowing for exceptionally fast and clean melting from the inside out.
The Hysteresis Effect (Ferromagnetic Metals)
For magnetic metals like iron and steel, a secondary heating effect occurs. The rapidly changing magnetic field causes the magnetic domains within the material to quickly flip back and forth, creating additional internal friction and heat.
This effect, called hysteresis heating, makes induction especially efficient for melting ferrous metals. It ceases to work, however, once the metal reaches its Curie temperature and loses its magnetic properties.
What Materials Can Be Melted?
The principles above dictate exactly what can and cannot be melted with this technology.
Prime Candidates: Conductive Materials
Any material that readily conducts electricity is a prime candidate for induction melting. This includes:
- Ferrous Metals: Iron, carbon steel, stainless steel.
- Non-Ferrous Metals: Copper, aluminum, gold, silver, platinum, brass, bronze.
- Other Conductors: Graphite and some advanced ceramics can also be heated and melted.
The Challenge with Non-Conductive Materials
Materials that are electrical insulators cannot be heated directly by induction. The magnetic field passes through them without inducing any significant eddy currents.
This group includes glass, plastics, wood, ceramics, sand, and quartz.
The Workaround: Using a Susceptor
To melt a non-conductive material, you can use a clever workaround. The material is placed inside a container made from a conductive material, such as a graphite or silicon carbide crucible.
The induction field heats the crucible, which is called a susceptor. The crucible then transfers its heat to the non-conductive material inside through thermal conduction and radiation, causing it to melt.
Key Factors That Determine Melting Success
Simply having a conductive material is not the only variable. The success and efficiency of the melting process depend on a few critical factors.
Power of the Induction Unit
The power of the heater, measured in kilowatts (kW), must be sufficient to overcome the material's heat loss and reach its melting point. Melting a large crucible of steel requires significantly more power than melting a small amount of gold.
System Frequency
The frequency of the alternating current affects the depth of heat penetration (the "skin effect"). Lower frequencies penetrate deeper and are better for melting larger billets, while higher frequencies are suited for smaller samples or surface heating.
Coil Design and Coupling
The efficiency of energy transfer depends heavily on the design of the work coil and its proximity to the material. A coil that is closely "coupled" to the workpiece will transfer energy far more effectively.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is melting ferrous metals (iron, steel): Induction is exceptionally effective and often the preferred method due to the combined power of eddy currents and hysteresis heating.
- If your primary focus is melting non-ferrous metals (gold, copper, aluminum): Induction is a clean, fast, and precise solution that relies on inducing strong eddy currents in these highly conductive materials.
- If your primary focus is melting non-conductive materials (glass, salts): You must plan to use a conductive crucible (a susceptor) to indirectly heat your material with the induction field.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently determine if induction heating is the precise and efficient solution for your material melting needs.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Can It Be Melted? | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Ferrous Metals (e.g., Iron, Steel) | Yes | Highly efficient due to hysteresis effect. |
| Non-Ferrous Metals (e.g., Gold, Copper, Aluminum) | Yes | Relies on strong eddy currents for heating. |
| Non-Conductive Materials (e.g., Glass, Plastics) | Indirectly | Requires a conductive susceptor crucible (e.g., graphite). |
| Other Conductors (e.g., Graphite) | Yes | Can be heated and melted directly. |
Need a precise and efficient melting solution for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction heating systems tailored for melting a wide range of conductive materials. Whether you're working with precious metals, alloys, or require a susceptor-based setup for specialized applications, our experts can help you configure the right system for superior results.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific material melting needs and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of heat transfer in a furnace? Mastering Conduction, Convection & Radiation
- What is the working temperature of a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise Heat Control for Your Lab
- What is the temperature for a furnace? It Depends on Your Material and Process Goal
- What is a furnace used in the lab? Your Guide to High-Temperature Precision
- What is the high temperature of a muffle furnace? From 1100°C to 1700°C+ for Your Lab Needs



















