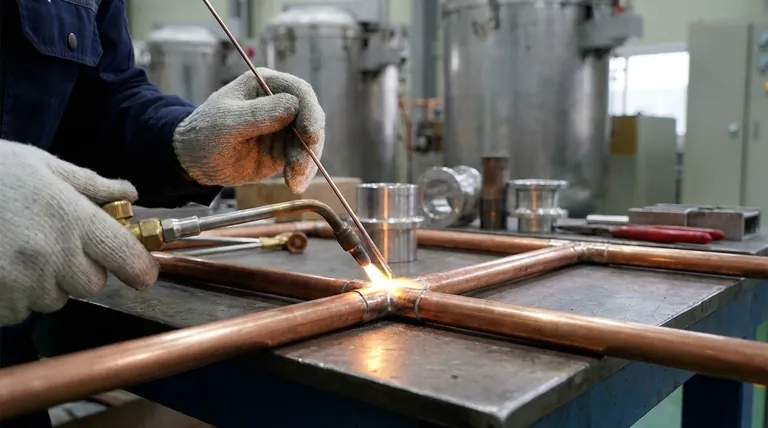
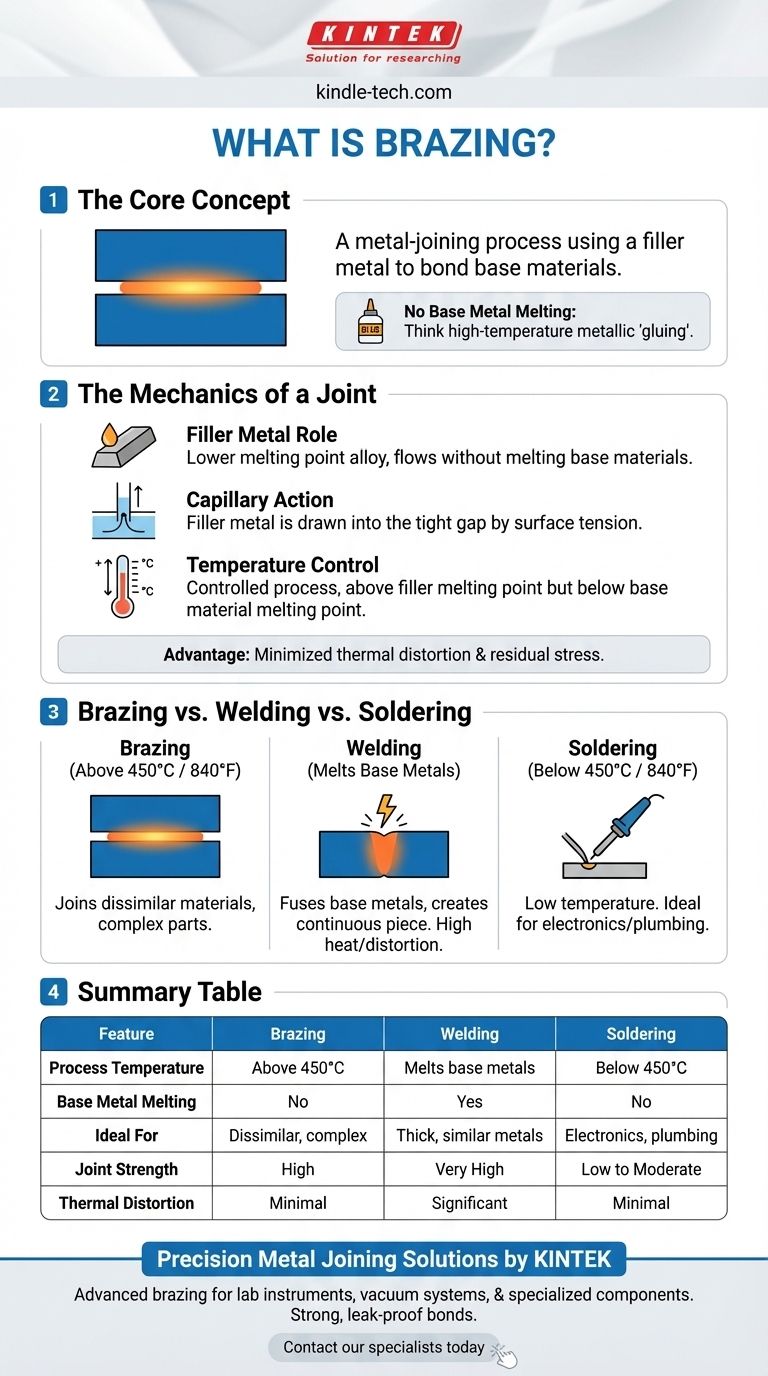
At its core, brazing is a metal-joining process that uses a filler metal to form a bond between two or more base materials. The key principle is that the filler metal has a lower melting point than the base materials, allowing it to be melted and flow into the joint without melting the components themselves. This creates a strong, permanent metallurgical bond upon cooling.
The fundamental difference between brazing and welding is that brazing joins materials without melting them. Think of it as high-temperature metallic "gluing," where the integrity and properties of the base materials are preserved.

The Mechanics of a Brazed Joint
To truly understand brazing, you must look beyond the simple definition and see how the process works on a physical level. The strength of a brazed joint comes from a combination of temperature control, material science, and a natural phenomenon.
The Role of the Filler Metal
The entire process hinges on the filler metal, an alloy specifically designed to melt at a temperature lower than the base materials being joined. This allows the process to operate at a much lower temperature than welding.
The filler metal is chosen based on its compatibility with the base materials and the intended application of the final component.
The Importance of Capillary Action
Once the filler metal is melted, it is drawn into the tight gap between the base materials through a process called capillary action. This is the same force that pulls water up a narrow straw.
For capillary action to work effectively, the parts must be designed with a very specific, small clearance. This ensures the molten filler completely fills the joint, creating a solid, void-free bond.
Why the Base Metal Doesn't Melt
The process temperature is carefully controlled to be above the melting point of the filler metal but safely below the melting point of the base materials.
This is the single most important advantage of brazing. By not melting the base materials, the process minimizes thermal distortion, reduces residual stress, and preserves their original metallurgical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Brazing vs. Other Methods
Brazing is not a universal solution. Its value becomes clear when compared to other common joining methods like welding and soldering.
Brazing vs. Welding
Welding fuses materials by melting the base metals along with a filler. This creates a single, continuous piece. Welding typically produces a stronger joint but introduces significant heat and stress, which can distort or weaken the base materials.
Brazing, in contrast, leaves the base metals intact. This makes it ideal for delicate parts, complex assemblies, and joining dissimilar materials (e.g., copper to steel) that cannot be easily welded.
Brazing vs. Soldering
Brazing and soldering are mechanically similar, but they are distinguished by one critical factor: temperature.
By formal definition, a process is considered brazing if the filler metal melts above 450°C (840°F). If the filler melts below this temperature, the process is called soldering. This higher temperature gives brazed joints significantly greater strength and temperature resistance than soldered joints.
When to Choose Brazing
Brazing excels in specific scenarios where welding is impractical or soldering is too weak. It is the preferred method for joining dissimilar materials, including metals to ceramics, and for creating leak-proof joints in complex assemblies like HVAC and refrigeration systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct joining process requires understanding the demands of your specific application, from strength requirements to the types of materials involved.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength for thick, similar metals: Welding is often the superior choice as it fuses the base metals directly.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials or minimizing thermal distortion: Brazing is the ideal solution due to its lower process temperature and ability to bond different material types.
- If your primary focus is low-temperature electronics or basic plumbing: Soldering is the correct and most cost-effective process, operating below the 450°C threshold.
Understanding these fundamental differences empowers you to select the precise joining method your project demands.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Brazing | Welding | Soldering |
|---|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | Above 450°C (840°F) | Melts base metals | Below 450°C (840°F) |
| Base Metal Melting | No | Yes | No |
| Ideal For | Dissimilar materials, complex assemblies | Thick, similar metals | Electronics, plumbing |
| Joint Strength | High | Very High | Low to Moderate |
| Thermal Distortion | Minimal | Significant | Minimal |
Need precision metal joining for your laboratory equipment? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced brazing solutions for laboratory instruments, vacuum systems, and specialized components. Our expertise ensures strong, leak-proof bonds for your most demanding applications.
Contact our brazing specialists today to discuss how we can enhance your product's performance and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What is the sputtering voltage of a magnetron? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- What would be an advantage of biomass over the use of coal? A Cleaner, Carbon-Neutral Energy Source
- What are the key differences between incineration and gasification? Explore Waste Management Solutions
- What are the disadvantages of biomass conversion? High Costs, Logistical Hurdles, and Environmental Trade-offs



















