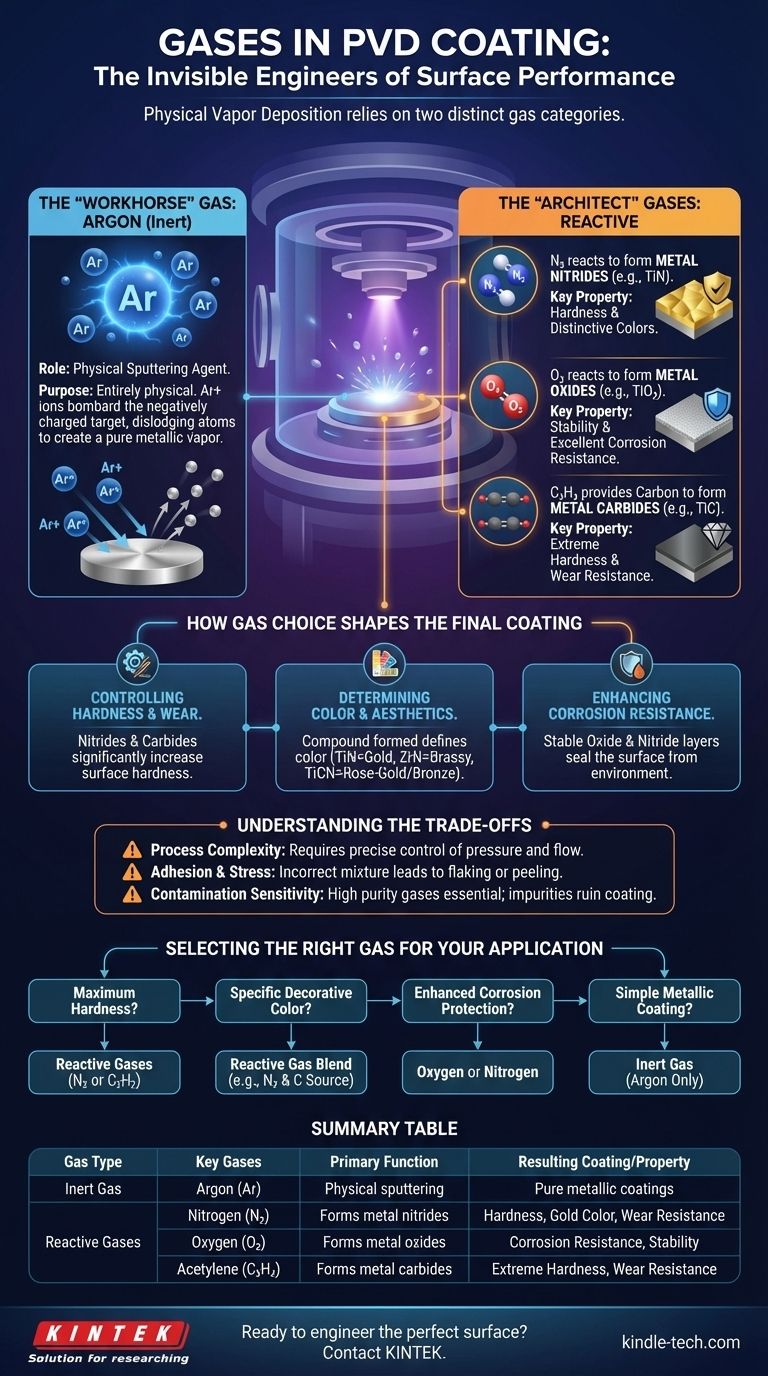
In Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), the process relies on two distinct categories of gases to achieve its results. The primary gases used are Argon (Ar), an inert gas, and a selection of reactive gases, most commonly Nitrogen (N₂), Oxygen (O₂), and Acetylene (C₂H₂). Argon acts as the physical agent to vaporize the source material, while the reactive gases are the chemical building blocks that determine the final coating's specific properties like color, hardness, and corrosion resistance.
The choice of gas in PVD is not incidental; it is a fundamental control parameter. Inert gases like Argon provide the physical force for deposition, while reactive gases like Nitrogen and Oxygen chemically combine with the vaporized metal to create the new, high-performance surface compound.
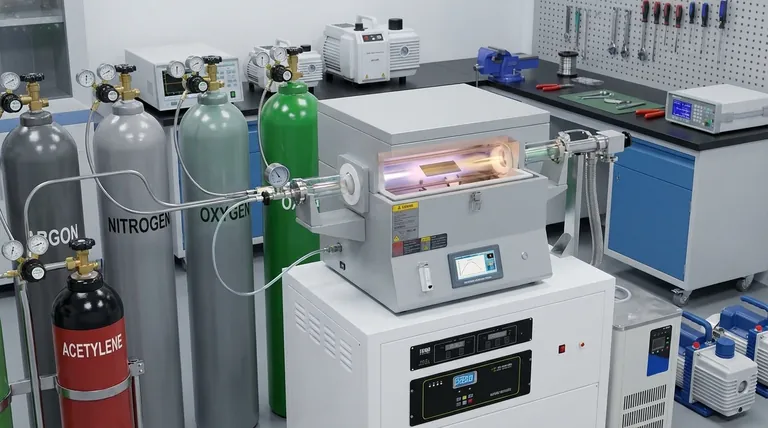

The Two Fundamental Roles of Gas in PVD
In any PVD process, gases are active participants that perform one of two critical functions: initiating the physical process or enabling the chemical reaction. Understanding this distinction is key to understanding PVD itself.
The "Workhorse" Gas: Argon (Inert)
Argon is the most common inert gas used in PVD. Its purpose is entirely physical, not chemical.
In processes like sputter deposition, a plasma is created with Argon. The positively charged Argon ions are then accelerated into the negatively charged source material, called the "target."
This high-energy bombardment physically dislodges, or "sputters," atoms from the target, vaporizing them into the vacuum chamber so they can be deposited onto the substrate. Argon provides the momentum transfer needed to begin the coating process.
The "Architect" Gases: Nitrogen, Oxygen, & Acetylene (Reactive)
Reactive gases are introduced into the vacuum chamber with a specific purpose: to chemically react with the vaporized metal atoms before they land on the substrate.
This intentional reaction forms a new ceramic or metallic compound on the surface of the part, which has vastly different properties than the original metal.
- Nitrogen (N₂) reacts with metal vapor to form metal nitrides (e.g., Titanium Nitride, TiN), which are known for their hardness and distinctive colors.
- Oxygen (O₂) reacts to form metal oxides (e.g., Titanium Oxide, TiO₂), which are exceptionally stable and provide excellent corrosion resistance.
- Acetylene (C₂H₂) acts as a source of carbon to form metal carbides (e.g., Titanium Carbide, TiC), which are among the hardest coatings available.
How Gas Choice Shapes the Final Coating
The precise mixture, pressure, and flow rate of the reactive gases are carefully controlled to engineer the desired surface properties.
Controlling Hardness and Wear Resistance
The formation of nitrides and carbides is the primary method for increasing a surface's hardness. A coating of Titanium Nitride (TiN) or Titanium Carbide (TiC) is significantly harder than the base stainless steel, providing superior resistance to scratching and wear.
Determining Color and Aesthetics
The final color of the coating is a direct result of the compound formed on the surface. For example:
- Titanium Nitride (TiN) produces a classic gold finish.
- Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) creates a pale, brassy-yellow color.
- Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN), formed using a mix of nitrogen and a carbon source, can range from rose-gold to bronze and gray depending on the ratio.
Enhancing Corrosion Resistance
Oxides and nitrides are extremely stable chemical compounds. By forming a dense, non-porous layer of a metal oxide or nitride on a substrate, the PVD process effectively seals the surface from the environment, drastically improving its resistance to rust and chemical attack.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the use of reactive gases introduces complexity and requires precise control to be successful.
Process Control vs. Performance
Introducing reactive gases makes the PVD process significantly more complex than simply depositing a pure metal. The system must precisely manage gas pressures and flow rates to ensure the correct chemical reaction occurs, adding a layer of difficulty in exchange for enhanced performance.
Adhesion and Internal Stress
If the gas mixture or pressure is incorrect, it can lead to high internal stress within the coating layer. This stress can cause poor adhesion, leading to the coating cracking, flaking, or peeling off the substrate over time.
Contamination and Purity
PVD processes are highly sensitive to impurities. The inert and reactive gases used must be of very high purity. Any contamination, such as water vapor or residual air in the chamber or gas lines, can cause unwanted chemical reactions and ruin the integrity of the coating.
Selecting the Right Gas for Your Application
Your choice of gas chemistry is determined entirely by the desired outcome for your component.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: Your best choice will likely involve reactive gases like Nitrogen or Acetylene to form hard nitride or carbide coatings.
- If your primary focus is a specific decorative color: The exact blend and ratio of reactive gases, such as Nitrogen and a carbon source, will be the most critical factor to control.
- If your primary focus is enhanced corrosion protection: You should consider processes that use Oxygen or Nitrogen to form stable, non-reactive oxide or nitride layers on the surface.
- If your primary focus is a simple metallic coating: You may only need an inert gas like Argon to sputter-deposit the pure metal without any chemical reaction.
Ultimately, mastering the use of these gases is what transforms PVD from a simple deposition technique into a precise tool for engineering surface properties at the molecular level.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Key Gases | Primary Function | Resulting Coating/Property |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inert Gas | Argon (Ar) | Physical sputtering of target material | Pure metallic coatings |
| Reactive Gases | Nitrogen (N₂) | Forms metal nitrides (e.g., TiN) | Hardness, gold color, wear resistance |
| Oxygen (O₂) | Forms metal oxides (e.g., TiO₂) | Corrosion resistance, stability | |
| Acetylene (C₂H₂) | Forms metal carbides (e.g., TiC) | Extreme hardness, wear resistance |
Ready to engineer the perfect surface properties for your components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-purity gases and expert support needed for precision PVD coating processes. Whether you're aiming for maximum hardness with nitride coatings, specific decorative colors, or superior corrosion resistance, our lab equipment and consumables are designed to meet your exact requirements.
Let us help you master your PVD process for superior results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover the KINTEK difference in laboratory performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the CVD method for synthetic diamonds? Grow Lab Diamonds from Gas with Precision
- What is the process of vacuum deposition? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision Coatings
- What is the thermal CVD technique? The High-Temperature Secret to Superior Coatings
- What is the apparatus of chemical vapor deposition? The Essential Components for Thin Film Deposition
- How does PVD differ from CVD? Choosing the Right Thin-Film Coating Process



















