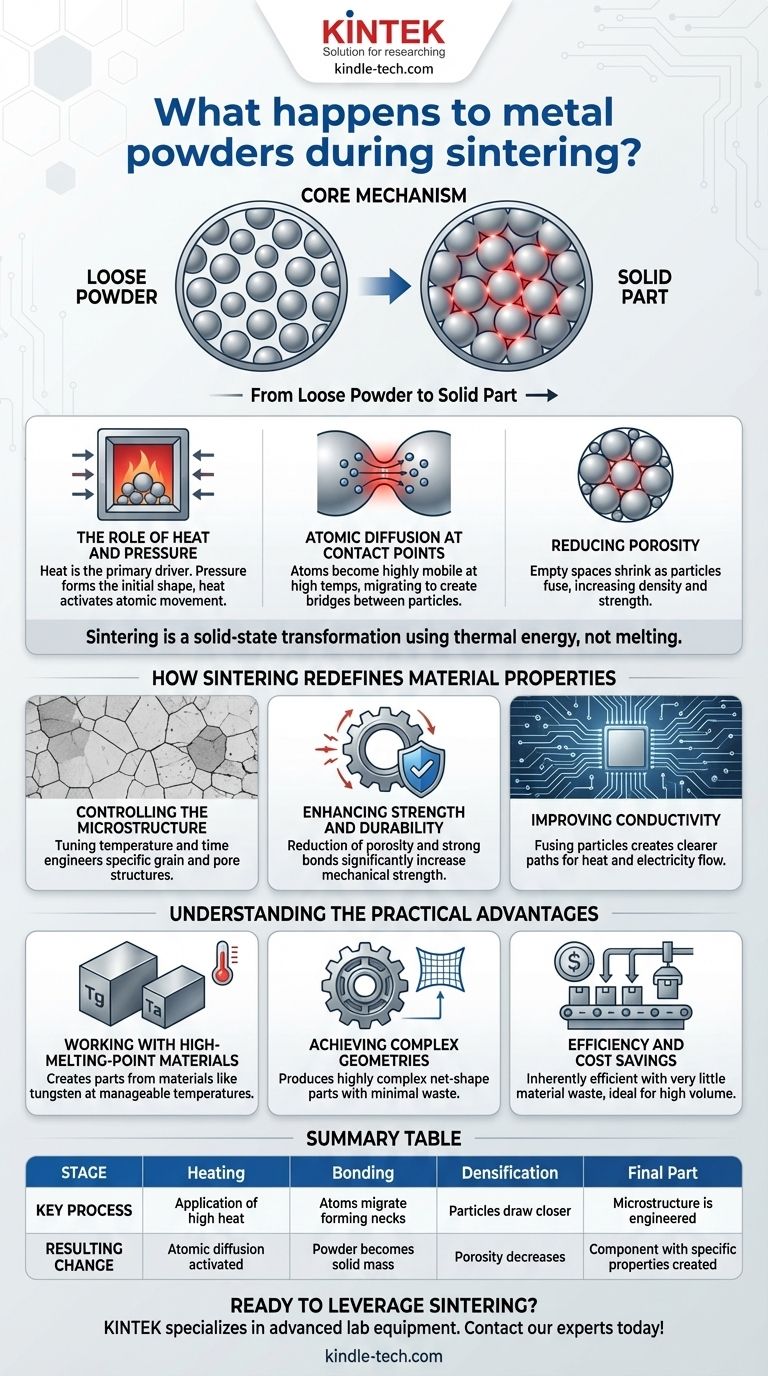
At its core, sintering transforms a collection of individual metal powder particles into a single, solid piece. This is achieved by applying high heat—typically below the material's melting point—which causes the atoms at the contact surfaces of the particles to diffuse and create strong chemical bonds, fusing the powder into a coherent shape.
Sintering is not a melting process; it is a solid-state transformation. It uses thermal energy to reduce the empty space between powder particles, fundamentally altering the material's microstructure to create a dense, strong, and functional component with engineered properties.

The Core Mechanism: From Loose Powder to Solid Part
To understand what happens during sintering, we must look at the process on a microscopic level. It's a carefully controlled journey from a compacted powder to a solid object.
The Role of Heat and Pressure
Heat is the primary driver of sintering. It provides the thermal energy necessary to activate atomic movement within the powder particles.
While the initial shape is often formed under pressure (creating a "green" compact), the sintering process itself relies on this thermal energy to initiate the bonding.
Atomic Diffusion at Contact Points
At high temperatures, atoms become highly mobile. They migrate across the boundaries where individual powder particles touch.
This process of atomic diffusion creates small "necks" or bridges between the particles. As the process continues, these necks grow wider, pulling the particles closer together and fusing them into a solid mass.
Reducing Porosity
The initial compacted powder contains a significant volume of empty space, or porosity, between the particles.
As the particles fuse and draw closer, these pores shrink and can even be eliminated. This densification is a primary goal of sintering, as it directly increases the strength and integrity of the final part.
How Sintering Redefines Material Properties
The true power of sintering lies in its ability to precisely control the final properties of a material. This is achieved by manipulating its internal structure during the process.
Controlling the Microstructure
Sintering directly influences the material's microstructure—its grain size, pore size, and the shape of the boundaries between grains.
By carefully tuning the temperature and duration of the process, engineers can design a microstructure that delivers specific performance characteristics.
Enhancing Strength and Durability
The reduction of porosity and the creation of strong, continuous bonds between particles significantly increase the material's mechanical strength and durability.
A well-sintered part can withstand higher loads and resist wear more effectively than its pre-sintered, "green" state.
Improving Conductivity
As empty spaces are removed and particles fuse, pathways for heat and electricity become clearer and more direct.
This results in a marked improvement in both thermal and electrical conductivity, a critical property for many electronic and heat-management applications.
Understanding the Practical Advantages
Sintering is not just a scientific curiosity; it is a foundational manufacturing process chosen for its distinct and powerful advantages over traditional methods like casting or machining.
Working with High-Melting-Point Materials
One of sintering's most significant benefits is its ability to create parts from materials with exceptionally high melting points, such as tungsten and tantalum.
It allows for the formation of solid components at temperatures that are far more manageable and energy-efficient than reaching the material's actual melting point.
Achieving Complex Geometries
Sintering enables the production of highly complex and net-shape parts with minimal material waste.
The intricate shape is formed during the initial powder compaction stage and is then locked in place by the sintering process, reducing or eliminating the need for costly secondary machining.
Efficiency and Cost Savings
Because it starts with powder, sintering is an inherently efficient process. It wastes very little raw material compared to subtractive manufacturing, where material is cut away from a solid block.
This efficiency, combined with its suitability for high-volume production, makes it a highly cost-effective method for creating components with excellent tolerances and surface finishes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The parameters you choose for sintering directly determine the outcome. Your specific goal dictates the approach.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and density: You will need to optimize for higher temperatures and longer sintering times, carefully managing the process to ensure full bonding and minimal porosity.
- If your primary focus is creating porous materials (like for filters or self-lubricating bearings): You will use lower temperatures or shorter times to intentionally preserve a network of interconnected pores while still ensuring the part is structurally sound.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production of complex shapes: Sintering is ideal, as it minimizes machining and material waste compared to traditional subtractive manufacturing, delivering net-shape parts directly from powder.
Ultimately, mastering sintering is about precisely controlling heat and time to transform simple powders into highly engineered components with specific, predictable properties.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Resulting Change |
|---|---|---|
| Heating | Application of high heat below melting point | Atomic diffusion is activated at particle contacts |
| Bonding | Atoms migrate, forming 'necks' between particles | Loose powder transforms into a solid mass |
| Densification | Particles draw closer together, pores shrink | Porosity decreases, strength and density increase |
| Final Part | Microstructure is engineered via temperature & time | A component with specific mechanical & conductive properties is created |
Ready to leverage sintering for your high-performance components?
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to perfect your sintering processes. Whether you are developing complex geometries, working with high-melting-point metals, or aiming for maximum density and strength, our solutions help you achieve precise control over material properties.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific sintering and materials development goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- What are the advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity, Strength, and Performance
- What is the process of sintering a furnace? Achieve Precise Material Densification and Lining Durability
- What is the density of sintered material? A Design Choice for Performance, Not a Fixed Number
- What is a sintering furnace? A Guide to High-Temperature Materials Processing



















