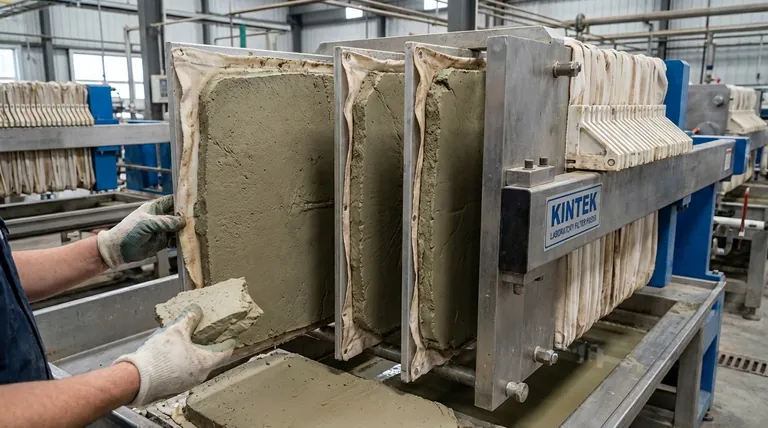
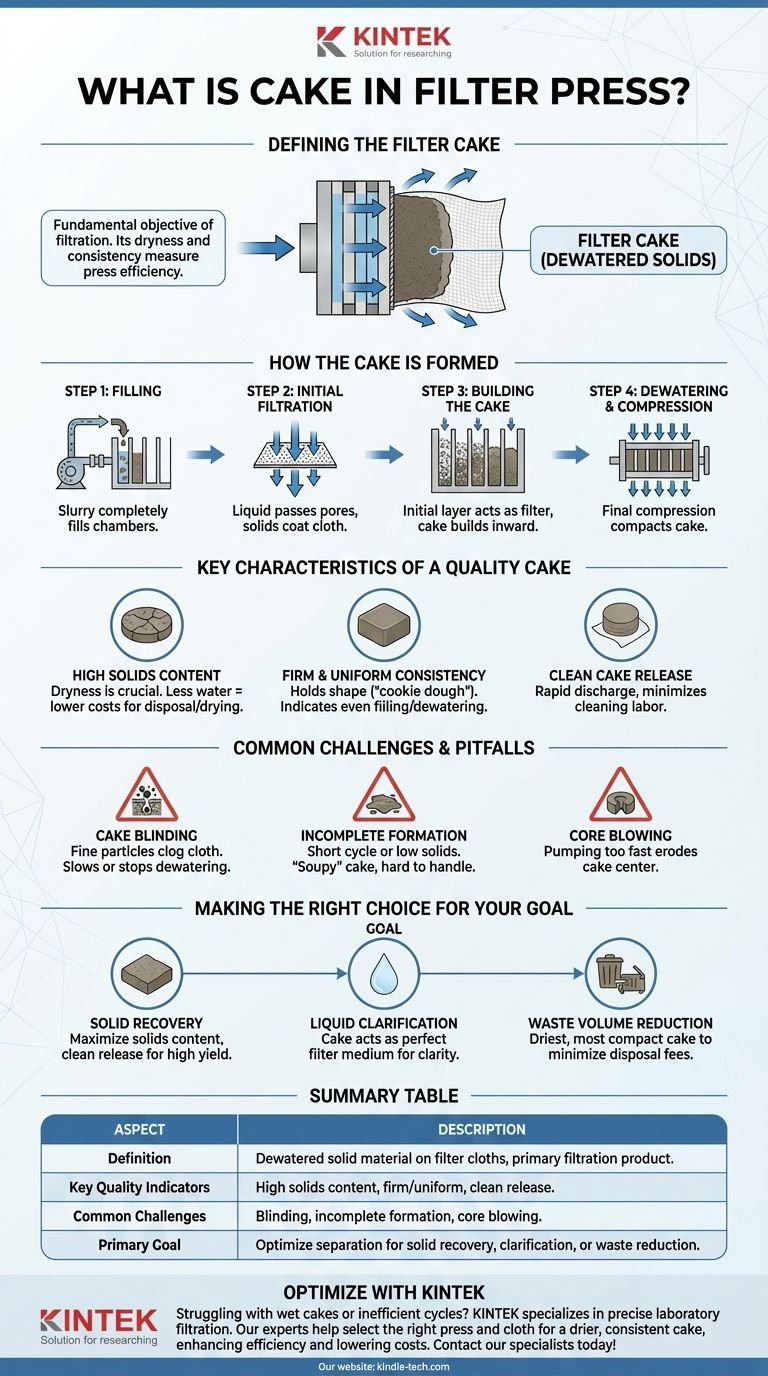
In a filter press operation, the "cake" is the collection of dewatered solid materials that accumulate on the filter cloths between the press plates. It is the end product of the solid-liquid separation process, formed as the liquid (filtrate) is forced through the filter medium, leaving the solids behind under immense pressure.
The filter cake is not merely a byproduct; it is the fundamental objective of the filtration process. The quality and characteristics of this cake—specifically its dryness and consistency—are the primary measures of a filter press's efficiency.

How the Filter Cake is Formed
Understanding the formation of the filter cake is essential to diagnosing and optimizing any filter press operation. The process occurs in distinct, sequential stages within each chamber of the press.
Step 1: Filling the Chambers
A pump forces the initial liquid-solid mixture, known as slurry, into the empty chambers between the filter plates. At this stage, the chambers are filled completely with the source material.
Step 2: Initial Filtration
As pressure builds, the liquid begins to pass through the microscopic pores of the filter cloth, while the larger solid particles are stopped. This first layer of solids begins to coat the surface of the cloth.
Step 3: Building the Cake
This initial layer of solids becomes the primary filter medium. As more slurry is pumped in, this developing cake traps progressively finer particles far more effectively than the cloth alone. The cake builds from the cloth inward toward the center of the chamber.
Step 4: Dewatering and Compression
Once the chamber is full of solids and flow of filtrate slows, the feed pump exerts maximum pressure. This final compression phase squeezes the remaining liquid from the cake, compacting it into a dense, semi-solid form.
Key Characteristics of a Quality Filter Cake
The goal is not just to form a cake, but to form a good cake. The quality is judged by a few critical characteristics that directly impact operational costs and efficiency.
High Solids Content
The most important characteristic is dryness. A high percentage of solids means less water, which translates to lower transportation and disposal costs for waste products or less energy needed for drying a valuable final product.
Firm and Uniform Consistency
A quality cake is firm and holds its shape, often described as having a "cookie dough" or "clay-like" consistency. This indicates that all chambers filled evenly and dewatered properly.
Clean Cake Release
The cake should cleanly separate from the filter cloth when the press is opened. This allows for a rapid discharge cycle and minimizes the labor required to clean the cloths between cycles.
Common Challenges and Pitfalls
Achieving a perfect filter cake is not always straightforward. Certain issues can compromise the entire process, leading to inefficiency and poor results.
Cake Blinding
Blinding occurs when very fine or slimy particles clog the pores of the filter cloth itself. This prevents liquid from passing through, drastically slowing or even stopping the dewatering process and resulting in a wet, poorly formed cake.
Incomplete Cake Formation
If the press cycle is too short or the slurry has an insufficient concentration of solids, the chambers may not fill completely. This results in a "soupy" or "sloppy" cake that is difficult to handle and has a very low solids content.
Core Blowing
In some cases, the center of the cake remains wet and unformed. This can be caused by trying to pump the slurry too fast, which can erode the cake as it forms rather than building upon it.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal filter cake is defined by your ultimate objective. Optimizing the process requires understanding what you are trying to achieve with the solids and the liquid.
- If your primary focus is recovering the solid product: Your goal is the highest possible solids content and a clean cake release to maximize your yield and minimize downstream drying costs.
- If your primary focus is clarifying the liquid (filtrate): The cake's ability to act as a perfect filter medium is paramount to ensuring you achieve the required clarity in your filtrate output.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction: You must produce the driest, most compact cake possible to minimize hauling weight and disposal fees.
Ultimately, mastering the properties of your filter cake is the key to mastering the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of your entire separation process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | The dewatered solid material that accumulates on filter cloths, the primary product of the filtration process. |
| Key Quality Indicators | High solids content (dryness), firm/uniform consistency, and clean release from the cloth. |
| Common Challenges | Cake blinding, incomplete formation, and core blowing, which reduce efficiency and increase costs. |
| Primary Goal | To achieve optimal separation, whether for solid recovery, liquid clarification, or waste volume reduction. |
Optimize Your Filtration Process with KINTEK
Struggling with wet cakes, blinding, or inefficient cycles? The quality of your filter cake directly impacts your operational costs and productivity. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving precise laboratory filtration needs. Our experts can help you select the right filter press and cloth media to achieve a drier, more consistent cake for your specific application—whether you're recovering a valuable product or reducing waste volume.
Let us help you enhance your separation efficiency and lower your costs. Contact our filtration specialists today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Hydraulic Diaphragm Lab Filter Press for Laboratory Filtration
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System



















