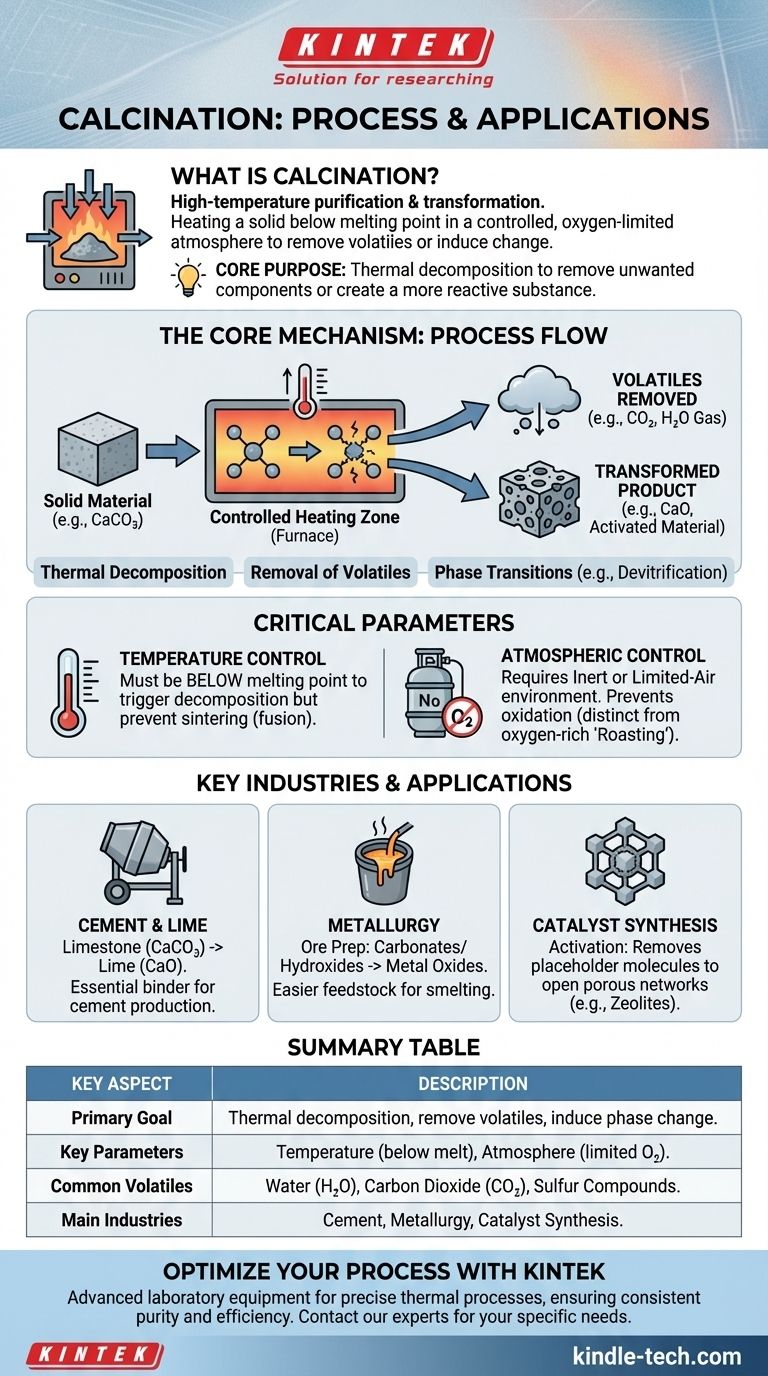
In essence, calcination is a high-temperature purification and transformation process. It involves heating a solid material to a temperature just below its melting point in a controlled atmosphere with little to no oxygen. This intense heat drives off volatile substances like water and carbon dioxide, causing the material to decompose or change its chemical structure, making it more suitable for its next industrial use.
The core purpose of calcination is not simply to heat a material, but to induce a specific chemical or physical change. It’s a method of thermal decomposition, designed to remove unwanted components or create a more reactive substance.

The Core Mechanism: What Happens During Calcination?
Calcination achieves its results by carefully manipulating heat and atmosphere to break down a compound into simpler, more useful forms.
Thermal Decomposition
The primary mechanism is thermal decomposition. The applied heat provides enough energy to break the chemical bonds within a compound, causing it to separate into two or more products.
A classic example is the production of lime from limestone. When calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) is heated, it decomposes into calcium oxide (CaO, or lime) and releases carbon dioxide gas (CO₂).
Removal of Volatiles
This decomposition is most often used to drive off volatile substances. These are parts of the compound that can easily turn into a gas when heated.
Common volatiles removed during calcination include water from hydrated minerals (dehydration), carbon dioxide from carbonates, and sulfur compounds from certain ores. The result is a more concentrated or purified solid material.
Inducing Phase Transitions
In more advanced applications, calcination is used not to decompose a material but to change its internal structure. This is called a phase transition.
By carefully heating a substance like glass, its disordered atomic structure can be rearranged into a more ordered crystalline state (a process called devitrification), altering its physical properties.
Understanding the Critical Parameters
The success of calcination depends on precise control over two key variables: temperature and atmosphere. Getting either wrong fundamentally changes the outcome.
Temperature Control
The material must be heated to a temperature high enough to trigger decomposition but below its melting point.
If the temperature is too low, the reaction won't occur. If it's too high and the material melts or fuses, you get a solid, glassy mass (sintering) instead of the desired porous solid or fine powder.
Atmospheric Control
Calcination is defined by its use of an inert or limited-air atmosphere. This is critical for preventing unwanted side reactions, chiefly oxidation.
If the same process were done in an oxygen-rich environment, it would be called roasting. Roasting is used when the goal is to add oxygen to a compound (e.g., converting sulfide ores to oxides), whereas calcination is used to drive off components without adding oxygen.
Key Applications Across Industries
Calcination is a foundational process in several major heavy industries due to its effectiveness and relative simplicity.
Cement and Lime Production
This is the most common application. The global cement industry is built upon the calcination of limestone to produce lime, the primary reactive ingredient in all modern cement.
Metallurgy and Ore Processing
In metallurgy, calcination is a preparatory step. It converts metal ores, such as carbonates and hydroxides, into their oxide forms. Metal oxides are much easier to process in a furnace to extract the pure metal.
Catalyst and Zeolite Synthesis
In specialty chemical manufacturing, calcination is used to activate materials. For instance, it can remove placeholder molecules from the crystalline structure of a zeolite, opening up the porous network that makes it a powerful catalyst.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding how calcination is applied depends on the industrial context.
- If your primary focus is basic chemistry: Think of calcination as thermal decomposition—using heat to break down a compound and drive off a gas.
- If your primary focus is civil engineering: See calcination as the essential step that turns inert rock (limestone) into the chemically reactive binder (lime) for cement.
- If your primary focus is metallurgy: View calcination as a crucial refining step that prepares ore by converting it into a metal oxide, the ideal feedstock for smelting.
Mastering this fundamental process is key to understanding a vast range of industrial chemical transformations.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Thermal decomposition to remove volatiles or induce a phase change. |
| Key Parameters | Temperature (below melting point) and atmosphere (limited oxygen). |
| Common Removed Volatiles | Water (H₂O), Carbon Dioxide (CO₂), Sulfur Compounds. |
| Main Industries | Cement Production, Metallurgy, Catalyst Synthesis. |
Optimize Your Industrial Processes with KINTEK
Calcination is a critical step for producing high-quality materials. Whether you are developing new catalysts, processing ores, or manufacturing cement, having the right equipment is essential for precise temperature and atmospheric control.
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables designed for demanding thermal processes. Our solutions help you achieve consistent, reliable results, improving product purity and process efficiency.
Ready to enhance your calcination process? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields



















