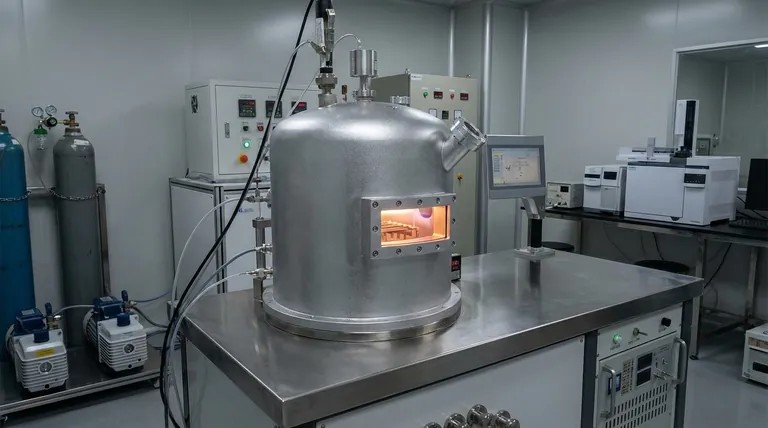
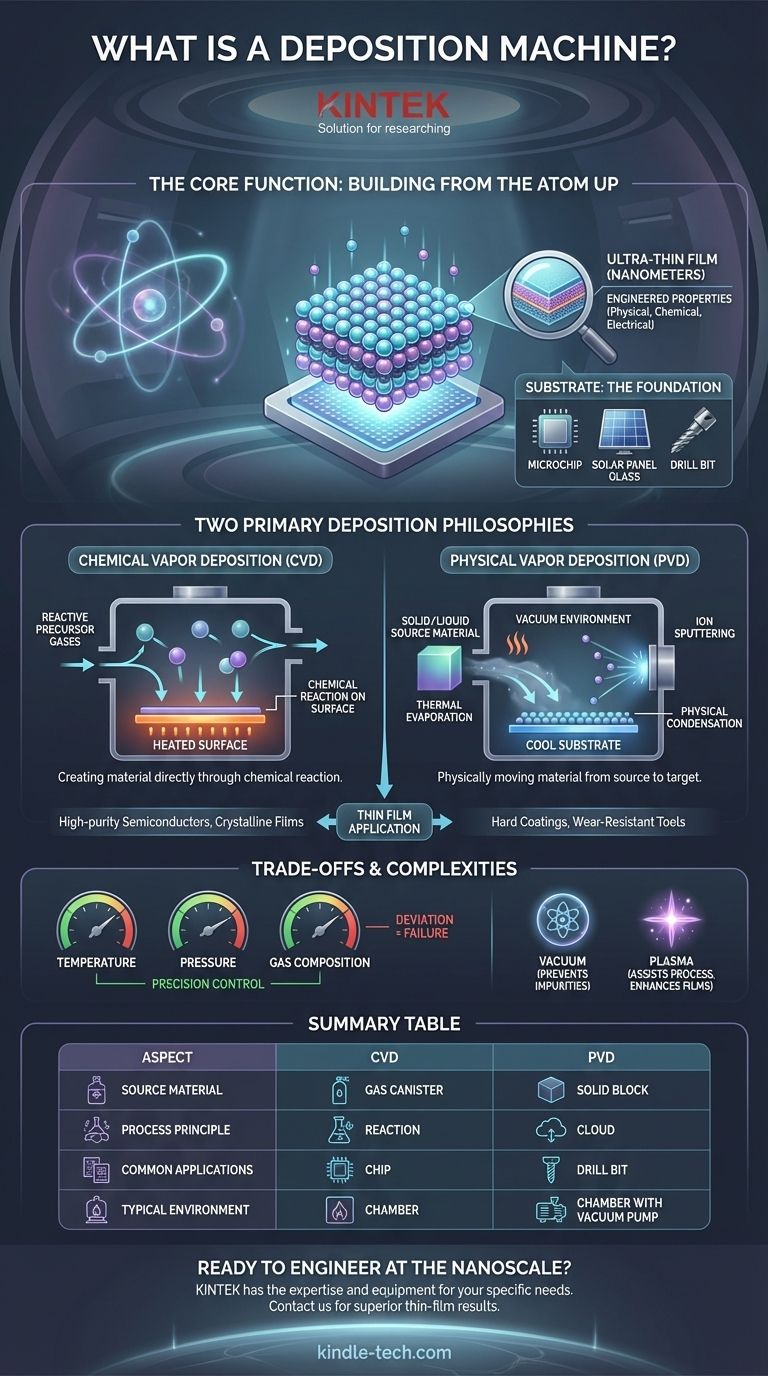
In essence, a deposition machine is a system designed to apply an ultra-thin, highly controlled layer of material—often just a few atoms thick—onto a surface or object. These machines are the critical tools used to create functional coatings and build the foundational layers of high-tech components, from semiconductor chips and solar cells to wear-resistant cutting tools.
The core function of any deposition machine is to transfer a source material onto a target surface, known as a substrate. The fundamental difference between methods lies in how that material is transferred: either as a reactive chemical gas (Chemical Vapor Deposition) or as a vaporized solid or liquid (Physical Vapor Deposition).

The Core Function: Building from the Atom Up
To understand the machine, you must first understand the process. Deposition is fundamentally a method of advanced manufacturing where materials are constructed one layer of atoms or molecules at a time.
What is a "Thin Film"?
The goal of deposition is to create a thin film. This is not like a coat of paint; it is an engineered layer with specific physical, chemical, or electrical properties.
These films are incredibly thin, often measured in nanometers, and must be perfectly uniform to function correctly.
The Substrate: The Foundation
The surface onto which the film is applied is called the substrate. This can be almost anything, including a silicon wafer for a microchip, a piece of glass for a solar panel, or a metal drill bit.
Why This Process is Necessary
This precise layering is essential for modern technology. It's used to build the complex, multi-layered structures inside computer chips or to apply coatings that give a material new properties.
For example, deposition is used in electronics for semiconductors, on cutting tools to prevent corrosion and wear, and to create the photovoltaic materials in thin-film solar cells.
The Two Primary Deposition Philosophies
While there are many variations, nearly all deposition processes fall into one of two major categories based on the state of the source material.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
In CVD, the machine introduces one or more volatile precursor gases into a reaction chamber. These gases decompose or react on the heated surface of the substrate, leaving behind the desired solid thin film.
It is a process of creating the material directly on the surface through a chemical reaction. This method is frequently used to grow highly ordered materials like carbon nanotubes and semiconductor layers.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
In PVD, the source material starts as a solid or liquid. Inside a vacuum chamber, this source is then vaporized through physical means, such as heating it until it evaporates (thermal evaporation) or bombarding it with ions until atoms are ejected (sputtering).
This vapor then travels through the vacuum and condenses onto the substrate, forming the thin film. It is a process of physically moving a material from a source to a target.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Complexities
The choice of deposition method is a critical engineering decision driven by the desired outcome, and the process is far from simple.
The Challenge of Control
Executing deposition successfully requires an extremely high level of skill and precision. The machine must perfectly control variables like temperature, pressure, gas composition, and power levels.
Any deviation can ruin the film's uniformity, adhesion, or functional properties.
Choosing the Right Method
The choice between CVD and PVD depends entirely on the application. Factors include the material to be deposited, the substrate it's being applied to, and the desired properties of the final film.
For example, CVD excels at creating high-purity, crystalline films for electronics, while PVD is often preferred for durable, metallic coatings on tools.
The Role of Plasma and Vacuum
Most deposition processes occur in a vacuum to prevent the source vapor from reacting with air and creating impurities.
Additionally, many advanced systems use plasma (an ionized gas) to assist the process. Plasma can help break down precursor gases in CVD at lower temperatures or increase the energy of atoms in PVD to create denser, more resilient films.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of deposition technology is dictated entirely by the properties you need in the final thin film.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, high-purity semiconductor or crystalline structures: CVD is often the preferred method for its ability to grow uniform, well-ordered layers through controlled chemical reactions.
- If your primary focus is applying hard, wear-resistant metallic or ceramic coatings: PVD methods like magnetron sputtering are frequently used for their strong adhesion and versatility with a wide range of source materials.
Ultimately, a deposition machine is a precision instrument for engineering materials at the nanoscale, enabling the performance and function of countless modern technologies.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Source Material | Reactive precursor gases | Solid or liquid source material |
| Process Principle | Chemical reaction on the substrate surface | Physical vaporization and condensation |
| Common Applications | High-purity semiconductor layers, crystalline films | Hard, wear-resistant metallic/ceramic coatings |
| Typical Environment | Controlled atmosphere, often with plasma | High vacuum chamber |
Ready to Engineer at the Nanoscale?
Choosing the right deposition technology is critical for your project's success. Whether you need to grow complex semiconductor layers with CVD or apply durable, wear-resistant coatings with PVD, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your laboratory's specific needs.
Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss how our precision lab equipment can help you achieve superior thin-film results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How do CVD diamonds grow? A Step-by-Step Guide to Lab-Grown Diamond Creation
- How is diamond coating made? A Guide to CVD and PVD Methods
- How do you calculate coating coverage? A Practical Guide to Accurate Material Estimation



















